Cytosine
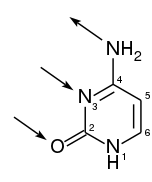
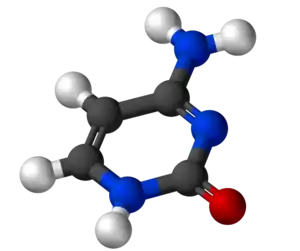
Cytosine (/ˈsaɪtəˌsiːn, -ˌziːn, -ˌsɪn/;[2][3] C) is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached (an amine group at position 4 and a keto group at position 2). The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-aminopyrimidin-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names
4-amino-1H-pyrimidine-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.681 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Cytosine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H5N3O | |
| Molar mass | 111.10 g/mol |
| Density | 1.55 g/cm3 (calculated) |
| Melting point | 320 to 325 °C (608 to 617 °F; 593 to 598 K) (decomposes) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.45 (secondary), 12.2 (primary)[1] |
| -55.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
History
Cytosine was discovered and named by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann in 1894 when it was hydrolyzed from calf thymus tissues.[4][5] A structure was proposed in 1903, and was synthesized (and thus confirmed) in the laboratory in the same year.
In 1998, cytosine was used in an early demonstration of quantum information processing when Oxford University researchers implemented the Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm on a two qubit nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computer (NMRQC).[6]
In March 2015, NASA scientists reported the formation of cytosine, along with uracil and thymine, from pyrimidine under the space-like laboratory conditions, which is of interest because pyrimidine has been found in meteorites although its origin is unknown.[7]
Chemical reactions
Methylation of cytosine occurs on carbon number 5.
Cytosine can be found as part of DNA, as part of RNA, or as a part of a nucleotide. As cytidine triphosphate (CTP), it can act as a co-factor to enzymes, and can transfer a phosphate to convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
In DNA and RNA, cytosine is paired with guanine. However, it is inherently unstable, and can change into uracil (spontaneous deamination). This can lead to a point mutation if not repaired by the DNA repair enzymes such as uracil glycosylase, which cleaves a uracil in DNA.
Cytosine can also be methylated into 5-methylcytosine by an enzyme called DNA methyltransferase or be methylated and hydroxylated to make 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. The difference in rates of deamination of cytosine and 5-methylcytosine (to uracil and thymine) forms the basis of bisulfite sequencing.[8]
Biological function
When found third in a codon of RNA, cytosine is synonymous with uracil, as they are interchangeable as the third base. When found as the second base in a codon, the third is always interchangeable. For example, UCU, UCC, UCA and UCG are all serine, regardless of the third base.
Active enzymatic deamination of cytosine or 5-methylcytosine by the APOBEC family of cytosine deaminases could have both beneficial and detrimental implications on various cellular processes as well as on organismal evolution.[9] The implications of deamination on 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, on the other hand, remains less understood.
Theoretical aspects
Cytosine has not been found in meteorites, which suggests the first strands of RNA and DNA had to look elsewhere to obtain this building block. Cytosine likely formed within some meteorite parent bodies, however did not persist within these bodies due to an effective deamination reaction into uracil.[10]
References
- Dawson, R.M.C.; et al. (1959). Data for Biochemical Research. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- "Cytosine". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- "Cytosine". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- A. Kossel and Albert Neumann (1894) "Darstellung und Spaltungsprodukte der Nucleïnsäure (Adenylsäure)" (Preparation and cleavage products of nucleic acids (adenic acid)), Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft zu Berlin, 27 : 2215–2222. The name "cytosine" is coined on page 2219: " … ein Produkt von basischen Eigenschaften, für welches wir den Namen "Cytosin" vorschlagen." ( … a product with basic properties, for which we suggest the name "cytosine".)
- Kossel, A.; Steudel, H. Z. (1903). "Weitere Untersuchungen über das Cytosin". Physiol. Chem. 38 (1–2): 49–59. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1903.38.1-2.49.
- Jones, J.A.; M. Mosca (1998-08-01). "Implementation of a quantum algorithm on a nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computer". J. Chem. Phys. 109 (5): 1648–1653. arXiv:quant-ph/9801027. Bibcode:1998JChPh.109.1648J. doi:10.1063/1.476739. S2CID 19348964. Archived from the original on 2008-06-12. Retrieved 2007-10-18.
- Marlaire, Ruth (3 March 2015). "NASA Ames Reproduces the Building Blocks of Life in Laboratory". NASA. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- Hayatsu, Hikoya (2008). "Discovery of bisulfite-mediated cytosine conversion to uracil, the key reaction for DNA methylation analysis — A personal account". Proceedings of the Japan Academy. Series B, Physical and Biological Sciences. 84 (8): 321–330. Bibcode:2008PJAB...84..321H. doi:10.2183/pjab.84.321. ISSN 0386-2208. PMC 3722019. PMID 18941305.
- Chahwan R.; Wontakal S.N.; Roa S. (2010). "Crosstalk between genetic and epigenetic information through cytosine deamination". Trends in Genetics. 26 (10): 443–448. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2010.07.005. PMID 20800313.
- Tasker, Elizabeth. "Did the Seeds of Life Come from Space?". Scientific American Blog Network. Retrieved 2016-11-24.
External links and citations
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cytosine. |
- Cytosine MS Spectrum
- EINECS number 200-749-5
- Shapiro R (1999). "Prebiotic cytosine synthesis: a critical analysis and implications for the origin of life". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (8): 4396–401. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.4396S. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.8.4396. PMC 16343. PMID 10200273.