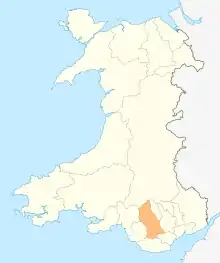
Rhondda Cynon Taf
Rhondda Cynon Taf (Welsh pronunciation: [ˈr̥ɔnða ˈkənən ˈtaːv], and popularly, 'RCT') is a county borough in south Wales. It consists of five valleys: the Rhondda Fawr, Rhondda Fach, Cynon, Taff (Welsh: Taf) and Ely valleys, plus a number of towns and villages away from the valleys. Results from the 2011 census showed 19.1% of its 234,410 residents self-identified themselves as having some ability in the use of the Welsh language.[1]
Rhondda Cynon Taf County Borough
Bwrdeistref Sirol Rhondda Cynon Taf | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Admin HQ | Clydach Vale |
| Largest town | Aberdare |
| Government | |
| • Type |  Rhondda Cynon Taf County Borough Council |
| • Control | Labour |
| • MPs | |
| • MSs | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 424 km2 (164 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 13th |
| Population (2017) | |
| • Total | 241,264 |
| • Rank | Ranked 3rd |
| • Density | 566/km2 (1,470/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | Ranked 8th |
| • Ethnicity | 98.9% White |
| Welsh language | |
| • Rank | Ranked 13th |
| • Any skills | 23.3% |
| Geocode | 00PF (ONS) W06000016 (GSS) |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-RCT |
The county borough borders Merthyr Tydfil and Caerphilly to the east, Cardiff and the Vale of Glamorgan to the south, Bridgend and Neath Port Talbot to the west and Powys to the north. Its principal towns are - Aberdare, Llantrisant with Talbot Green and Pontypridd, with other key settlements/towns being - Maerdy, Ferndale, Hirwaun, Llanharan, Mountain Ash, Porth, Tonypandy, Tonyrefail and Treorchy.
The most populous town in Rhondda Cynon Taf is Aberdare (Welsh: Aberdâr) with a population of 31,200 (2018), followed by Pontypridd with 30,860 (2018).
History
The county borough was formed on 1 April 1996, by the merger of the former Mid Glamorgan districts of Rhondda, Cynon Valley and Taff-Ely (with the exceptions of Creigiau and Pentyrch, which were added to Cardiff). Its name reflects all these, and thus also the rivers Rhondda, Cynon and Taff.
Industry
The district developed from the discovery and mining, primarily for export, of high-quality Welsh coals, such as steam coal, via Cardiff and Barry docks. The landscape was dominated by coal-waste heaps and deep mine pit-heads. Many of the roads are lined with semi-ribbon development of closely packed Victorian terraces of houses which have given the Rhondda and Cynon valleys their distinctive appearance. In the nineteenth century the Rhondda had over 60 mines.
As deep mines closed, a number of very large open-cast coal mines were created and remain in operation, especially towards the north of the area.
The Welsh Development Agency, which was formed in 1976 to help reverse the economic down-turn in Wales caused by the recession in both the coal and steel industries, was very active in the Rhondda Cynon Taf area in supporting and encouraging industrial and commercial regeneration. Recent investment in the area has included the Dragon International Film Studios, on the site of Llanilltyd open-cast mine. The location of the project has led it to become known locally as "Valleywood", even though the Welsh valleys are some miles away.
Environment
The coal industry has had major adverse impacts on the quality of the environment, such that most of the rivers were severely polluted to the exclusion of all fish life. Recent decades have shown great improvement with the return of salmon recorded in the River Taff and the River Rhondda but the continued presence of man-made obstacles in the rivers is inhibiting regeneration of their pre-industrial numbers and condition.
The chemical industry has also had adverse effects due to the dumping of toxic waste in the now disused Brofiscin Quarry in the village of Groes-faen. Dumping took place over a 6-year period between 1965 and 1970 by the Monsanto Company.[2] Clean-up costs have been estimated to be over £100 million. A Dr Papageorge, formerly Monsanto's chief scientist, estimates that between 60,000 and 80,000 tonnes of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) contaminated wastes were dumped there.[3] Works costing £1.25 million to reduce health risks to local residents and members of the public using a nearby footpath were completed at the quarry in 2012.[4] Monsanto, BP and Veolia contributed to the cost of the cleanup while continuing to deny liability.[4]
Government
The area is governed by Rhondda Cynon Taf County Borough Council from headquarters in Clydach Vale and is the host authority to the South East Wales Improvement Collaborative (SEWIC), Excellence Wales award winner 2010. The Rhondda Cynon Taf has four MPs represented in the UK Parliament. There are also four constituencies represented in the Senedd (Welsh Parliament).
Freedom of the Borough
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the Borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf.
Individuals
- Stuart Burrows OBE: 31 January 2008.[5]
- Elaine Morgan OBE FRSL: 10 April 2013.[6]
Military units
- The Royal Welsh: 2010.[7]
- The Welsh Guards: 15 May 2013.[8]
- MOD St Athan: 2 June 2018.[9]
See also
References
- "Population Density, 2011". Office for National Statistics. neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- "Brofiscin Quarry: What's happened so far?". Environment Agency. Retrieved 11 December 2010.
- Hughes, John; Thomas, Pat (May 2007). "Burying The Truth". The Ecologist. 37 (4): 33–63.
- Levitt, Tom (14 July 2015). "Monsanto, BP and Veolia agree to pay for cleanup of contaminated Welsh site". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- "Tenor granted freedom of borough". WalesOnline. 31 January 2008.
- Best, Jessica (10 April 2013). "Award-winning columnist Elaine Morgan given the freedom of Rhondda Cynon Taf". WalesOnline.
- McCarthy, James (8 October 2016). "Royal Welsh soldiers marched through Pontypridd watched by thousands".
- "Welsh Guards hold freedom parade". 15 May 2013 – via www.bbc.com.
- "Freedom Of County Borough". www.rctcbc.gov.uk.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rhondda Cynon Taf. |