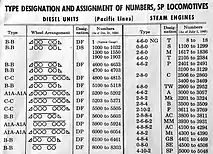
Southern Pacific Transportation Company
The Southern Pacific (reporting mark SP) (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company.
.png.webp) | |
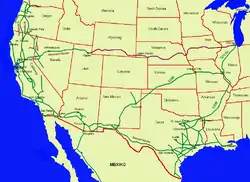 SP system map (before the 1988 DRGW merger) | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California |
| Reporting mark | SP |
| Locale | Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Illinois, Kansas, Louisiana, Missouri, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Oregon, Tennessee, Texas, Utah |
| Dates of operation | 1865–1996
|
| Predecessor | Central Pacific Railroad |
| Successor | Union Pacific Railroad (in name only) Caltrain (San Francisco Peninsula) |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge with some 3 ft (914 mm) gauge branches |
The original Southern Pacific began in 1865 as a land holding company. The last incarnation of the Southern Pacific, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, was founded in 1969 and assumed control of the Southern Pacific system. The Southern Pacific Transportation Company was acquired in 1995 by the Union Pacific Corporation and merged with their Union Pacific Railroad.
The Southern Pacific legacy founded hospitals in San Francisco, Tucson, and Houston. In the 1970s, it also founded a telecommunications network with a state-of-the-art microwave and fiber optic backbone. This telecommunications network became part of Sprint, a company whose name came from the acronym for Southern Pacific Railroad Internal Networking Telephony.[1] Sprint ceased to exist in 2020 after acquisition by T-Mobile.
History
The original Southern Pacific, Southern Pacific Railroad, was founded as a land holding company in 1865, later acquiring in 1885 the Central Pacific Railroad through leasing.[2][3] By 1900, the Southern Pacific system was a major railroad system incorporating many smaller companies, such as the Texas and New Orleans Railroad and Morgan's Louisiana and Texas Railroad. It extended from New Orleans through Texas to El Paso, Texas, across New Mexico and through Tucson, to Los Angeles, through most of California, including San Francisco and Sacramento. Central Pacific lines extended east across Nevada to Ogden, Utah, and reached north through Oregon to Portland. Other subsidiaries eventually included the St. Louis Southwestern Railway (Cotton Belt), El Paso and Southwestern Railroad, the Northwestern Pacific Railroad at 328 miles (528 km), the 1,331-mile (2,142 km) Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico, and a variety of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge routes. The SP was the defendant in the landmark 1886 United States Supreme Court case Santa Clara County v. Southern Pacific Railroad, which is often interpreted as having established certain corporate rights under the Constitution of the United States. The Southern Pacific Railroad was replaced by the Southern Pacific Company and assumed the railroad operations of the Southern Pacific Railroad. In 1929, Southern Pacific/Texas and New Orleans operated 13,848 route-miles not including Cotton Belt, whose purchase of the Golden State Route circa 1980 nearly doubled its size to 3,085 miles (4,965 km), bringing total SP/SSW mileage to around 13,508 miles (21,739 km).

In 1969, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company was established and took over the Southern Pacific Company; this Southern Pacific railroad is the last incarnation and was at times called "Southern Pacific Industries", though "Southern Pacific Industries" is not the official name of the company. By the 1980s, route mileage had dropped to 10,423 miles (16,774 km), mainly due to the pruning of branch lines. In 1988, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company (including its subsidiary, St. Louis Southwestern Railway) was taken over by Rio Grande Industries, the parent company that controlled the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad. Rio Grande Industries did not merge the Southern Pacific Transportation Company and the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad together, but transferred direct ownership of the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad to the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, allowing the combined Rio Grande Industries railroad system to use the Southern Pacific name due to its brand recognition in the railroad industry and with customers of both the Southern Pacific Transportation Company and the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad. A long time Southern Pacific subsidiary, the St. Louis Southwestern Railway was also marketed under the Southern Pacific name. Along with the addition of the SPCSL Corporation route from Chicago to St. Louis, the total length of the D&RGW/SP/SSW system was 15,959 miles (25,684 km). Rio Grande Industries was later renamed Southern Pacific Rail Corporation.
