Surface ectoderm
The surface ectoderm (or external ectoderm) forms the following structures:
- Skin (only epidermis; dermis is derived from mesoderm) (along with glands, hair, and nails)
- Epithelium of the mouth and nasal cavity and glands of the mouth and nasal cavity
- Tooth enamel (as a side note, dentin and dental pulp are formed from ectomesenchyme which is derived from ectoderm (specifically neural crest cells and travels with mesenchmyal cells)
- Epithelium of anterior pituitary
- Lens, cornea, lacrimal gland, tarsal glands and the conjunctiva of the eye
- Apical ectodermal ridge inducing development of the limb buds of the embryo.
- Sensory receptors in epidermis
| Surface ectoderm | |
|---|---|
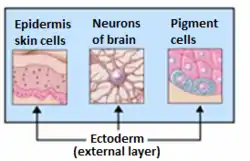 Organs derived from ectoderm. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | ectoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| FMA | 87656 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20071213145329/http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/martini10/chapter18/custom3/deluxe-content.html
- Thomas, Jane Coad with Melvyn Dunstall; foreword by Meryl (2001). Anatomy and physiology for midwives. Edinburgh; New York: Mosby. ISBN 0723429790.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.