Sinope (moon)
Sinope /sɪˈnoʊpiː/ is a retrograde irregular satellite of Jupiter discovered by Seth Barnes Nicholson at Lick Observatory in 1914,[1] and is named after Sinope of Greek mythology.
 Sinope photographed by the Haute-Provence Observatory on 14 August 1998 | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Seth B. Nicholson |
| Discovery site | Lick Observatory |
| Discovery date | 21 July 1914 |
| Designations | |
Designation | Jupiter IX |
| Pronunciation | /sɪˈnoʊpiː/[2][3] |
Named after | Σινώπη Sinōpē |
| Adjectives | Sinopean[4] /saɪnəˈpiːən/[5] |
| Orbital characteristics [6] | |
| Epoch 23 March 2018 (JD 2458200.5) | |
| Observation arc | 103.87 yr (37,938 days) |
| 0.1629144 AU (24,371,650 km) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3366550 |
| –777.29 d (2.13 years) | |
| 71.53524° | |
| 0° 27m 47.33s / day | |
| Inclination | 158.63840° (to ecliptic) |
| 8.61437° | |
| 60.30205° | |
| Satellite of | Jupiter |
| Group | Pasiphae group |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 35.0±0.6 km[7] |
| 13.16±0.10 h[8] | |
| Albedo | 0.042±0.006[7] |
| 18.3[9] | |
| 11.1[6] | |
Sinope did not receive its present name until 1975;[10][11] before then, it was simply known as Jupiter IX. It was sometimes called "Hades"[12] between 1955 and 1975.
Sinope was the outermost known moon of Jupiter until the discovery of Megaclite in 2000.
Orbit
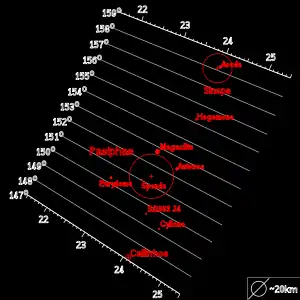
Sinope orbits Jupiter on a high-eccentricity and high-inclination retrograde orbit. Its orbit is continuously changing due to solar and planetary perturbations.[13] Sinope is believed to belong to the Pasiphae group of retrograde irregular moons.[14] However, given its mean inclination and different colour, Sinope could be also an independent object, captured independently, unrelated to the collision and break-up at the origin of the group.[15] The diagram illustrates Sinope's orbital elements in relation to other satellites of the group.
Sinope is also known to be in a secular resonance with Jupiter, similar to Pasiphae. However, Sinope can drop out of this resonance and has periods of both resonant and non-resonant behaviour in time scales of 107 years.[16]
Physical characteristics

From measurements of its thermal emission, Sinope has an estimated diameter of 35 km (22 mi).[7] Sinope is red (colour indices B−V=0.84, R−V=0.46),[15] unlike Pasiphae, which is grey.
Sinope's infrared spectrum is similar to those of D-type asteroids but different from that of Pasiphae.[17] These dissimilarities of the physical parameters suggest a different origin from the core members of the group.
See also
References
- Nicholson, S. B. (1914). "Discovery of the Ninth Satellite of Jupiter". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 26 (1): 197–198. Bibcode:1914PASP...26..197N. doi:10.1086/122336. PMC 1090718. PMID 16586574.
- "Sinope". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- Noah Webster (1884) A Practical Dictionary of the English Language
- Sergey Vnukov (2010) "Sinopean Amphorae of the Roman Period", Ancient Civilizations from Scythia to Siberia 16
- Hector Stuart (1876) Ben Nebo, and Other Poems, p. 22
- "M.P.C. 111777" (PDF). Minor Planet Circular. Minor Planet Center. 25 September 2018.
- Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Mainzer, A. K.; Masiero, J. R.; Nugent, C. R.; Cutri, R. M.; et al. (August 2015). "NEOWISE: Observations of the Irregular Satellites of Jupiter and Saturn". The Astrophysical Journal. 809 (1): 9. arXiv:1505.07820. Bibcode:2015ApJ...809....3G. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/809/1/3. S2CID 5834661. 3.
- Luu, Jane (September 1991). "CCD photometry and spectroscopy of the outer Jovian satellites". Astronomical Journal. 102: 1213–1225. Bibcode:1991AJ....102.1213L. doi:10.1086/115949. ISSN 0004-6256.
- Sheppard, Scott. "Scott S. Sheppard - Jupiter Moons". Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. Carnegie Institution for Science. Retrieved 26 November 2020.
- Nicholson, S. B. (April 1939). "The Satellites of Jupiter". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 51 (300): 85–94. Bibcode:1939PASP...51...85N. doi:10.1086/125010. (in which he declines to name the recently discovered satellites (pp. 93–94))
- IAUC 2846: Satellites of Jupiter 1974 October (naming the moon)
- Payne-Gaposchkin, Cecilia; Katherine Haramundanis (1970). Introduction to Astronomy. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0-13-478107-4.
- Jacobson, R. A. (2000). "The orbits of outer Jovian satellites" (PDF). Astronomical Journal. 120 (5): 2679–2686. Bibcode:2000AJ....120.2679J. doi:10.1086/316817.
- Sheppard, S. S.; and Jewitt, D. C.; An Abundant Population of Small Irregular Satellites Around Jupiter, Nature, Vol. 423 (May 2003), pp. 261-263
- Grav, T.; Holman, M. J.; Gladman, B. J.; and Aksnes, K.; Photometric Survey of the Irregular Satellites, Icarus, Vol. 166 (2003), pp. 33-45
- Nesvorný, D.; Beaugé, C. & Dones, L. (2004). "Collisional Origin of Families of Irregular Satellites". The Astronomical Journal. 127 (3): 1768–1783. Bibcode:2004AJ....127.1768N. doi:10.1086/382099.
- Grav, T.; Holman, M. J. (2004). "Near-Infrared Photometry of the Irregular Satellites of Jupiter and Saturn". The Astrophysical Journal. 605 (2): L141–L144. arXiv:astro-ph/0312571. Bibcode:2004ApJ...605L.141G. doi:10.1086/420881. S2CID 15665146.