RP2 (gene)
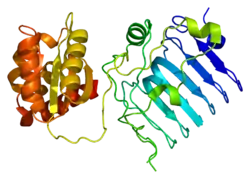
Protein XRP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RP2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
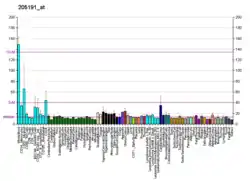
The RP2 locus has been implicated as one cause of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. The predicted gene product shows homology with human cofactor C, a protein involved in the ultimate step of beta-tubulin folding. Progressive retinal degeneration may therefore be due to the accumulation of incorrectly-folded photoreceptor or neuron-specific tubulin isoforms, followed by progressive cell death.[7] The RP2 protein is also involved in regulating the function and extension of the outer segment of cone photoreceptors in mice.[8][9]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000102218 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000060090 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Bhattacharya SS, Wright AF, Clayton JF, Price WH, Phillips CI, McKeown CM, Jay M, Bird AC, Pearson PL, Southern EM (Jun 1984). "Close genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and a restriction fragment length polymorphism identified by recombinant DNA probe L1.28". Nature. 309 (5965): 253–5. doi:10.1038/309253a0. PMID 6325945.
- Schwahn U, Lenzner S, Dong J, Feil S, Hinzmann B, van Duijnhoven G, Kirschner R, Hemberger M, Bergen AA, Rosenberg T, Pinckers AJ, Fundele R, Rosenthal A, Cremers FP, Ropers HH, Berger W (Sep 1998). "Positional cloning of the gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 2". Nat Genet. 19 (4): 327–332. doi:10.1038/1214. PMID 9697692.
- "Entrez Gene: RP2 retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive)".
- Li L, Rao KN, Zheng-Le Y, Hurd TW, Lillo C, Khanna H (Sep 2015). "Loss of Retinitis Pigmentosa 2 (RP2) protein predominantly affects cone photoreceptor sensory cilium elongation in mice". Cytoskeleton. 72 (9): 447–54. doi:10.1002/cm.21255. PMC 4715527. PMID 26383048.
- Li L, Khan N, Hurd T, Ghosh AK, Cheng C, Molday R, Heckenlively JR, Swaroop A, Khanna H (2013). "Ablation of the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 2 (Rp2) gene in mice results in opsin mislocalization and photoreceptor degeneration". Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54 (7): 4503–11. doi:10.1167/iovs.13-12140. PMC 3700388. PMID 23745007.
Further reading
- Clayton JF, Wright AF, Jay M, McKeown CM, Dempster M, Jay BS, Bird AC, Bhattacharya SS (1986). "Genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and DNA probe DXS7 (L1.28): further linkage data, heterogeneity testing, and risk estimation". Hum. Genet. 74 (2): 168–71. doi:10.1007/BF00282083. PMID 2876947.
- Thiselton DL, Hampson RM, Nayudu M, Van Maldergem L, Wolf ML, Saha BK, Bhattacharya SS, Hardcastle AJ (1997). "Mapping the RP2 locus for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa on proximal Xp: a genetically defined 5-cM critical region and exclusion of candidate genes by physical mapping". Genome Res. 6 (11): 1093–102. doi:10.1101/gr.6.11.1093. PMID 8938433.
- Mears AJ, Gieser L, Yan D, Chen C, Fahrner S, Hiriyanna S, Fujita R, Jacobson SG, Sieving PA, Swaroop A (1999). "Protein-truncation mutations in the RP2 gene in a North American cohort of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64 (3): 897–900. doi:10.1086/302298. PMC 1377809. PMID 10053026.
- Hardcastle AJ, Thiselton DL, Van Maldergem L, Saha BK, Jay M, Plant C, Taylor R, Bird AC, Bhattacharya S (2000). "Mutations in the RP2 gene cause disease in 10% of families with familial X-linked retinitis pigmentosa assessed in this study". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64 (4): 1210–5. doi:10.1086/302325. PMC 1377846. PMID 10090907.
