Pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.
| Pharyngeal arch | |
|---|---|
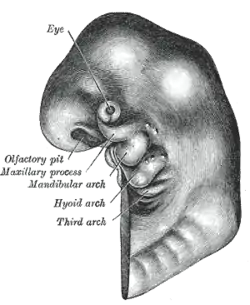 Schematic of developing human fetus with first, second and third arches labelled | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 10 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arcus pharyngei |
| MeSH | D001934 |
| TE | E5.4.2.0.0.0.2 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
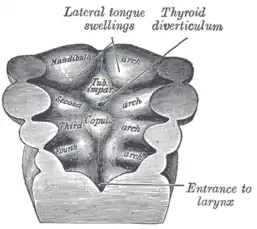

- I–IV: pharyngeal arches
- 1–4: pharyngeal pouches (inside) and/or pharyngeal grooves (outside)
- a: Tuberculum laterale
- b: Tuberculum impar
- c: Foramen cecum
- d: Ductus thyreoglossus
- e: Sinus cervicalis
In the human embryo, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of development. They appear as a series of outpouchings of mesoderm on both sides of the developing pharynx. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches is known as the aortic arches.
In fish, the branchial arches support the gills.
Structure
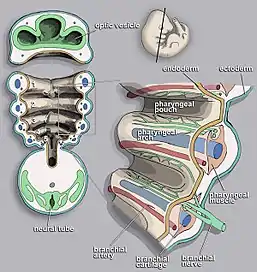
In vertebrates, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three germ layers (the primary layers of cells that form during embryogenesis).[1] Neural crest cells enter these arches where they contribute to features of the skull and facial skeleton such as bone and cartilage.[1] However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existence of neural crest-independent mechanisms of pharyngeal arch development.[2] The first, most anterior pharyngeal arch gives rise to the oral jaw. The second arch becomes the hyoid and jaw support.[1] In fish, the other posterior arches contribute to the branchial skeleton, which support the gills; in tetrapods the anterior arches develop into components of the ear, tonsils, and thymus.[3] The genetic and developmental basis of pharyngeal arch development is well characterized. It has been shown that Hox genes and other developmental genes such as DLX are important for patterning the anterior/posterior and dorsal/ventral axes of the branchial arches.[4] Some fish species have a second set of jaws in their throat, known as pharyngeal jaws, which develop using the same genetic pathways involved in oral jaw formation.[5]
During human and all vertebrate development, a series of pharyngeal arch pairs form in the developing embryo. These project forward from the back of the embryo toward the front of the face and neck. Each arch develops its own artery, nerve that controls a distinct muscle group, and skeletal tissue. The arches are numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the arch closest to the head of the embryo, and arch 5 existing only transiently.[6]
These grow and join in the ventral midline. The first arch, as the first to form, separates the mouth pit or stomodeum from the pericardium. By differential growth the neck elongates and new arches form, so the pharynx has six arches ultimately.
Each pharyngeal arch has a cartilaginous stick, a muscle component that differentiates from the cartilaginous tissue, an artery, and a cranial nerve. Each of these is surrounded by mesenchyme. Arches do not develop simultaneously but instead possess a "staggered" development.
Pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the arches, and pharyngeal grooves (or clefts) form from the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches.[7] In fish the pouches line up with the clefts, and these thin segments become gills. In mammals the endoderm and ectoderm not only remain intact but also continue to be separated by a mesoderm layer.
The development of the pharyngeal arches provides a useful landmark with which to establish the precise stage of embryonic development. Their formation and development corresponds to Carnegie stages 10 to 16 in mammals, and Hamburger–Hamilton stages 14 to 28 in the chicken. Although there are six pharyngeal arches, in humans the fifth arch exists only transiently during embryogenesis.[8]
First arch
The first pharyngeal arch also mandibular arch (corresponding to the first branchial arch or gill arch of fish), is the first of six pharyngeal arches that develops during the fourth week of development.[9] It is located between the stomodeum and the first pharyngeal groove.
Processes
This arch divides into a maxillary process and a mandibular process, giving rise to structures including the bones of the lower two-thirds of the face and the jaw. The maxillary process becomes the maxilla (or upper jaw), and palate while the mandibular process becomes the mandible or lower jaw. This arch also gives rise to the muscles of mastication.