By 1996, years of financial problems had dropped Southern Pacific's mileage to 13,715 miles (22,072 km). The financial problems caused the Southern Pacific Transportation Company to be taken over by the Union Pacific Corporation; the parent Southern Pacific Rail Corporation (formerly Rio Grande Industries), the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, the St. Louis Southwestern Railway and the SPCSL Corporation was also taken over by the Union Pacific Corporation. The Union Pacific Corporation merged the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, the St. Louis Southwestern Railway and the SPCSL Corporation into their Union Pacific Railroad, but did not merge the Southern Pacific Transportation Company into the Union Pacific Railroad. Instead, the Union Pacific Corporation merged the Union Pacific Railroad into the Southern Pacific Transportation Company in 1998; the Southern Pacific Transportation Company became the surviving railroad and at the same time the Union Pacific Corporation renamed the Southern Pacific Transportation Company to Union Pacific Railroad. Thus, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company became, and is still operating as, the current incarnation of the Union Pacific Railroad.
Locomotive paint and appearance
Like most railroads, the SP painted most of its steam locomotives black during the 20th century, but after 1945 SP painted the front of the locomotive's smokebox silver (almost white in appearance), with graphite colored sides, for visibility.
As locomotives are being restored, some pacific type 4-6-2 locomotive boilers show signs of having been painted dark green. The soft cover book "Steam Glory 2" by Kalmbach Publications (2007) has an article "Southern Pacific's Painted Ladies" which shows color photos from the 1940s and 1950s revealing that a number of SP 0-6-0 yard engines, usually assigned to passenger terminals were painted in various combinations with red cab roof and cab doors, pale silver smokeboxes and smokebox fronts, dark green boilers, multi colored SP heralds on black cab, green cylinder covers and other details pointed out in color. Some other SP steam passenger locomotives may have been so painted, or at least had dark green boilers. The article indicates that these paint jobs lasted years and were not special paint for a single event.
Some passenger steam locomotives bore the Daylight scheme, named after the trains they hauled, most of which had the word Daylight in the train name. This scheme, carried on the tender, was a bright red on the top and bottom thirds, with the center third being a bright orange. The parts were separated with narrow silver-gray bands. Some of the color continued along the locomotive. The most famous "Daylight" locomotives were the GS-4 steam locomotives. The most famous Daylight-hauled trains were the Coast Daylight and the Sunset Limited.
Well known were the Southern Pacific's unique "cab-forward" steam locomotives.[4] These were 2-8-8-4 locomotives set up to run in reverse, with the tender attached to the smokebox end of the locomotive.[4] Southern Pacific had a number of snow sheds in mountain terrain, and locomotive crews nearly asphyxiated from smoke in the cab.[4] After a number of engineers began running their engines in reverse (pushing the tender), Southern Pacific asked Baldwin Locomotive Works to produce cab-forward designs.[4] No other North American railroad ordered cab-forward locomotives.
 SP 3491, in the Black Widow scheme, leads SP 6506, in the Bloody Nose scheme (April 1966)
SP 3491, in the Black Widow scheme, leads SP 6506, in the Bloody Nose scheme (April 1966) SP 7561 in the Kodachrome scheme (June 1986)
SP 7561 in the Kodachrome scheme (June 1986) SP 6051 in the Daylight scheme (2012)
SP 6051 in the Daylight scheme (2012)
Early diesel locomotives were also painted black. Yard switchers had diagonal orange stripes on the ends for visibility, earning this scheme the nickname of Tiger Stripe. Road freight units were black with a red band at the bottom of the car body and a silver and orange "winged" nose. "SOUTHERN PACIFIC" was in a large serif font in Lettering Gray (a very light gray). Railfans call this paint scheme Black Widow. An experimental scheme, all-over black with a variety of orange end and side sill treatments was called the Halloween scheme. Over 200 locomotives were so painted between March 1957 and mid-1958.
