Thymidine monophosphate
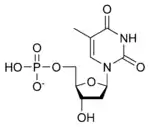
Thymidine monophosphate (TMP), also known as thymidylic acid (conjugate base thymidylate), deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP), or deoxythymidylic acid (conjugate base deoxythymidylate), is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in DNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside thymidine. dTMP consists of a phosphate group, the pentose sugar deoxyribose, and the nucleobase thymine. Unlike the other deoxyribonucleotides, thymidine monophosphate often does not contain the "deoxy" prefix in its name; nevertheless, its symbol often includes a "d" ("dTMP").[1] Dorland’s Illustrated Medical Dictionary[2] provides an explanation of the nomenclature variation at its entry for thymidine.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Thymidine monophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | dTMP |
| 3916216 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N2O8P1− | |
| Molar mass | 321.2005 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
As a substituent, it is called by the prefix thymidylyl-.
See also
References
- Coghill, Anne M.; Garson, Lorrin R., eds. (2006). The ACS style guide: effective communication of scientific information (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society. p. 244. ISBN 978-0-8412-3999-9.
- Elsevier, Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary, Elsevier.