River Liffey
The River Liffey (Irish: An Life) is a river in Ireland that flows through the centre of Dublin. Its major tributaries include the River Dodder, the River Poddle and the River Camac. The river supplies much of Dublin's water and a range of recreational activities.[1]
| River Liffey | |
|---|---|
 Boardwalks of Liffey from O'Connell Bridge, in Dublin | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Kippure, County Wicklow |
| • elevation | 500 m (1,600 ft) |
| Mouth | |
• location | Irish Sea at Dublin Bay |
• coordinates | 53.343316°N 6.181303°W |
| Length | 125 km (78 mi) |
| Basin size | 1,256 km2 (485 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | Annual: 13.8 m3/s (490 cu ft/s) Aug: 3.7 m3/s (130 cu ft/s) Dec: 29.8 m3/s (1,050 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Ballylow Brook, King's River, Lemonstown Stream, Kilcullen Stream, Pinkeen Stream, Rye Water, Silleachain Stream, Furry Glen Stream, Magazine Stream, Finisk Stream, Bradogue River |
| • right | Sraghoe, Cransillagh, Athdown Brook, Shankill River, Brittas River, Morell River, Griffeen River, Glenaulin Stream, Creosote Stream, Camac River, River Poddle, Stein River, River Dodder |
Name
Ptolemy's Geography (2nd century AD) described a river, perhaps the Liffey, which he labelled Οβοκα (Oboka). Ultimately this led to the name of the River Avoca.[2]
The Liffey was previously named An Ruirthech, meaning "fast (or strong) runner".[3] The word Liphe (or Life) referred originally to the name of the plain through which the river ran, but eventually came to refer to the river itself.[4] The word derives from the same root as Welsh llif (flow, stream), namely Proto-Indo-European lē̆i-4.[5]It was also known as the Anna Liffey,[6] possibly from an anglicisation of Abhainn na Life, the Irish phrase that translates into English as "River Liffey".[7] James Joyce embodies the river as "Anna Livia Plurabelle" in Finnegans Wake.
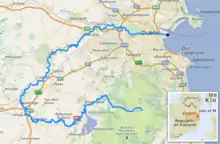
Course and system

The Liffey rises in the Liffey Head Bog between the mountains of Kippure 742 metres (2,434 ft) and Tonduff 642 metres (2,106 ft) in the northern section of the Wicklow Mountains, forming from many streamlets at Sally Gap. It flows for 132 km (82 mi)[8] through counties Wicklow, Kildare and Dublin before entering the Irish Sea at its mouth at the midpoint of Dublin Bay, on a line extending from the Baily lighthouse to the Muglin Rocks. It crosses from County Wicklow into County Kildare at Poulaphouca and from County Kildare into County Dublin at Leixlip, with most of its length being in Kildare.
The catchment area of the Liffey is 1,256 km2 (485 sq mi).[9] The long term average flow rate of the river is 18.0 m3/s (640 cu ft/s).[9]
Tributaries
The Liffey system includes dozens of smaller rivers and streams. Early tributaries include the Athdown Brook, Shankill River, Ballylow Brook, Brittas River and Woodend Brook, as well as the substantial King's River.
Downstream of Poulaphouca are the Lemonstown Stream, Kilcullen Stream and Pinkeen Stream, followed by the Painestown River (with tributaries including the Morell River), Rye Water (with tributaries including the Lyreen), and the Griffeen River.
Within Dublin are the various Phoenix Park streams on the left bank, interspersed with right bank tributaries such as the Glenaulin Stream and Creosote Stream.[10]
Within the quays area tributaries include the River Camac, possibly Colman's Brook, the Bradogue River, River Poddle, Stein River and the River Dodder, some of which have numerous tributaries of their own.
In earlier times, the River Tolka was also arguably a tributary of the Liffey or at least shared its mouth, but it now enters Dublin Bay distinctly, some distance to the north.
Dams, reservoirs and falls
There are dams for three ESB hydroelectric power stations along the river, at Poulaphouca, Golden Falls and Leixlip. Major reservoir facilities also exist at Poulaphouca. The Liffey does not feature natural lakes and has few islands.
Significant falls at Poulaphouca and at Golden Falls were flooded by reservoir construction. There remain areas of rapids, including as the river approaches Dublin city.
Navigation and uses
The River Liffey in Dublin city has been used for many centuries for trade, from the Viking beginnings of the city up to recent times. It is connected to the River Shannon via the Grand Canal and the Royal Canal.
Water supply
Around 60% of the Liffey's flow is abstracted for drinking water and to supply industry. Much of this makes its way back into the river after purification in wastewater treatment plants. Despite a misconception that the Guinness brewery is one such commercial user,[11] the facility uses water piped from the Wicklow Mountains.[12]
Electricity generation
ESB hydroelectric power stations exist along the river, at Poulaphouca, Golden Falls and Leixlip, in addition to a number of minor private installations.
Traffic
_p131_SARAH'S_BRIDGE%252C_ON_THE_RIVER_ANNA_LIFFEY.jpg.webp)
A well-known sight on the Liffey up to the 1990s, the Lady Patricia[13] and Miranda Guinness[13] cargo ships were used to export Guinness from the St. James's Gate Brewery.
As of the early 21st century, the only regular traffic on the river within the city is the Liffey Voyage water tour bus service, which runs guided tours along the River Liffey through Dublin City centre. Departing from the boardwalk downstream of the Ha'penny Bridge, the Spirit of the Docklands was built by Westers Mekaniska in Sweden as a 50-passenger water taxi. Its variable ballast tanks (not unlike a submarine) and low air draught mean that at low tide it can float high, but at high tide it can ride low and still pass below the Liffey's bridges.
Downstream of the East-Link bridge, the river is still mainly used for commercial and ferry traffic, with some recreational use also. High speed trips out the mouth of the Liffey were also previously available from Sea Safari.[14]
Recreational use