Most passenger units were painted originally in the Daylight scheme as described above, though some were painted red on top, silver below for the Golden State (operated with the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad) between Chicago and Los Angeles. Silver cars with a narrow red band at the top were used for the Sunset Limited and other trains into Texas. In 1958 SP standardized on a paint scheme of dark grey ("Lark Dark Gray") with a red "winged" nose; railfans dubbed this scheme Bloody Nose. Lettering was again in Lettering Gray.
Anticipating the (ultimately failed) Southern Pacific Santa Fe merger in the mid 1980s, the "Kodachrome" paint scheme (named for the colors of the Kodak boxes that the film came in) was applied to many Southern Pacific locomotives. When the Southern Pacific Santa Fe merger was denied by the Interstate Commerce Commission, the Kodachrome units were not immediately repainted, some even lasting up to the Southern Pacific's end as an independent company. The Interstate Commerce Commission's decision left Southern Pacific in a decrepit state, the locomotives were not repainted immediately, although some were repainted into the Bloody Nose scheme as they were overhauled after months to years of deferred maintenance.
.jpg.webp) SP 8578 wearing the Bloody Nose scheme with "speed lettering" in 2008
SP 8578 wearing the Bloody Nose scheme with "speed lettering" in 2008 UP 1512 (ex-SP 7134, ex-BO 3706) in Bloody Nose with "speed lettering" and added Union Pacific patches after SP acquisition
UP 1512 (ex-SP 7134, ex-BO 3706) in Bloody Nose with "speed lettering" and added Union Pacific patches after SP acquisition.jpg.webp) UP 1996 in a Heritage scheme based on Daylight and Black Widow
UP 1996 in a Heritage scheme based on Daylight and Black Widow.jpg.webp) The Southern Pacific "Popsicles" scheme on TE-70 locomotives
The Southern Pacific "Popsicles" scheme on TE-70 locomotives
Southern Pacific road switcher diesels often had elaborate lighting clusters front and rear, with a large red Mars Light for emergency signaling, and often two pairs of sealed-beam headlamps, one on top of the cab and the other below the Mars Light on the nose. Starting in the 1970s SP had cab air conditioning on all new locomotives and the unit is visible on the cab roof. Southern Pacific placed large snowplows on the pilots of their road switchers for the heavy snowfall on Donner Pass. Many Southern Pacific road switchers had a Nathan-AirChime model P3 or P5 air horn with chords distinct to Southern Pacific locomotives in the western states.
The Southern Pacific and Cotton Belt were the only buyers of the EMD SD45T-2 "Tunnel Motor" locomotive. This locomotive was necessary because the standard configuration EMD SD45 could not get a sufficient amount of cool air into the diesel locomotive's radiator while working Southern Pacific's through snow sheds and tunnels in the Cascades and Donner Pass. These "Tunnel Motors" were EMD SD45-2's with radiator air intakes at the locomotive car body's walkway level, rather than EMD's typical setup with fans on the locomotive's long hood roof pulling air through radiators at the top/side of the locomotive's body. Inside tunnels and snow sheds hot exhaust from lead units would accumulate near the top of the tunnel or snow shed and be drawn into the radiators of trailing EMD (non-tunnel motor) locomotives, leading these locomotives to shut down as their diesel prime mover overheated. The Southern Pacific also operated EMD SD40T-2s, as did the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad.

Southern Pacific was known for L-shaped engineer's windshields. Introduced by EMD on SD45 demonstrator 4353, this design improves visibility by omitting the pillar which in conventional designs splits the engineer's windshield into two panes. Southern Pacific selected this option on new EMD locomotive orders starting in 1967 through the early 1980s, one of the few railroads to do so (Illinois Central was another buyer of this option), and ordered a similar windshield design from General Electric. After the "wide nose" design became popular, most of Southern Pacific's locomotives kept their L-shaped windshields before being rebuilt or sold to different private railroads after its merger.
Unlike other railroads whose locomotive number boards bore the locomotive number, SP used them for the train number until 1967. (SP's San Francisco-San Jose commute trains continued displaying train numbers for the convenience of passengers.) The other railroad that used locomotive number boards for train numbers into the 1960s was SP's transcontinental partner, Union Pacific.
