Siege of the Acropolis (1821–22)
The Siege of the Acropolis in 1821–1822 involved the siege of the Acropolis of Athens by the Greek rebels, during the early stages of the Greek War of Independence.
| Siege of the Acropolis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Greek War of Independence | |||||||
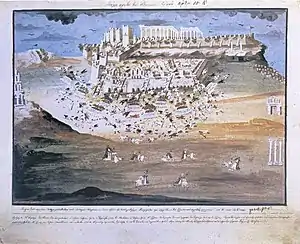 "The first battle of Athens", by Panagiotis Zografos | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Meletios Vasileiou Dimos Antoniou Olivier Voutier |
Omer Vrioni Omar Bey of Karystos | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 600, later increasing to 3,000 | Muslim inhabitants of Athens, later Vrioni's army | ||||||
Following the outbreak of the Greek uprising against the Ottoman Empire in March 1821, Athens fell into Greek hands on 28 April without a fight. Its garrison and Muslim inhabitants, along with the Greek population's leaders as hostages, retired to the Acropolis, which served as the garrison commander's residence. The initial Greek force, some 600 Athenians led by Meletios Vasileiou, was soon augmented by volunteers from Aegina, Hydra, Cephallonia and Kea to ca. 3,000, and maintained a loose siege of the fortified hill. A handful of Ottoman soldiers managed to break through the siege, and went to Karystos in Euboea to request the aid of the local governor, Omar Bey, and of the general Omer Vrioni. The two Ottoman leaders united their forces and descended on Attica. The Greek rebels scattered before them, and the Ottoman forces entered Athens on 20 July. Vrioni remained in Attica to pursue the Greek forces, while Omar of Karystos returned to his home province. After Vrioni's departure, however, the siege recommenced. In spring 1822, the Greek forces were reinforced with artillery commanded by French Philhellenes, under Olivier Voutier, who began a bombardment of the fortress. The Ottoman garrison surrendered on 9 June 1822 (O.S.).
Aftermath
Terms of surrender
After nearly a year of being under siege, the Ottoman garrison at the Acropolis fortress surrendered on June 9, 1822. The terms of surrender were as follows:[1]
- The Ottoman troops and civilians would be given free passage to Asia Minor on foreign ships not aligned with Greece
- Allow the Turks who wanted to stay in Athens to do so without significant trouble or harassment
Instances of violence
The general Omer Vrioni was known to have a habit of going on 'Greek hunts' to chase and kill Greek civilians. In response to these acts, Greek soldiers stationed in Athens retaliated by killing nearly half of the Ottomans who surrendered following the siege.[1] Various other acts of retribution occurred usually involving the killing of Albanian civilians.
Footnotes
- David, Brewer (2011). The Greek War of Independence: The Struggle for Freedom and the Birth of Modern Greece, 1st Edition. New York, NY: The Overlook Press. ISBN 1590206916.
References and further reading
- David, Brewer (2011). The Greek War of Independence: The Struggle for Freedom and the Birth of Modern Greece, 1st Edition. New York, NY: The Overlook Press. ISBN 1590206916