Meckel's cartilage
Meckel's cartilage forms in the mesoderm of the mandibular process and eventually regresses to form the incus and malleus of the middle ear, the anterior ligament of the malleus and the sphenomandibular ligament. The mandible or lower jaw forms by perichondral ossification using Meckel's cartilage as a 'template', but the maxillary does not arise from direct ossification of Meckel's cartilage.
Derivatives
The skeletal elements and muscles are derived from mesoderm of the pharyngeal arches.
Skeletal
- malleus and incus of the middle ear
- maxilla and mandible
- spine of sphenoid bone
- sphenomandibular ligament
- palatine bone
- squamous part of temporal bone
- anterior ligament of malleus
Muscles
- muscles of mastication (chewing)
- mylohyoid muscle
- digastric muscle, anterior belly
- tensor veli palatini muscle
- tensor tympani muscle
Other
Mucous membrane and glands of the anterior two thirds of the tongue are derived from ectoderm and endoderm of the arch.
Nerve supply
The mandibular and maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) innervate the structures derived from the corresponding processes of the first arch. In some lower animals, each arch is supplied by two cranial nerves. The nerve of the arch itself runs along the cranial side of the arch and is called post-trematic nerve of the arch. Each arch also receives a branch from the nerve of the succeeding arch called the pre-trematic nerve which runs along the caudal border of the arch. In human embryo, a double innervation is seen only in the first pharyngeal arch. The mandibular nerve is the post-trematic nerve of the first arch and chorda tympani (branch of facial nerve) is the pre-trematic nerve. This double innervation is reflected in the nerve supply of anterior two-thirds of tongue which is derived from the first arch.[10]
Blood supply
The artery of the first arch is the first aortic arch,[11] which partially persists as the maxillary artery.
Second arch
The second pharyngeal arch or hyoid arch, is the second of fifth pharyngeal arches that develops in fetal life during the fourth week of development[9] and assists in forming the side and front of the neck.
Reichert's cartilage
Cartilage in the second pharyngeal arch is referred to as Reichert's cartilage and contributes to many structures in the fully developed adult.[12] In contrast to the Meckel's cartilage of the first pharyngeal arch it does not constitute a continuous element, and instead is composed of two distinct cartilaginous segments joined by a faint layer of mesenchyme.[13] Dorsal ends of Reichert's cartilage ossify during development to form the stapes of the middle ear before being incorporated into the middle ear cavity, while the ventral portion ossifies to form the lesser cornu and upper part of the body of the hyoid bone. Caudal to what will eventually become the stapes, Reichert's cartilage also forms the styloid process of the temporal bone. The cartilage between the hyoid bone and styloid process will not remain as development continues, but its perichondrium will eventually form the stylohyoid ligament.
Derivatives
Skeletal
From the cartilage of the second arch arises
- Stapes,
- Temporal styloid process,
- Stylohyoid ligament, and
- Lesser cornu of the hyoid bone.
Muscles
- Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis muscle
- Platysma
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Stapedius muscle
- Auricular muscles
Nerve supply
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Blood supply
The artery of the second arch is the second aortic arch,[11] which gives origin to the stapedial artery in some mammals but atrophies in humans.
Muscles derived from the pharyngeal arches
Pharyngeal muscles are striated muscles of the head and neck. Unlike skeletal muscles that developmentally come from somites, pharyngeal muscles are developmentally formed from the pharyngeal arches.
Most of the skeletal musculature supplied by the cranial nerves (special visceral efferent) is pharyngeal. Exceptions include, but are not limited to, the extraocular muscles and some of the muscles of the tongue. These exceptions receive general somatic efferent innervation.
First arch
All of the pharyngeal muscles that come from the first pharyngeal arch are innervated by the mandibular divisions of the trigeminal nerve.[14] These muscles include all the muscles of mastication, the anterior belly of the digastric, the mylohyoid, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini.
Second arch
All of the pharyngeal muscles of the second pharyngeal arch are innervated by the facial nerve. These muscles include the muscles of facial expression, the posterior belly of the digastric, the stylohyoid muscle, the auricular muscle[14] and the stapedius muscle of the middle ear.