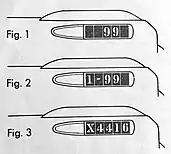
On either side of the boiler near the smoke stack or further back, indicators are displayed. These are train numbers (figure 1). All trains going toward San Francisco are called 'westward' and are odd-numbered such as 1, 3, and so on. A train going away from SF are called 'eastward' and are even-numbered. The example in figure 1 shows 99 as the train number which is the number of the streamlined Daylight, northbound.

In order to carry all the people wishing to ride on the same train, sometimes it was necessary to operate the train in two or more separate parts, which are called 'sections.' When a train is operated in sections, the first section carries a '1' preceding the train number (figure 2). The second section carries a '2', etc., and the last section carries the train number only. Special trains or 'extras' carry the locomotive number preceded by an 'X' (figure 3).[5]
In 2006, the Union Pacific Railroad unveiled UP 1996, the sixth and final of its Heritage Series EMD SD70ACe locomotives. Its paint scheme appears to be based on the Daylight and Black Widow schemes. Today there are still locomotives in SP paint, including ten AC4400CWs with original SP numbers as of January 2013.
Passenger train service
Until May 1, 1971 (when Amtrak took over long-distance passenger operations in the United States), the Southern Pacific at various times operated the following named passenger trains. Trains with names in italicized bold text still operate under Amtrak:
- 49er
- Apache [note 1]
- Argonaut
- Arizona Limited [note 2]
- Beaver
- Californian
- Cascade [note 3]
- City of San Francisco [note 4]
- Coast Daylight [note 5]
- Coast Mail
- Coaster
- Del Monte
- Fast Mail
- Golden Rocket [note 6]
- Golden State [note 7]
- Grand Canyon
- Hustler
- Imperial [note 8]
- Klamath
- Lark
- Oregonian
- Overland
- Owl
- Pacific Limited
- Peninsula Commute [note 9]
- Loop Service
- Rogue River
- Sacramento Daylight
- San Francisco Challenger [note 10]
- San Joaquin Daylight
- Senator
- Shasta Daylight
- Shasta Express[7]
- Shasta Limited
- Shasta Limited De Luxe[7]
- Starlight
- Sunbeam
- Sunset Limited
- Suntan Special
- Tehachapi
- West Coast
- El Costeño [note 11]
- El Yaqui [note 12]
Steam locomotives
Notable accidents
- John Sontag, a young Southern Pacific employee, was injured c. 1888 while coupling cars in the railroad yard in Fresno. He accused the company of not providing him with medical care while he was recuperating from his on-the-job injury and then not rehiring him when he had healed. He soon turned to a life of crime (mostly train robberies) and died of gunshot wounds and tetanus in the Fresno jail in 1893 aged 32 years.[8]
- Sontag's partner in crime, Chris Evans also hated the Southern Pacific, which Evans accused of forcing farmers to sell their lands at reduced rates to the company.[8]
- On 28 March 1907, the Southern Pacific Sunset Express, descending the grade out of the San Timoteo Canyon, entered the Colton rail yard traveling about 60 miles per hour (97 km/h), hit an open switch and careened off the track, resulting in 24 fatalities. Accounts said 9 of the train's 14 cars disintegrated as they piled on top of one another, leaving the dead and injured in "a heap of kindling and crumpled metal". Of the dead, 18 were Italian immigrants traveling to jobs in San Francisco from Genoa, Italy.[9]
- The Coast Line Limited was heading for Los Angeles, California, on 22 May 1907, when it was derailed just west of Glendale, California. Passenger cars reportedly tumbled down the embankment. At least 2 people were killed and others injured. "The horrible deed was planned with devilish accurateness" the Pasadena Star News reported at the time. It said spikes were removed from the track and a hook placed under the end of the rail. The Star's coverage was extensive and its editorial blasted the criminal elements behind the wreck:
The man or men who committed this horrible deed near Glendale may not be anarchists, technically speaking. But if they are sane men, moved by motive, they are such stuff as anarchists are made of. If the typical anarchist conceived that a railroad corporation should be terrorized, he would not scruple to wreck a passenger train and send scores and hundreds to instant death.[10]
- In the early hours of 1 June 1907, an attempt to derail a Southern Pacific train near Santa Clara, California, was foiled when a pile of railway ties was discovered on the tracks. A work train crew found that someone had driven a steel plate into a switch near Burbank, California, intending to derail the Santa Barbara local.
