Regional Council of Lombardy
The Regional Council of Lombardy (Consiglio Regionale della Lombardia) is the legislative assembly of Lombardy.
Regional Council of Lombardy | |
|---|---|
| 11th legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Established | 6 July 1970 |
| Leadership | |
President | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 80 |
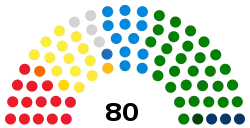 | |
Political groups | Government (49)
Opposition (31) |
Length of term | 5 years |
| Salary | €75,924/year + refunds |
| Elections | |
| Party-list semi-proportional representation with majority bonus D'Hondt method | |
Last election | 4 March 2018 |
Next election | March 2023 |
| Meeting place | |
| Pirelli Tower, Milan | |
| Website | |
| Official website | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Lombardy |
|
It was first elected in 1970, when the ordinary regions were instituted, on the basis of the Constitution of Italy of 1948.
Composition
The political system of the Regions of Italy was changed in 1995, when a semi-presidential system was introduced. If until that year the Council was elected under a pure proportional system and the President of Lombardy was chosen and dismissed by the Council, since 1995 the President and the Council are jointly elected by the people.
The Regional Council of Lombardy is composed of 80 members. From 1995 to 2012, 64 councillors were elected in provincial constituencies by proportional representation using the largest remainder method with a Droop quota and open lists, while 16 councillors (elected in bloc) came from a "regional list", including the President-elect. One seat was reserved for the candidate who came second. If a coalition won more than 40 seats with PR, as happened during the 2000 election, only 8 candidates from the regional list would be chosen and the number of those elected in provincial constituencies will be 72. If the winning coalition received less than 50% of votes, as happened during the 1995 election, special seats were added to the Council to ensure a large majority for the President's coalition.[1][2][3]
A new Lombard electoral law was adopted on 26 October 2012. While the President of Lombardy and the leader of the opposition are still elected at-large, 78 councillors, instead of 64 as it was before, are elected by party lists under a form of semi-proportional representation. The winning coalition receives a jackpot of at least 45 seats, which are divided between all majority parties using the D'Hondt method, as it happens between the losing lists. Each party then distributes its seats to its provincial lists, where candidates are openly selected.
The Council is elected for a five-year term, but, if the President suffers a vote of no confidence, resigns or dies, under the simul stabunt, simul cadent clause introduced in 1999 (literally they will stand together or they will fall together), also the Council is dissolved and a snap election is called.[4][5]
The Council chooses its speaker, called President of the Council (Presidente del Consiglio).
Political groups (2018–2023)
The Council is composed of the following political groups:[6]
| Party | Seats | Status | |
|---|---|---|---|
| League – Lombard League | 29 / 80 |
Government | |
| Democratic Party | 14 / 80 |
Opposition | |
| Five Star Movement | 13 / 80 |
Opposition | |
| Forza Italia | 12 / 80 |
Government | |
| Brothers of Italy | 3 / 80 |
Government | |
| Energies for Italy | 1 / 80 |
Government | |
| Us with Italy | 1 / 80 |
Government | |
| Ideal Lombardy – Fontana for President | 1 / 80 |
Government | |
| European Civic Lombards | 1 / 80 |
Opposition | |
| +Europe – Radicals | 1 / 80 |
Opposition | |
| Mixed[lower-alpha 1] | 4 / 80 |
||
- Patrizia Baffi (Italia Viva)
Viviana Beccalossi (Independent)
Paolo Franco (Cambiamo!)