Third arch
There is only one muscle of third pharyngeal arch, the stylopharyngeus. The stylopharyngeus and other structures from the third pharyngeal arch are all innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Fourth and sixth arches
All the pharyngeal muscles of the fourth and sixth arches are innervated by the superior laryngeal and the recurrent laryngeal branches of the vagus nerve.[14] These muscles include all the muscles of the palate (exception of the tensor veli palatini which is innervated by the trigeminal nerve), all the muscles of the pharynx (except stylopharyngeus which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve), and all the muscles of the larynx.
In humans
Since no human structures result from the fifth arch, the arches in humans are I, II, III, IV, and VI.[8] More is known about the fate of the first arch than the remaining four. The first three contribute to structures above the larynx, whereas the last two contribute to the larynx and trachea.
The recurrent laryngeal nerves are produced from the nerve of arch 6, and the laryngeal cartilages from arches 4 and 6. The superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve arises from arch 4. Its arteries, which project between the nerves of the fourth and sixth arches, become the left-side arch of the aorta and the right subclavian artery. On the right side, the artery of Arch 6 is obliterated while, on the left side, the artery persists as the ductus arteriosus; circulatory changes immediately following birth cause the vessel to close down, leaving a remnant, the ligamentum arteriosum. During growth, these arteries descend into their ultimate positions in the chest, creating the elongated recurrent paths.[6]
See also
References
- Graham A (2003). "Development of the pharyngeal arches". Am J Med Genet A. 119A (3): 251–256. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.10980. PMID 12784288. S2CID 28318053.
- Graham A, Smith A (2001). "Patterning the pharyngeal arches". BioEssays. 23 (1): 54–61. doi:10.1002/1521-1878(200101)23:1<54::AID-BIES1007>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID 11135309.
- Kardong KV (2003). "Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution". Third Edition. New York (McGraw Hill).
- Depew MJ, Lufkin T, Rubenstein JL (2002). "Specification of jaw subdivisions by Dlx genes". Science. 298 (5592): 381–385. doi:10.1126/science.1075703. PMID 12193642. S2CID 10274300.
- Fraser GJ, Hulsey D, Bloomquist RF, Uyesugi K, Manley NR, Streelman T (2009). Jernvall J (ed.). "An Ancient Gene Network Is Co-opted for Teeth on Old and New Jaws". PLOS Biology. 7 (2): 0233–0247. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000031. PMC 2637924. PMID 19215146.
- Larsen, William J. (1993). Human embryology. New York: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 318–323. ISBN 0-443-08724-5.
- McKenzie, James C. "Lecture 24. Branchial Apparatus". Howard University. Archived from the original on 2003-05-02. Retrieved 2007-09-09.
- Marino, Thomas A. "Text for Pharyngeal Arch Development". Temple University. Archived from the original on 2007-09-09. Retrieved 2007-09-09.
- William J. Larsen (2001). Human embryology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06583-7
- Inderbir Sing, G.P Pal-Human Embryology
- McMinn, R., 1994. Last's anatomy: Regional and applied (9th ed).
- Sudhir, Sant, 2008.Embryology for Medical Students 2nd edition
- Rodríguez-Vázquez JF (2008). "Morphogenesis of the second pharyngeal arch cartilage (Reichert's cartilage) in human embryos". J. Anat. 208 (2): 179–189. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00524.x. PMC 2100189. PMID 16441562.
- Sadler, Thomas W. (February 2009). Langman's Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 366–369. ISBN 978-0781790697.
- "marshall.edu". Archived from the original on 2009-02-27. Retrieved 2007-09-09.
- Sadler, Thomas W. (February 2009). Langman's Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 366–372. ISBN 978-0781790697.
- Higashiyama H, Kuratani S (2014). "On the maxillary nerve". Journal of Morphology. 275 (1): 17–38. doi:10.1002/jmor.20193. PMID 24151219. S2CID 32707087.
- Netter, Frank H.; Cochard, Larry R. (2002). Netter's Atlas of human embryology. Teterboro, N.J: Icon Learning Systems. p. 227. ISBN 0-914168-99-1.
- Kyung Won Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, Maryland: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
External links
- Graham A, Okabe M, Quinlan R (2005). "The role of the endoderm in the development and evolution of the pharyngeal arches". J. Anat. 207 (5): 479–87. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00472.x. PMC 1571564. PMID 16313389.