- On 12 August 1939, the westbound City of San Francisco derailed from a bridge in Palisade Canyon, between Battle Mountain and Carlin in the Nevada desert. Among the passengers and crew members 24 people were killed and many more injured, and 5 cars were destroyed. An act of sabotage was determined to be the most likely cause; however, no suspect(s) was(were) ever identified.
- On New Year's Eve 1944 a rear-end collision west of Ogden in thick fog killed 48 people.[11]
- On 17 January 1947, the Southern Pacific nightflier wrecked 12 miles (19 km) outside of Bakersfield; 7 people were killed and over 50 injured. Four coaches and a tourist sleeper were overturned, landing far off the tracks; the other seven cars remained upright. The locomotive stayed on the tracks and its crew was uninjured. A 29-year-old passenger, Robert Crowley from Miami, Florida, had been conversing with a man across the aisle who was killed instantly. Crowley, who was a combat war veteran, said “I never saw such a mess” even on a battlefield.[12]
- On 8 May 1948, in Monterey, California, a Southern Pacific passenger train, the Del Monte Express struck a car driven by influential marine biologist Ed Ricketts at the now defunct railroad crossing at Drake Avenue. Ricketts subsequently succumbed to his injuries three days later in the hospital.[13]
- On 17 September 1963, a Southern Pacific freight train crashed into an illegally converted bus at a grade crossing in Chualar, California, killing 32 bracero workers. It would later be a factor in the decision by Congress in 1964 to terminate the bracero program, despite its strong support among farmers. It also helped spur the Chicano civil rights movement.[14][15] As of 2014, it was the deadliest automobile accident in United States history, according to the National Safety Council[14][16]
- On 12 May 1989, a Southern Pacific train carrying fertilizer derailed in San Bernardino, California. The train failed to slow while descending a nearby slope, and sped up to about 110 miles per hour (180 km/h) before derailing, causing the San Bernardino train disaster. The crash destroyed 7 homes along Duffy Street and killed 2 train workers and 2 residents. Thirteen days later on 25 May 1989, an underground pipeline running along the right-of-way ruptured and caught fire due to damage done to the pipeline during cleanup from the derailment, destroying 11 more homes and killing 2 more people.[17]

- On the night of 14 July 1991, a Southern Pacific train derailed into the upper Sacramento River at a sharp bend of track called “the Cantara Loop”, upstream from Dunsmuir, California, in Siskiyou County. Several cars made contact with the water, including a tank car. Early in the morning of 15 July, it became apparent that the tank car had ruptured and spilled its entire contents into the river – approximately 19,000 US gallons (72 m3) of metam sodium, a soil fumigant. Ultimately, over a million fish, and tens of thousands of amphibians and crayfish were killed. Millions of aquatic invertebrates, including insects and mollusks, which form the basis of the river's ecosystem, were destroyed. Hundreds of thousands of willows, alders, and cottonwoods eventually died; many more were severely injured.[18]
- The chemical plume left a 41 miles (66 km) wake of destruction from the spill site to the entry point of the river into Shasta Lake.[19] The accident still ranks as the largest hazardous chemical spill in California history.[18] At the time of the incident, metam sodium was not classified as a hazardous material.
