Rudbar
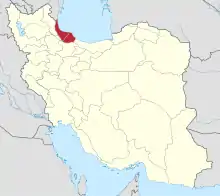
Rudbar (Persian: رودبار, romanized: Rudbār) (Gilaki:, rubâr)[2] is a city and capital of Rudbar County, Gilan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 11,454, in 3,303 families.[3]
Rudbar
رودبار | |
|---|---|
City | |
 | |
 Rudbar | |
| Coordinates: 36°48′N 49°24′E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Gilan |
| County | Rudbar |
| Bakhsh | Central |
| Population (2016 Census) | |
| • Total | 14,747 [1] |
| Time zone | UTC+3:30 (IRST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+4:30 (IRDT) |
| Area code(s) | +98(013) |
Rudbar is 268 kilometres (167 mi) from Tehran and with a variable climate. It is located on the fringes of a valley through which the Sefid River (Rud-e Safid) flows. Rudbar can be considered as a gateway to the Gīlān Province from central Iran.
Its name (meaning "by the river" in Persian) is a reference to the river named Sepid Rood (Sepid Roud) that passes by the city. Rudbar is also called "Roodbar Zeitoun (olive)" for the olive gardens in the area.
Rudbar's local economy notably includes olives and olive-based products. Groves of olive trees surround the city. Olive oil is produced locally. Rudbar is also known for its cream-hued, handcrafted carpets of fine quality. Despite the olive gardens that may suggest presence of a Mediterranean climate, the winters are very cold in the area. The winds in the Sepid Rood valley (Manjil) are well known in the country.
There are three main dialects of Gilaki Language but larger cities in Gilan have slight variations to the way they speak. These "sub-dialects" are Rashti, Rudbari, Some’e Sarai, Lahijani, Langerudi, Rudesari, Bandar Anzali and Fumani. People of Rudbar are Gilaks and they speak Gilaki Language with Galeshi Dialect and Rudbari Sub-dialect.[4][5]
History
The civilization of Rudbar and its surroundings date back to 2000 years BCE. The Marlik bowl, a famous archeological artifact and one of the oldest gold bowls in the world from 1st millennium BC, was found there. With the advent of Islam, tribes from Damascus and Halab (Aleppo) immigrated and became settlers there. Later, Nizari Isma'ili da'i made inroads and eventually established an Assassin stronghold. In the era of Nader Shah Afshar, groups from the Kurds of Quchan and areas of northern Khorassan also settled there.
Rudbar was near the epicenter of the 1990 Manjil–Rudbar earthquake of magnitude 7.3 on the Richter scale (MS=7.7, MW=7.3, mb=6.4) at 12:31am local time on June 21, 1990, that killed around 50,000 and injured 100,000 city residents.[6] Despite reconstruction, it has not regained its former glory.
Shahrestan Rudbar
Rudbar County (Shahrestan) was formed after a meeting between some Rudbari politicians such as Ziaeddin Tavakkoli and Reza Shah.
References
- https://www.amar.org.ir/english
- Rudbar can be found at GEOnet Names Server, at this link, by opening the Advanced Search box, entering "-3081436" in the "Unique Feature Id" form, and clicking on "Search Database".
- "Census of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 1385 (2006)". Islamic Republic of Iran. Archived from the original (Excel) on 2011-11-11.
- "Gilaki".
- Guyeš-e Tāti-y-e Rudbār (The Tati Dialect of Rudbar), Jahandoost Sabzalipour, Rasht: Farhang-e Iliya Press, 2011
- ReliefWeb Report of Earthquake, ReliefWeb, June 1990
- Book of Amarlu - M.M.Zand
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rudbar. |