Royal Moroccan Gendarmerie
The Royal Gendarmerie (Arabic: الدرك الملكي المغربي ad-darak al-malikiyy al-maḡribiyy) is the gendarmerie body of Morocco, and comes under the authority of the Ministry of Interior.
| Royal Gendarmerie | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Founded | 1957 |
| Country | |
| Part of | Royal Moroccan Armed Forces |
| Garrison/HQ | Rabat, Morocco |
| Commanders | |
| Supreme Commander | Mohammed VI of Morocco |
| Commander | General Mohamed Haramou |
History
The Moroccan Royal Gendarmerie was founded in 1957 by the late King Mohammed V. The structure of its functions has been determined by the two major different but complementary traditions. One of them has its roots in the history and culture of Morocco. The gendarmerie was born of Moroccan administrative and political system which has ensured public security and maintenance of public order for centuries. The second tradition (Makhzen) is much newer.
Description
Like other members of the FIEP organization, the legislation which founded the Royal Moroccan Gendarmerie describes it as a public force designed to guarantee public security and public order and the implementation of laws. This legislation text attaches the Gendarmerie to the Royal Moroccan Army, then constituting a military force in its structure, administration and command forms. It consists of officers and NCOs.
Duties
The duties of The Royal Moroccan Gendarmerie are numerous and various in kind. However, the legislative body has given great importance to policing duties. The seventh Article of the founding text indicates that "The service aim of the gendarmerie is to ensure especially administrative, judicial and military policing activities directly and to help to the competent authorisations with the envisaged laws." This situation implies three attachments as to the utilisation of the Royal Gendarmerie:
To the National Defence Administration especially on the subjects of organisation equipment and military judicial policing ; To the Ministry of Justice for the implementation of judicial policing; and, To the Ministry of the Interior on the subject of Common Administration Policing.
The duties of the Royal Gendarmerie, in this field, have been determined by the code of Penal Trial Procedures of 1959. It performs all these duties under the administration of the royal prosecutor and control of the Court of Appeal. Duties consist of determination of the crime before the prosecution gathering the evidence, detection of perpetrators and bringing them before the authorised courts ;
And executing the orders of the judges after the prosecution. The personnel of the Royal Gendarmerie participates in the implementation Judicial Policing. The Royal Gendarmerie who acts with the characteristics of being a judicial oriented police officer according to the Court of Penal Proceedings
Detects and determines the violation of the laws as a judicial police; and As a police of public force, informs the royal prosecutor of crimes and offences over which they have no jurisdiction. To struggle against the continuous increase of crime and its international aspects and, on the other hand, the increase of the texts and their complexity the Royal Gendarmerie is modernising its methods and equipment continuously and reinforcing its efficiency by evaluating technical and scientific policing and criminal data. With this aim, two laboratories, which are under the administration of senior researchers, were established.
Administrative Police
There are two major policing families within the Royal Gendarmerie sharing specific preventive activities. They are, the General Administrative Police and the Special Administrative Police. The first one gathers the general and individual measures relating to the maintenance of public order, public security, health, peace and morality. This Police is attached to the Ministry of the Interior. The other one consists of a number of special police functions according to varieties and sectors. These units such as Traffic, Hunting, Fishing, Explosives are arranged according to special laws and attached to units of different ministries. This units have, sometimes, their own police but, due to the existing personnel they are not always able to be ready in time. According to the principle of assistance and the accomplishment of the administrative police tasks, the need implied by these functions are satisfied. The administrative police ensures the continuation among the units of ministries with its description in the second place. However, policing the traffic and security of the transportation roads represent according to the ruling texts, one of its fundamental functions. The Royal Gendarmerie gives priority to the preventive measures by accompanying the activities of the Government. This is the reason why it reinforces the administrative police with its all in hand a unit which is securing and discouraging as much widely and continuously as possible. Territorial Authority in the Country : The text put forwards for the gendarmerie to be active throughout the country and to show itself in the army as a special condition. The gendarmerie is especially responsible for securing the roads of villages and transportation. However its activities generally are generally conducted out of city surroundings. The Royal Gendarmerie sometimes becomes active in the cities when the situation requires. To put it in a more concrete way, it is responsible for watching coasts and borders of the whole country which (approximately 3,400 km), more than half of the population; most of the transportation roads and important points of the social life.