Preserved locomotives
There are many Southern Pacific locomotives still in revenue service with railroads such as the Union Pacific Railroad, and many older and special locomotives have been donated to parks and museums, or continue operating on scenic or tourist railroads. Most of the engines now in use with Union Pacific have been "patched", where the SP logo on the front is replaced by a Union Pacific shield, and new numbers are applied over the old numbers with a Union Pacific sticker, however some engines remain in Southern Pacific "bloody nose" paint. Over the past couple years, most of the patched units were repainted into the full Union Pacific scheme and as of January 2019, less than ten units remain in their old paint. Among the more notable equipment is:
- Southern Pacific 3100, SP 3100 (former SP6800 Bicentennial) U25B owned and operated by the Orange Empire Railway Museum,[20] Perris, CA

- 4294 (AC-12, 4-8-8-2), located at the California State Railroad Museum, Sacramento, California
- 4449 (GS-4, 4-8-4), formerly located at the Brooklyn Roundhouse before being relocated to the Oregon Rail Heritage Center in June 2012, Portland, Oregon
- 2479 (P-10, 4-6-2), owned and being restored by the California Trolley and Railroad Corporation, San Jose, California
- 2472 (P-8, 4-6-2), owned and operated by the Golden Gate Railroad Museum, Redwood City, California
- 2467 (P-8, 4-6-2), on loan by the Pacific Locomotive Association, Fremont, California to the California State Railroad Museum
- 3420 (C-19, 2-8-0), owned by El Paso Historic Board, stored at Phelps Dodge copper refinery, El Paso, Texas
- 745 (Mk-5, 2-8-2), owned by the Louisiana Rail Heritage Trust, operated by the Louisiana Steam Train Association, and based in Jefferon (near New Orleans), Louisiana
- 4460 (GS-6, 4-8-4), located at the Museum of Transportation, Kirkwood, Missouri
- 1518 (EMD SD7), former EMD demonstrator 990 and first SD7 built, located at the Illinois Railway Museum, Union, Illinois
- 3769 (EMD GP9), On display and used as a switch engine for the Utah State Railroad Museum in Ogden, Utah.
- 4450 (EMD SD9), located at the Western Pacific Railroad Museum, Portola, California – former commute train engine scrapped in 2013
- 7457 (EMD SD45) the first GM Electro-Motive Division SD45 diesel-electric switcher locomotive to be built for that railroad in 1966.It last saw service on Donner Pass. It was donated to the Utah State Railroad Museum in 2002.
- 794 (Mk-5, 2-8-2), the last Mikado built for the Texas and New Orleans Railroad in 1916 out of spare parts in their Houston shops. It currently resides with cosmetic restoration at San Antonio Station, San Antonio, Texas, but plans are to restore it to operating condition.
For a complete list, see: List of preserved Southern Pacific Railroad rolling stock.
Company officers
Presidents
- Timothy Guy Phelps (1865–1868)
- Charles Crocker (1868–1885)
- Leland Stanford (1885–1890)
- Collis P. Huntington (1890–1900)
- Charles Melville Hays (1900–1901)
- E. H. Harriman (1901–1909)
- Robert S. Lovett (1909–1911)
- William Sproule (1911–1918)
- Julius Kruttschnitt (1918–1920)
- William Sproule (1920–1928)
- Paul Shoup (1929–1932)
- Angus Daniel McDonald (1932–1941)
- Armand Mercier (1941–1951)
- Donald J. Russell (1952–1964)
- Benjamin F. Biaggini (1964–1976)
- Denman McNear (1976–1979)
- Alan Furth (1979–1982)
- Robert Krebs (1982–1988)
- D. M. "Mike" Mohan (1988–1993)
- Edward L. Moyers (1993–1995)
- Jerry R. Davis (1995–1996)
Chairmen of Executive Committee
- Leland Stanford (1890–1893)
- (vacant 1893–1909)
- Robert S. Lovett (1909–1913)
- Julius Kruttschnitt (1913–1925)
- Henry deForest (1925–1928)
- Hale Holden (1928–1932)
Chairmen of Board of Directors
- Henry deForest (1929–1932)
- Hale Holden (1932–1939)
- (position nonexistent 1939–1964)
- Donald J. Russell (1964–1972)
- Benjamin F. Biaggini (1976–1982)
- Denman K. McNear (1982–1988)
- Edward L. Moyers (1993–1995) Chairman/C.E.O.
