SMS Nürnberg (1916)
SMS Nürnberg was a Königsberg-class light cruiser built during World War I by Germany for the Imperial Navy. She had three sisters: Königsberg, Karlsruhe, and Emden. The ship was named after the previous light cruiser Nürnberg, which had been sunk at the Battle of the Falkland Islands. The new cruiser was laid down in 1915 at the AG Weser shipyard in Bremen, launched in April 1916, and commissioned into the High Seas Fleet in February 1917. Armed with eight 15 cm SK L/45 guns, the ship had a top speed of 27.5 kn (50.9 km/h; 31.6 mph).
 One of the Königsberg-class cruisers en route to Scapa Flow | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Nürnberg |
| Namesake: | Nürnberg |
| Ordered: | 1913 |
| Builder: | Howaldtswerke, Kiel |
| Laid down: | December 1914 |
| Commissioned: | February 1917 |
| Fate: | Sunk as target 7 July 1922 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Königsberg-class light cruiser |
| Displacement: | |
| Length: | 151.4 m (497 ft) |
| Beam: | 14.2 m (47 ft) |
| Draft: | 5.96 m (19.6 ft) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 27.5 knots (50.9 km/h) |
| Range: | 4,850 nmi (8,980 km; 5,580 mi) at 12 kn (22 km/h; 14 mph) |
| Crew: |
|
| Armament: |
|
| Armor: | |
Nürnberg saw relatively limited service during the war, due to her commissioning late in the conflict. She participated in Operation Albion in October 1917 against the Russian Navy in the Baltic. The following month, she was engaged in the Second Battle of Helgoland Bight, but was not significantly damaged during the engagement. She was assigned to the final, planned operation of the High Seas Fleet that was to have taken place in the closing days of the war, though a major mutiny forced the cancellation of the plan. After the end of the war, the ship was interned in Scapa Flow. In the scuttling of the German fleet in June 1919, British ships managed to beach Nürnberg and she was later refloated and sunk as a gunnery target in 1922.
Design
Nürnberg was 151.4 meters (497 ft) long overall and had a beam of 14.2 m (47 ft) and a draft of 5.96 m (19.6 ft) forward. She displaced 5,440 t (5,350 long tons) normally and up to 7,125 t (7,012 long tons) at full load. Her propulsion system consisted of two sets of steam turbines powered by ten coal-fired and two oil-fired Marine-type boilers. These provided a top speed of 27.5 kn (50.9 km/h; 31.6 mph) and a range of 4,850 nautical miles (8,980 km; 5,580 mi) at 12 kn (22 km/h; 14 mph). The ship had a crew of 17 officers and 458 enlisted men.[1]
The ship was armed with a main battery of eight 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/45 guns in single pedestal mounts. Two were placed side by side forward on the forecastle, two were located on either side amidships, and two were arranged in a superfiring pair aft.[2] They were supplied with 1,040 rounds of ammunition, for 130 shells per gun. Nürnberg also carried two 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/45 anti-aircraft guns mounted on the centerline astern of the funnels. She was also equipped with a pair of 50 cm (19.7 in) torpedo tubes with eight torpedoes in deck-mounted swivel launchers amidships. She also carried 200 mines. The ship was protected by a waterline armored belt that was 60 mm (2.4 in) thick amidships. The conning tower had 100 mm (3.9 in) thick sides, and the deck was covered with 60 mm thick armor plate.[1]
Service history
Operation Albion
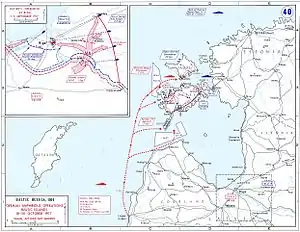
Nürnberg was ordered under the contract name "Ersatz Thetis" and was laid down at the AG Weser shipyard in Bremen in 1915. She was launched on 14 April 1916, after which fitting-out work commenced. She was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 15 February 1917.[1] In early September 1917, following the German conquest of the Russian port of Riga, the German navy decided to eliminate the Russian naval forces that still held the Gulf of Riga. The Admiralstab (the Navy High Command) planned an operation to seize the Baltic island of Ösel, and specifically the Russian gun batteries on the Sworbe Peninsula.[3] On 18 September, the order was issued for a joint operation with the army to capture Ösel and Moon Islands; the primary naval component was to comprise the flagship, Moltke, along with III and IV Battle Squadrons of the High Seas Fleet. The invasion force amounted to approximately 24,600 officers and enlisted men.[4] Nürnberg and the rest of II Scouting Group, commanded by Rear Admiral Ludwig von Reuter, provided the cruiser screen for the task force.[5]
The operation began on the morning of 12 October, when Moltke and the III Squadron ships engaged Russian positions in Tagga Bay while the IV Squadron shelled Russian gun batteries on the Sworbe Peninsula on Ösel[6] After the beginning of the bombardment, Nürnberg entered Tagga Bay with II Transport Section and began landing troops, while Königsberg covered the landing of I Transport Section.[7] On 18–19 October, the rest of II Scouting Group covered minesweepers operating off the island of Dagö, but due to insufficient minesweepers and bad weather, the operation was postponed.[8] On the 19th, Nürnberg, Königsberg, and Danzig were sent to intercept two Russian torpedo boats reported to be in the area. Reuter could not locate the vessels, and broke off the operation.[9] By 20 October, the islands were under German control and the Russian naval forces had either been destroyed or forced to withdraw. The Admiralstab ordered the naval component to return to the North Sea.[10]
Second Battle of Helgoland Bight