- Rosenberg T, Schwahn U, Feil S, Berger W (1999). "Genotype-phenotype correlation in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 2 (RP2)". Ophthalmic Genet. 20 (3): 161–172. doi:10.1076/opge.20.3.161.2278. PMID 10520237.
- Wada Y, Nakazawa M, Abe T, Tamai M (2000). "A new Leu253Arg mutation in the RP2 gene in a Japanese family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41 (1): 290–3. PMID 10634633.
- Thiselton DL, Zito I, Plant C, Jay M, Hodgson SV, Bird AC, Bhattacharya SS, Hardcastle AJ (2000). "Novel frameshift mutations in the RP2 gene and polymorphic variants". Hum. Mutat. 15 (6): 580. doi:10.1002/1098-1004(200006)15:6<580::AID-HUMU15>3.0.CO;2-3. PMID 10862093.
- Sharon D, Bruns GA, McGee TL, Sandberg MA, Berson EL, Dryja TP (2000). "X-linked retinitis pigmentosa: mutation spectrum of the RPGR and RP2 genes and correlation with visual function". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41 (9): 2712–21. PMID 10937588.
- Chapple JP, Hardcastle AJ, Grayson C, Spackman LA, Willison KR, Cheetham ME (2000). "Mutations in the N-terminus of the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa protein RP2 interfere with the normal targeting of the protein to the plasma membrane". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (13): 1919–26. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.13.1919. PMID 10942419.
- Miano MG, Testa F, Filippini F, Trujillo M, Conte I, Lanzara C, Millán JM, De Bernardo C, Grammatico B, Mangino M, Torrente I, Carrozzo R, Simonelli F, Rinaldi E, Ventruto V, D'Urso M, Ayuso C, Ciccodicola A (2001). "Identification of novel RP2 mutations in a subset of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families and prediction of new domains". Hum. Mutat. 18 (2): 109–19. doi:10.1002/humu.1160. PMID 11462235.
- Liu L, Wei Y, Chen H (2002). "[Identification of a nonsense mutation causing X-linked RP2 in two Chinese families]". Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 81 (2): 71–2. PMID 11798852.
- Bartolini F, Bhamidipati A, Thomas S, Schwahn U, Lewis SA, Cowan NJ (2002). "Functional overlap between retinitis pigmentosa 2 protein and the tubulin-specific chaperone cofactor C". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (17): 14629–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200128200. PMID 11847227.
- Breuer DK, Yashar BM, Filippova E, Hiriyanna S, Lyons RH, Mears AJ, Asaye B, Acar C, Vervoort R, Wright AF, Musarella MA, Wheeler P, MacDonald I, Iannaccone A, Birch D, Hoffman DR, Fishman GA, Heckenlively JR, Jacobson SG, Sieving PA, Swaroop A (2002). "A comprehensive mutation analysis of RP2 and RPGR in a North American cohort of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70 (6): 1545–54. doi:10.1086/340848. PMC 379141. PMID 11992260.
- Bader I, Brandau O, Achatz H, Apfelstedt-Sylla E, Hergersberg M, Lorenz B, Wissinger B, Wittwer B, Rudolph G, Meindl A, Meitinger T (2003). "X-linked retinitis pigmentosa: RPGR mutations in most families with definite X linkage and clustering of mutations in a short sequence stretch of exon ORF15". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44 (4): 1458–63. doi:10.1167/iovs.02-0605. PMID 12657579.
- Sharon D, Sandberg MA, Rabe VW, Stillberger M, Dryja TP, Berson EL (2004). "RP2 and RPGR mutations and clinical correlations in patients with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73 (5): 1131–46. doi:10.1086/379379. PMC 1180492. PMID 14564670.
- Andréasson S, Breuer DK, Eksandh L, Ponjavic V, Frennesson C, Hiriyanna S, Filippova E, Yashar BM, Swaroop A (2004). "Clinical studies of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa in three Swedish families with newly identified mutations in the RP2 and RPGR-ORF15 genes". Ophthalmic Genet. 24 (4): 215–23. doi:10.1076/opge.24.4.215.17228. PMID 14566651.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.