Notable employees
- Carl Ingold Jacobson, Los Angeles, California, City Council member, 1925–33
- W. Burch Lee, employee in New Orleans office, along with his father, John Martin Lee, Jr., before serving in the Louisiana House of Representatives[21]
- Blake R Van Leer, President of Georgia Tech, United States Army Officer and Hydraulic process inventor
- Charles Wright, Land Surveyor for the railway, before becoming a botanist
- Jack Kerouac, Novelist
- Jimmie Rodgers (country singer), Father of Country Music, Singer-Songwriter
See also
- History of rail transportation in California
- El Paso and Southwestern Railroad
- Long Wharf (Santa Monica)
- Mussel Slough Tragedy
- Pacific Fruit Express
- Santa Fe–Southern Pacific merger
- Southern Pacific 4449
- Southern Pacific Depot
- St. Louis Southwestern Railway
- Texas and New Orleans Railroad
- TOPS (Total Operations Processing System), rolling stock management system jointly developed with IBM and Stanford University and used by SP until 1980, still used by British Rail and successor system
Notes
- operated jointly with the Rock Island Railroad 1926–1938)[6]
- operated jointly with the Rock Island Railroad
- operates today as part of the Coast Starlight train
- operated jointly with the Chicago and North Western Railway and the Union Pacific Railroad; SP portion operates today as part of Amtrak's California Zephyr
- operates today as part of the Coast Starlight train
- proposed, was to have been operated jointly with the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad
- operated jointly with the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad
- operated jointly with the Rock Island Railroad 1946–1967)[6]
- operated until 1985, now Caltrain
- operated jointly with the Chicago and North Western Railway and the Union Pacific Railroad
- operated from 1927 till 1949 as an international train under the subsidiary Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico between Tucson and Guadalajara, featuring through sleepers from Los Angeles to Mexico City
- operated from 1927 till 1951 as an international train under the subsidiary Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico between Tucson and Guadalajara
- see SP 6051
- SSW only
- see SP 5623
- see SP 4450
- leased from Amtrak
References
- Block, Melissa; Neff, Brijet (2012-10-15). "Sprint Born From Railroad, Telephone Businesses". NPR. NPR. Archived from the original on 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2013-01-14.
It all began in Kansas in the late 19th century and came to include a long-distance system created by the Southern Pacific Railroad Internal Network Telecommunications, or SPRINT.
- Yenne (1996), p. 29.
- Yenne (1996), p. 51.
- Yenne (1996), p. 96.
- Rail Lore, Southern Pacific, 1955
- "Imperial and Apache consists". Rock Island Technical Society. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- Schwantes, Carlos A. (1993). Railroad Signatures across the Pacific Northwest. University of Washington Press, Seattle, WA. ISBN 0-295-97210-6. OCLC 27266208.
- "Sontag and Evans". eshomvalley.com. Retrieved 6 August 2013.
- "[no title cited]". San Bernardino Sun. 29 March 1907.
- "Diabolism Incarnate". Editorial. Pasadena Star News. May 1907.
- Arave, Lynn (26 Dec 2014). "Remembering Utah's Worst Train Wreck". Standard-Examiner. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- "7 Dead in "Owl" Wreck". The Bakersfield Californian. 17 January 1947. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- "Doc Ricketts Memorial". Atlas Obscura. n.d. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- Flores, Lori A. (Summer 2013). "A Town Full of Dead Mexicans: The Salinas Valley Bracero Tragedy of 1963, the End of the Bracero Program, and the Evolution of California's Chicano Movement". The Western Historical Quarterly. 44 (2): 124–143. doi:10.2307/westhistquar.44.2.0124.
- Martin, Philip L. (2003). Promise Unfulfilled: Unions, Immigration, and the Farm Workers. ILR Press. p. 50. ISBN 0801488753.
- "Second survivor of 1963 Chualar bus crash emerges". Monterey Herald. March 1, 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- Malnic, Eric; Warren, Jennifer (13 May 1989). "3 Die as Runaway Train Tumbles Onto Homes". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- "20th anniversary of largest chemical spill in California history". California Department of Toxic Substance Control. 2007.
- Final Report on the Recovery of the Upper Sacramento River. Cantara Trustee Council. 2007.
- "Orange Empire Railway Museum – Bringing Southern California's Railway History to Life".
- "W. Burch Lee Funeral Here in Afternoon: Former Clerk of Federal Court Expires After Week of Illness". The Shreveport Times through findagrave.com. Retrieved March 22, 2015.