Upstream from the city, at Chapelizod, the river is used by private, university and Garda rowing clubs.
The Liffey Descent canoeing event, held each year since 1960, covers a 27 km (17 mi) course from Straffan to Islandbridge. The Normal Tidal Limit (NTL) of the river is Islandbridge (weir). The Liffey Swim takes place every year in late August or early September between Watling Bridge and The Custom House. The Islandbridge stretch of river accommodates a number of rowing clubs including Trinity College, UCD, Commercial, Neptune, and the Garda rowing club.
The Liffey is widely used for recreational activities – such as canoeing, rafting,[15] fishing, swimming, significant facilities are at Poulaphouca, Kilcullen, Newbridge, where a seven-acre Liffey Linear Park has been developed, and other facilities are located further downriver at Leixlip and other towns.
Crossings
History
The earliest stone bridge over the Liffey of which there is solid evidence was the Bridge of Dublin (on the site of the current Fr. Mathew Bridge), built by the Dominicans in 1428, which survived well into the 18th century.[16] This four-arch bridge included various buildings such as a chapel, bakehouse and possibly an inn[17] and replaced an earlier wooden bridge (Dubhghalls Bridge) on the same site. Island Bridge (a predecessor of the current bridge) was added in 1577.
With the development of commercial Dublin in the 17th century, four new bridges were added between 1670 and 1684: Barrack, or Bloody Bridge, (the forerunner of the current Rory O'More Bridge), Essex Bridge (Grattan Bridge), Ormond Bridge (O'Donovan Rossa Bridge) and Arran Bridge. The oldest bridge still standing is Mellows Bridge, (originally Queens Bridge) constructed in 1764 on the site of Arran Bridge, which was destroyed by floods in 1763. The first iron bridge was the Ha'penny Bridge built in 1816. Farmleigh Bridge, also iron, was built around 1872 at the end of a tunnel and connected Farmleigh estate to Palmerstown.[18]
The Millennium Bridge was opened in December 1999, and 21st century additions include Seán O'Casey Bridge (2005), Samuel Beckett Bridge (2009),[19][20] and Rosie Hackett Bridge (2014).[21]
Present day

Dividing the Northside of Dublin from the Southside, the Liffey is today spanned by numerous bridges, mostly open to vehicular traffic. These include the West-Link Bridge on the M50 motorway, Seán Heuston Bridge and O'Connell Bridge. There are 3 pedestrian bridges in the city: the Millennium Bridge, Seán O'Casey Bridge and the Ha'penny Bridge. 21st century additions include the Samuel Beckett Bridge (2009) and James Joyce Bridge (2003), both designed by Santiago Calatrava.
Crossings further upriver include the Liffey Bridge at Celbridge, "The Bridge at 16" (a 19th-century pedestrian suspension bridge at what is now the K Club), and the Leinster Aqueduct – which carries the Grand Canal over the Liffey at Caragh.[1]
Art works along the river and its quays include the Famine Memorial Statues (near the IFSC) and the World Hunger Stone.[22]
Quays
The song about Seamus Rafferty refers to the "bowsies on the quay"; However, from the late 20th-century there was some renewed development on the quays, with the addition of linear parks and overhanging boardwalks.
There are quays on the north and south banks of the Liffey, extending from the weir at Islandbridge to Ringsend bridge over the river Dodder, just before the East-Link toll bridge.
From west to east, the quays on the north bank are:
- Bridgewater, Wolfe Tone, Sarsfield, Ellis, Arran, Inns, Ormond Upper, Ormond Lower, Bachelors Walk, Eden, Custom House, and North Wall.
From west to east, the quays on the south bank are:
- Victoria, Usher's Island, Usher's, Merchants, Wood, Essex, Wellington, Crampton, Aston, Burgh, George's, City, Sir John Rogerson's, and Great Britain.
Incidents
In December 2000, a Bus Éireann bus, crossing the Liffey at Butt Bridge, collided with another bus and skidded into the Liffey. There were some injuries, but no-one was killed.[23]
In July 2011, a long-term homeless man rescued his pet rabbit after it had been thrown into the river. Diving off O'Connell Bridge in front of hundreds of people, videos of the rescue circulated on the internet, and the man received an honour (and job offer at an animal shelter) for his actions.[24][25][26][27] The man who threw the rabbit into the river was arrested.[28]
Annalistic references
In the Annals of Inisfallen for the year 808, an entry reads:
- AI808.2 A defeat [inflicted] by the Laigin on Áed, son of Niall, at the river of Liphe.
Popular culture references


