Pesisir Selatan Regency
Pesisir Selatan Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Pesisir Selatan, Minangkabau: Kabupaten Pasisia Salatan) is a regency (kabupaten) of West Sumatra, Indonesia. It has an area of 5,749.89 km² and a population of 457,285 people in 2017.[1] The regency seat is Painan.
Pesisir Selatan Regency
Kabupaten Pesisir Selatan | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
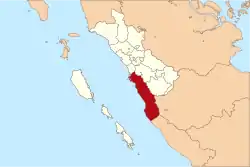 Location within West Sumatra | |
| Coordinates: 1.35°S 100.567°E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | West Sumatra |
| Regency seat | Painan |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Hendrajoni |
| • Vice Regent | Rusma Yul Anwar |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,749.89 km2 (2,220.04 sq mi) |
| Population (2017) | |
| • Total | 457,285 |
| • Density | 80/km2 (210/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (IWST) |
| Area code | (+62) 751/756/757 |
| Website | pesisirselatankab.go.id |
Pesisir Selatan is located on the coast of West Sumatra (the word "pesisir" means "coast" in Indonesian) and is bordered on the north by the city of Padang, in the east by the regencies of Solok Regency, South Solok Regency and by Kerinci Regency (in the province of Jambi) and in the south by the regency of Muko-Muko (Bengkulu province).
Pesisir Selatan is known for its traditional music, the Rabab Pesisir. The music includes the playing of a rebab (a stringed instrument), accompanied by one or more musicians singing.
Administrative districts
As at 2010 South Pesisir Regency consisted of twelve districts (kecamatan), but subsequently three additional districts have been created by the splitting of existing districts. All these are tabulated below with their areas and populations at the 2010 Census,[2] and the latest official estimates as at mid 2017:[3]
| District | Area in km2 | Population 2010 Census | Population 2017 Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silaut | 365.50 | 1 | 15,093 |
| Lunang | 564.00 | 1 | 21,530 |
| Basa Ampek Balai Tapan | 365.28 | 2 | 13,793 |
| Ranah Ampek Hulu Tapan | 312.22 | 2 | 15,159 |
| Pancung Soal | 426.10 | 3 | 26,495 |
| Airpura | 319.71 | 3 | 16,019 |
| Linggo Sari Baganti | 315.41 | 42,319 | 45,180 |
| Ranah Pesisir | 564.39 | 30,089 | 30,313 |
| Lengayang | 590.60 | 51,623 | 52,592 |
| Sutera | 445.65 | 47,019 | 50,516 |
| Batang Kapas | 359.07 | 30,829 | 31,480 |
| IV Jurai | 373.80 | 43,302 | 46,502 |
| Bayang | 77.50 | 36,697 | 36,781 |
| IV Nagari Bayang Utara | 250.74 | 7,276 | 7,277 |
| Koto XI Tarusan | 425.63 | 47,898 | 48,555 |
Notes:
- 1 The former Lunang Silaut district had a population of 30,450 at the 2010 Census prior to its division into separate Lunang and Silaut districts.
- 2 The Basa Ampek Balai Tapan district had a population of 25,742 at the 2010 Census prior to the splitting off of a separate Ranah Ampek Hulu Tapan district.
- 3 The Pancung Soal district had a population of 37,006 at the 2010 Census prior to the splitting off of a separate Aipura district.
Siamang rehabilitation
Marak Island is 7.37 kilometres from Nagari Sungai Pinang land which 500 hectares area has used as Siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) and Owa ungko (Hylobates agilis) rehabilitation center complete with quarantine, medical, social and rehabilitation cages since 2003. The plan is to release some Siamang which have could use upper room with sufficient activities, not depend on human anymore and match with his/her spouse to Bukit Tiga Puluh National Park. The island is now home for 30 butterfly species and 50 kinds of birds, and is suitable for a conservation area.[4]
References
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2019.
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2019.
- "Owa dan Siamang Dilepasliarkan di Pulau Marak". Retrieved November 1, 2013.