Organisation
Further information: Groupe d'Intérvention de La Gendarmerie Royale
To perform various duties, the Royal Gendarmerie is organised as follows :
- Headquarters: which conducts the overall main duties of the force;
- 22 Regional Gendarmeries,
- 64 Companies of Gendarmerie and
- 322 posts of Gendarmerie where they are deployed to divided small security areas.
There is a Mobile Gendarmerie specifically in charge of maintaining public order and helping the regional gendarmerie occasionally. They are ; Air Gendarmerie, Maritime Gendarmerie, Beside these major units, specialised units have been founded with the commitment to perform the duties to meet special needs which requires special capabilities. But it is worth indicating that the regional posts have a special place among these units. They are rightly accepted as a main pole of the army. The base of the services is performed according to their levels. The remaining Headquarter and specialised units are available to provide needed supports to these posts. Within the hierarchical organisation posts become more autonomous which allows them to co-operate with the local authorities and public prosecutors office. The most recent units are the environment posts. They are specifically assigned to the protection of nature. Their activities are co-ordinated by the central unit for environment founded for this aim. Commanding on top of the organisation is a chief of staff gathering all the central units together. Today the Moroccan Royal Gendarmerie is commanded by a lieutenant general.
Ranks
Officers
| Equivalent NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) and student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
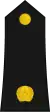
| Général de corps d'armée | Général de division | Général de brigade | Colonel Major | Colonel | Lieutenant-Colonel | Commandant | Capitaine | Lieutenant | Sous-Lieutenant | Aspirant | Eleve Officier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enlisted
| Equivalent NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Officer Class 1 Adjudant-chef |
Warrant Officer Class 2 Adjudant |
Sergeant Major Sergent-major |
Staff Sergeant Sergent-chef |
Sergeant Sergent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
International co-operation
Since its foundation, the Royal Gendarmerie has laid efficient mutual co-operation basis with the different brotherhood organisations and also joined in the FIEP organization in 1999 which provides the framework the improvement of mutual relations and the maintenance of security in the region.
Inventory
- Small arms & Vehicles
- Pistols:
- SMG's:
- Assault Rifles:
- SAR 21
- M16 rifle
- M4 carbine
- FN FAL
- HK G36
- FN2000
- Steyr AUG
- Sniper Rifles:
- Shotguns:
- Vehicles:
- MRAP(unknown model/type)
- Chevrolet Suburban
Aircraft
| Aircraft | Origin | Type | Variant | In service | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helicopters | ||||||
| SA 315B Lama | France | liaison | 7[1] | |||
| SA342 Gazelle | France | observation | 5[1] | |||
| Eurocopter Fennec | France | utility / observation | 6[1] | |||
| Eurocopter EC135 | Germany | utility / MEDIVAC | 3[2] | |||
| Eurocopter EC145 | Germany | utility / MEDIVAC | 2[2] | |||
| SA 330 Puma | France | utility / aerial firefighting | C/F/H | 7[1] | ||
| Sikorsky S-70 | United States | utility / transport | S-70A-26 | 2[2] | ||
| Eurocopter AS332 | France | VIP | AS332/EC225 | 2[3] | one of which is an EC225 Super Puma | |
See also
References
- "World Air Forces 2004 pg. 75". Flightglobal Insight. 2004. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- "Royal Moroccan Gendarmerie". helis.com. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- "MOROCCAN ROYAL GENDARMERIE: THE MULTI-MISSION SPECIALIST". airbushelicopters.com. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
External links
- (in French) Gendarmerie Royale Marocaine sur le réseau social Facebook
- (in French) Gendarmerie royale marocaine
- (in French) Portail la Gendarmerie Royale du Maroc
- (in French) Actualités de la Gendarmerie Royale du Maroc