On 17 November, Nürnberg, Königsberg, Frankfurt, and Pillau were assigned to cover a minesweeping operation in the Helgoland Bight, still under the command of Reuter. The force was supported by two battleships—Kaiser and Kaiserin. Six British battlecruisers supported a force of light cruisers that attacked the German minesweepers. Königsberg and the other three cruisers covered the fleeing minesweepers before retreating under a smoke screen.[11] Nürnberg opened fire on the British cruisers at 08:55, at a range of 11 km (6.8 mi). Heavy smoke and fog obscured the British ships, however, and Nürnberg was quickly forced to cease firing.[12]
At around 10:00, Nürnberg came under heavy fire from the British cruisers, as well as the powerful battlecruisers Courageous and Glorious, armed with 15-inch (380 mm) guns. Nürnberg was not hit directly, but shell splinters from near misses rained down on her deck and killed one man and wounded four more, one of whom later died of his wounds. One of her rangefinders was also damaged by the shell fragments. She returned fire briefly before the haze again concealed the British ships. Kaiser and Kaiserin intervened at almost exactly the same time, prompting the British to break off the engagement immediately. Within an hour, the German forces were reinforced by several capital ships, including the battlecruiser Hindenburg; after realizing the British had fled, the German forces returned to port.[13]
Fate
In October 1918, Admirals Reinhard Scheer and Franz von Hipper planned a final, climactic attack on the British by the High Seas Fleet. The planned operation called for raids on Allied shipping in the Thames estuary and Flanders to draw out the Grand Fleet. The German fleet would then attack the Grand Fleet and do as much damage as possible in order to enhance Germany's military position in the coming peace talks. Nürnberg, Karlsruhe and Graudenz were assigned to the force tasked with attacking Flanders.[14] On the morning of 29 October 1918, the order was given to sail from Wilhelmshaven the following day. Starting on the night of 29 October, sailors on Thüringen and then on several other battleships mutinied. The unrest spread to the rest of the fleet and ultimately forced Hipper and Scheer to cancel the operation.[15]
Following the capitulation of Germany in November 1918, most of the High Seas Fleet's ships, under the command of Reuter, were interned in the British naval base in Scapa Flow.[16] Nürnberg was among the ships interned.[1] The fleet remained in captivity during the negotiations that ultimately produced the Versailles Treaty. Reuter believed that the British intended to seize the German ships on 21 June 1919, which was the deadline for Germany to have signed the peace treaty. Unaware that the deadline had been extended to the 23rd, Reuter ordered the ships to be sunk at the next opportunity. On the morning of 21 June, the British fleet left Scapa Flow to conduct training maneuvers, and at 11:20 Reuter transmitted the order to his ships.[17] British sailors used explosive charges to blast away Nürnberg's anchor chains so she could be dragged aground before she sank.[18]
The ship was refloated in July and towed to Portsmouth, where she was converted into a target ship. The first trial, conducted with the monitor HMS Terror, was held on 5 November 1920; the monitor was moored just 370 m (400 yd) away to ensure hits. Coal was shifted to one side to make Nürnberg take on a list of 10 degrees to simulate the angle a shell would hit the cruiser at long range. Terror had been fitted with a 7.5 in (190 mm) gun and a 6 in (150 mm) gun for the purposes of the tests, which involved several different shell types for both calibers. Terror made hits on specific parts of the ship, including the conning tower, the belt armor, the upper deck, and the unarmored superstructure. Flooding from the belt hits caused the list to be reduced to 7.5 degrees. Another round of tests was held on 8 November, and this time Nürnberg's coal bunkers were flooded to bring her list to 20 degrees. On 7 July 1922, the battlecruiser Repulse sank Nürnberg off the Isle of Wight at a depth of 62 m (203 ft).[1][19]
Notes
- Gröner, p. 113.
- Gardiner & Gray, p. 162.
- Halpern, p. 213.
- Halpern, p. 214–215.
- Barrett, p. 127.
- Halpern, p. 215.
- Staff 2008, p. 27.
- Barrett, p. 218.
- Staff 2008, p. 140.
- Halpern, p. 219.
- Halpern, p. 377.
- Staff 2011, pp. 195, 201.
- Staff 2011, pp. 202, 204–205.
- Woodward, pp. 115–116.
- Tarrant, pp. 281–282.
- Tarrant, p. 282.
- Herwig, p. 256.
- van der Vat, pp. 178–179.
- Dodson, p. 145.
References
- Barrett, Michael B. (2008). Operation Albion. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-34969-9.
- Dodson, Aidan (2017). "After the Kaiser: The Imperial German Navy's Light Cruisers after 1918". In Jordan, John (ed.). Warship 2017. London: Conway. pp. 140–159. ISBN 978-1-8448-6472-0.
- Gardiner, Robert & Gray, Randal, eds. (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1906–1921. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-907-8.
- Gröner, Erich (1990). German Warships: 1815–1945. Vol. I: Major Surface Vessels. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-790-6.
- Halpern, Paul G. (1995). A Naval History of World War I. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-352-7.
- Herwig, Holger (1998) [1980]. "Luxury" Fleet: The Imperial German Navy 1888–1918. Amherst: Humanity Books. ISBN 978-1-57392-286-9.
- Staff, Gary (2008). Battle for the Baltic Islands. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Maritime. ISBN 978-1-84415-787-7.
- Staff, Gary (2011). Battle on the Seven Seas. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Maritime. ISBN 978-1-84884-182-6.
- Tarrant, V. E. (1995). Jutland: The German Perspective. London: Cassell Military Paperbacks. ISBN 978-0-304-35848-9.
- van der Vat, Dan (1982). The Grand Scuttle: The Sinking of the German Fleet at Scapa Flow in 1919. London: Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 0-340-27580-4.
- Woodward, David (1973). The Collapse of Power: Mutiny in the High Seas Fleet. London: Arthur Barker Ltd. ISBN 978-0-213-16431-7.