Sakurai, Nara
Sakurai (桜井市, Sakurai-shi) is a city located in Nara Prefecture, Japan.
Sakurai
桜井市 | |
|---|---|
 View of Omiwa Shrine, one of the sightseeing spots in Sakurai | |
 Flag | |

| |
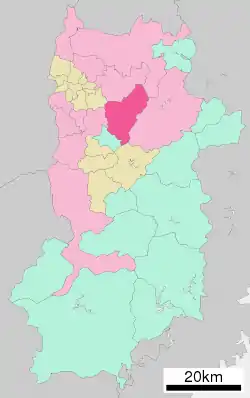 Location of Sakurai in Nara Prefecture | |
 Sakurai | |
| Coordinates: 34°31′N 135°51′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Nara Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Akira Hasegawa |
| Area | |
| • Total | 98.92 km2 (38.19 sq mi) |
| Population (March 31, 2017) | |
| • Total | 58,386 |
| • Density | 590/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 633-8585 |
| - Tree | Cryptomeria |
| - Flower | Prunus jamasakura |
| Phone number | 0744-42-9111 |
| Address | 432-1 Ōaza Ōdono 633-8585 |
| Website | City of Sakurai |
| Sakurai | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 桜井市 | ||||
| Hiragana | さくらいし | ||||
| Katakana | サクライシ | ||||
| |||||
As of March 31, 2017, the city has an estimated population of 58,386, and 24,629 households.[1] The population density is 590 persons per km², and the total area is 98.92 km².[2]
History
Sakurai was briefly the capital of Japan during the reign of Emperor Yūryaku.[3] The life of the Imperial court was centered at Hatsuse no Asakura Palace where the emperor lived in 457–479.[4] Other emperors also built palaces in the area, including
- Iware no Mikakuri Palace, 480–484[4] in reign of Emperor Seinei[5]
- Nimiki Palace, 499–506 in reign of Emperor Buretsu[6]
- Iware no Tamaho Palace, 526–532[4] in reign of Emperor Keitai[7]
- Hinokuma no Iorino Palace, 535-539[4] in reign of Emperor Senka[8]
- Osata no Sakitama Palace or Osada no Miya, 572–585[9] in reign of Emperor Bidatsu[10]
The modern city was founded on September 1, 1956.
Sakurai is home to Ōmiwa Shrine, traditionally considered one of the oldest Shinto shrines in Japan dedicated to the god of sake. Sake dealers across Japan often hang a wooden sugi ball, made at Ōmiwa Shrine, as a talisman to the god of sake. It was featured in Yukio Mishima's novel Runaway Horses.
Famous places
- Buddhist temples
- Miwasanbyōdō-ji
- Hase-dera
- Asuka-dera
- Tachibana-dera
- Abe Monju-in
- Seirin-ji
- Shinto shrines
- Ōmiwa Shrine
- Tanzan Shrine
- Kasayamakō Shrine
- Tamatsura Shrine
Transportation
Rail
- West Japan Railway Company
- Sakurai Line (Man-yō Mahoroba Line): Makimuku Station - Miwa Station - Sakurai Station
- Kintetsu Railway
References
- "Official website of Sakurai city" (in Japanese). Japan: Sakurai City. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "面積および地勢" (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Sakurai City. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- Ponsonby-Fane. (1915). The Imperial Family of Japan, p. 13.
- Koch, W. (1904). Japan; Geschichte nach japanischen Quellen und ethnographische Skizzen. Mit einem Stammbaum des Kaisers von Japan, p. 13.
- Ponsonby-Fane, p. 14; excerpt, "Mikaguri Palace"
- Ponsonby-Fane, p. 15.
- Ponsonby-Fane, p. 16.
- Ponsonby-Fane, p. 17.
- Brown, Delmer. (1979). Gukanshō, pp. 262-263; excerpt, "... palace was Osada no Miya of Iware in the province of Yamato."
- Ponsonby-Fane, p. 18.
External links
![]() Media related to Sakurai, Nara at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sakurai, Nara at Wikimedia Commons
- Sakurai City official website (in Japanese) at the Library of Congress Web Archives (archived 2002-09-14)
- Sakurai City official website (in English)
 Geographic data related to Sakurai, Nara at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Sakurai, Nara at OpenStreetMap