Phonerpeton
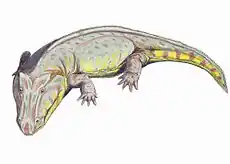
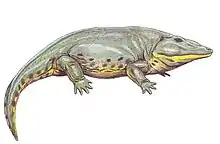
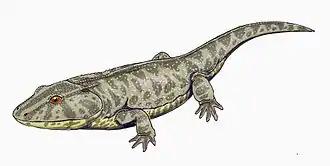
Phonerpeton is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl within the family Trematopidae that is known from the early Permian of Texas.[1]
| Phonerpeton Temporal range: Early Permian | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Temnospondyli |
| Family: | †Trematopidae |
| Genus: | †Phonerpeton Dilkes, 1990 |
| Species | |
History of study
Phonerpeton was first named by Dilkes (1990), with Phonerpeton pricei as the only species.[1] The genus name comes from the Greek words 'phonos' (murderous) and 'herpeton' (creeper). The holotype of P. pricei was previously described by Olson (1941) as Acheloma pricei.[2] Dilkes also synonymized this species with Acheloma whitei, which was also described by Olson (1941). Material referred to the taxon comes from the Archer City, Nocona, and Petrolia Formations and was collected between 1934 and 1952 by parties led by A.S. Romer, L.I. Price, and R.V Witter. Schoch & Milner (2014) separated the former 'Acheloma whitei' from P. pricei, distinguishing it by the shorter and more rounded external naris and an otic notch that was not slit-like.[3] They restricted P. pricei to the specimens from the Archer City Formation and P. whitei to the specimens from the Petrolia Formation.
Anatomy
Phonerpeton is represented only by relatively small specimens compared to the much larger Acheloma. Dilkes (1990) diagnosed Phonerpeton by the semilunar curvature of the squamosal, doming of the parietals along the midline, a closed basicranial joint with a clear suture between the pterygoid and the basipterygoid process of the parasphenoid (the basicranial joint), an unossified sphenethmoid, long and slender mid-dorsal ribs, a radius with a semicircular cross section, and a ridge along the anterolateral edge of the ulna. He differentiated it from Acheloma by the large and posteriorly open otic notch, a posterodorsal process of the quadrate consisting of two sheets of bone separated by a poorly ossified region, a semilunar curvature of the squamosal, and an unfused basicranial joint. Schoch & Milner (2014) retained only the absence of a slit-like notch (which is found in Acheloma) in the diagnosis.
Phylogeny
Phonerpeton is typically recovered as being most closely related to the other long-snouted trematopid from North America, Acheloma. Phylogeny below from Polley & Reisz (2011):[4]
| Dissorophoidea |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Dilkes, D.W. (1990). "A new trematopsid amphibian (Temnospondyli: Dissorophoidea) from the Lower Permian of Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (2): 222–243. doi:10.1080/02724634.1990.10011809.
- Olson, Everett Claire (1941). "The Family Trematopsidae". The Journal of Geology. 49 (2): 149–176. doi:10.1086/624952. ISSN 0022-1376.
- Schoch, Rainer R.; Milner, Andrew R. (2014). Sues, Hans-Dieter (ed.). Handbuch der Paläoherpetologie Part 3A2. Temnospondyli I. Stuttgart: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. ISBN 9783931516260. OCLC 580976.
- Polley, Brendan P.; Reisz, Robert R. (2011). "A new Lower Permian trematopid (Temnospondyli: Dissorophoidea) from Richards Spur, Oklahoma". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 161 (4): 789–815. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2010.00668.x.