From Joyce to Radiohead, the Liffey is often referenced in literature and song:
James Joyce, Finnegans Wake (first sentence of novel).
That is the first of a number of references to the Liffey in the Wake: insofar as the book has characters, the female protagonist of the novel, Anna Livia Plurabelle, is herself an allegory of the river.
Radiohead, "How to Disappear Completely" from album Kid A
The Wolfe Tones, "Flow Liffey Waters"
Brendan Behan, Confessions of an Irish Rebel.
Canon Charles O'Neill, The Foggy Dew.
Fare thee well, Sweet Anna Liffey, it's the Ganges I love best
I found a place in India so far across the foam
Gaelic Storm, "Punjab Paddy from album How Are We Getting Home?" .
I watch the new glass cages, that spring up along the quay
My mind's too full of memories, too old to hear new chimes

See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to River Liffey, Ireland. |
- HMS Liffey
- List of rivers in Ireland
- Rivers of Ireland
References
- "River Liffey Information". Irelandbyways.com. Retrieved 25 January 2013.
- "Ireland" (PDF). Romaneranames.uk. Roman Era Names. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- Archive index at the Wayback Machine
- Byrne, F. J. 1973. Irish Kings and High-Kings. Dublin. p.150
- Julius Pokorny, Indogermanisches etymologisches Wörterbuch (Francke, 1959), word 1136 https://www.win.tue.nl/~aeb/natlang/ie/pokorny.html
- As indicated by the caption of an engraving published in 1831
- "Seanad Éireann – Vol 159, May, 1999 – Motion on National Archives – David Norris (senator and Trinity lecturer) referencing Georgian Society records". Oireachtas Debates (Hansard). 1999.
- "Table of Reference". Rivers and their Catchment Basins. Ordnance Survey of Ireland. 1958.
- SERBD Report - Physical Description (Chapter) (PDF) (Report). South Eastern River Basin District Management System. p. 38. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016.
- "River Liffey". fishinginireland.info. Retrieved 25 January 2013.
- "'Is it made with Liffey water?' Philip enquires of Guinness". Irish Independent. 18 May 2011. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- "Frequently Asked Questions". Guinness.com. Archived from the original on 11 June 2017.
[I]s Guinness made with water from the River Liffey? [..] No. While [..] situated on the banks of the River Liffey [..] the water used [..] comes from the Wicklow mountains
- "Background on the Guinness boats on the Liffey". IrishShips.com. Archived from the original on 19 March 2006.
- "Sea Safari". Sesafari.ie. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
Tours Suspended for 2016
- "Liffey River - River Guide". IWW.ie. IrishWhitewater. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- Project history of Dublin's River Liffey bridges (PDF). Bridge Engineering 156 Issue BE4 (Report). Phillips & Hamilton. December 2003. pp. 161–179.
- Liffey Bridges Survey team (1987). The Liffey bridges from Islandbridge to Eastlink: A historical and technical report. Liberties Association. p. 4.
- "IrishCycle.com Guinness Bridge/Silver Bridge". Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- "Samuel Beckett Bridge opens". Irish Times. 11 December 2009.
- "Samuel Beckett Bridge". Dublin City Council. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011.
- "Rosie Hackett Bridge to open at 6am tomorrow". Irish Times. 20 May 2014.
- Kaufman, R (2014). Kaufman Green Guide Dublin. p. 132. ASIN B00OR0W1QK.
- "Investigation launched into bus crash". RTE.ie. 4 December 2000.
- "Honour for homeless hero who rescued rabbit". Evening Herald. Retrieved on 12 July 2011.
- "Reward for river rabbit rescuer". The Irish Times. Retrieved on 12 July 2011.
- "Rabbit rescuer offered job at animal shelter". The Irish Emigrant. Retrieved on 12 July 2011.
- "Rabbit river rescue hero is offered animal care job". Evening Herald. Retrieved on 12 July 2011.
- "Award for River Liffey rabbit rescuer". RTÉ News. Retrieved on 12 July 2011.