- General
- Beale, Edwin I. (1907). Highways & Byways of the Virginia Peninsula. Newport News, Virginia: E. I. Beale. LCCN 07009602.
- Beebe, Lucius (1963). The Central Pacific and The Southern Pacific Railroads. Berkeley, California: Howell-North Books. ISBN 0-8310-7034-X.
- Colton, T. (May 2, 2014). "Newport News Shipbuilding, Newport News VA". ShipbuildingHistory. Archived from the original on 26 October 2014. Retrieved 23 February 2015.
- Cooper, Bruce C. (2005). Riding the Transcontinental Rails: Overland Travel on the Pacific Railroad 1865–1881. Philadelphia: Polyglot Press. ISBN 1-4115-9993-4.
- Cooper, Bruce Clement, ed. (2010). The Classic Western American Railroad Routes. New York: Chartwell Books/Worth Press. ISBN 978-0-7858-2573-9. BINC: 3099794.
- Coscia, David (2018). Southern Pacific in the San Fernando Valley 1876-1996. Bellflower: Shade Tree Books. ISBN 978-0-93-074253-8.CS1 maint: ignored ISBN errors (link)
- Daggett, Stuart. Chapters on the History of the Southern Pacific (1922) online. detailed history
- Darton, D. H. (1933). Guidebook of the Western United States; Part F. The Southern Pacific Lines, New Orleans to Los Angeles. Geological Survey Bulletin 845. Washington (D.C.): Government Printing Office.
- Darton, D.H. Guidebook of the Western United States; Part F. The Southern Pacific Lines, New Orleans to Los Angeles. Geological Survey Bulletin 845. Washington (D.C.): Government Printing Office, 1933.
- Diebert, Timothy S. & Strapac, Joseph A. (1987). Southern Pacific Company steam locomotive compendium. Huntington Beach, California: Shade Tree Books. ISBN 0-930742-12-5. OCLC 18401969.
- Hofsommer, Donovan; The Southern Pacific, 1901–1985. Texas A&M University Press; (1986) ISBN 9781603441278.
- Johnson, Emory R. (1912). The Relation of the Panama Canal to the Traffic and Rates of American Railroads. United States Senate Reports. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office. Retrieved February 22, 2015.
- Jungen, C. W. (1922). "Ocean Unit of Lines That Span Continent". Southern Pacific Bulletin. San Francisco: Southern Pacific. 11 (January 1922). Retrieved February 22, 2015.
- Lewis, Daniel (2007). Iron Horse Imperialism: The Southern Pacific of Mexico, 1880–1951. Tucson, Arizona: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-2604-8. OCLC 238833401.
- Mayo, H. M. (1900). "Cuba and the Way There". Sunset. San Francisco: Passenger Department Southern Pacific Company. 4 (January, 1900): 95–98. Retrieved March 15, 2015.
- Lewis, Oscar (1938). The Big Four. New York, New York: Alfred A. Knopf, Inc.
- Orsi, Richard J. (2005). Sunset Limited: The Southern Pacific Railroad and the Development of the American West 1850–1930. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-20019-5. OCLC 55055386.
- Thompson, Anthony W. (1992). Pacific Fruit Express. Wilton, California: Signature Press. ISBN 1-930013-03-5. OCLC 48551573.
- White, Richard (2011). Railroaded: The Transcontinentals and the Making of Modern America. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-06126-0.
- Woodman (Editor), E. H. (1899). "Transportation". Sunset. San Francisco: Passenger Department Southern Pacific Company. 2 (March, 1899). Retrieved March 15, 2015.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Yenne, Bill (1996). The History of the Southern Pacific. New York, New York: Smithmark Pub. ISBN 0-8317-3788-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Southern Pacific Transportation Company. |
- Sphts.org: Southern Pacific Historical & Technical Society
- Harvard Business School, Lehman Brothers Collection: "History of the Southern Pacific Transportation Company"
- Union Pacific Railroad.com: Union Pacific History
- "Across the Great Salt Lake, The Lucin Cutoff" — 1937 article.
- Abandoned Rails.com: History of the Santa Ana and Newport Railroad.