Niccolò Carretta (Action)
By coalition:
| Party | Seats | Status |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centre-right coalition | 49 / 80 |
Government | ||
| Centre-left coalition | 18 / 80 |
Opposition | ||
| Five Star Movement | 13 / 80 |
Opposition | ||
Historical composition

| Election | DC | PCI | PSI | PLI | PRI | PSDI | MSI | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 June 1970 | 36 | 19 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 80 |
| 15 June 1975 | 32 | 25 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 80 |
| 8 June 1980 | 34 | 23 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 80 |
| 12 May 1985 | 31 | 22 | 12 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 80 |
| 6 May 1990 | 25 | 15 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 22 | 80 |
| Election | Majority | Opposition | Total | Council | President of the Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 April 1995 | 38 FI 12 AN 4 CCD |
12 LN 11 PDS 5 PRC 4 PPI 2 Greens 2 PdD |
90 |  |
 Roberto Formigoni |
| 16 April 2000 | 27 FI 11 LN 8 AN 2 CCD 2 CDU 1 PP |
20 The Olive Tree 5 PRC 3 Bonino List 1 SDI |
80 |  | |
| 3 April 2005 | 25 FI 15 LN 9 AN 3 UDC |
20 The Olive Tree 3 PRC 2 Greens 1 Greens 1 PP 1 PdCI |
80 |  | |
| 28 March 2010 | 29 PdL 20 LN |
22 PD 4 IdV 3 UDC 1 PP 1 SEL |
80 |  | |
| 24 February 2013 (snap election) |
19 PdL 16 LN 11 Maroni List 2 FdI 1 PP |
17 PD 9 M5S 5 Ambrosoli List |
80 |  |
 Roberto Maroni |
| 4 March 2018 | 29 LN 14 FI 3 FdI 1 Fontana List 1 NcI 1 EpI |
16 PD 13 M5S 2 Gori List 1 +Eu |
80 |  |
 Attilio Fontana |
Presidents
This is a list of the Presidents of the Regional Council (Italian: Presidenti del Consiglio regionale):
| Name | Period | Regional Legislature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gino Colombo (DC) | 6 July 1970 | 24 July 1975 | I (1970) | |
| Sergio Marvelli (PSI) | 24 July 1975 | 20 April 1978 | II (1975) | |
| Carlo Smuraglia (PCI) | 20 April 1978 | 24 July 1980 | ||
| Sergio Marvelli (PSI) | 24 July 1980 | 6 October 1983 | III (1980) | |
| Renzo Peruzzotti (PSI) | 6 October 1983 | 18 June 1985 | ||
| Ugo Finetti (PSI) | 18 June 1985 | 5 August 1985 | IV (1985) | |
| Fabio Semenza (PRI) | 5 August 1985 | 27 June 1990 | ||
| Giampietro Borghini (PCI) | 27 June 1990 | 12 February 1992 | V (1990) | |
| Claudio Bonfanti (PSI) | 12 February 1992 | 9 December 1992 | ||
| Francesco Zaccaria (PSI) | 9 December 1992 | 19 June 1995 | ||
| Giancarlo Morandi (FI) | 19 June 1995 | 12 June 2000 | VI (1995) | |
| Attilio Fontana (LN) | 12 June 2000 | 6 June 2005 | VII (2000) | |
| 6 June 2005 | 6 July 2006 | VIII (2005) | ||
| Ettore Albertoni (LN) | 6 July 2006 | 15 July 2008 | ||
| Giulio De Capitani (LN) | 15 July 2008 | 11 May 2010 | ||
| Davide Boni (LN) | 11 May 2010 | 17 April 2012 | IX (2010) | |
| Fabrizio Cecchetti (LN) | 17 April 2012 | 27 October 2012 | ||
| Regional Council suspended[lower-alpha 1] | ||||
| Raffaele Cattaneo (FI) | 28 March 2013 | 5 April 2018 | X (2013) | |
| Alessandro Fermi (FI) | 5 April 2018 | incumbent | XI (2018) | |
- Notes
- On 27 October 2012, 74 members of the Regional Council resigned. The Council was automatically dissolved.
References
- Regional Council of Lombardy – Electoral law
- Regional Council of Lombardy – Scheme for allocation of seats
- Ministry of the Interior – Electoral Archive
- Regional Council of Lombardy – 1999 Constitutional Law
- Regional Council of Lombardy – Autonomy Statute
- "I Gruppi Consiliari". www.consiglio.regione.lombardia.it (in Italian). Retrieved 4 July 2019.