Timeline of the 2019 Pacific hurricane season
The 2019 Pacific hurricane season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific—east of 140°W—and June 1 in the central Pacific—between the International Date Line and 140°W, and ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the eastern Pacific basin.
| Timeline of the 2019 Pacific hurricane season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
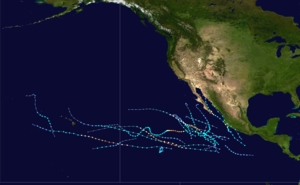 Season summary map | |||||
| Season boundaries | |||||
| First system formed | June 25, 2019 | ||||
| Last system dissipated | November 18, 2019 | ||||
| Strongest system | |||||
| Name | Barbara | ||||
| Maximum winds | 155 mph (250 km/h) (1-minute sustained) | ||||
| Lowest pressure | 930 mbar (hPa; 27.46 inHg) | ||||
| Longest lasting system | |||||
| Name | Kiko | ||||
| Duration | 12 days | ||||
| |||||
Four time zones are utilized in the basin: Central for storms east of 106°W, Mountain between 114.9°W and 106°W, Pacific between 140°W and 115°W, and Hawaii–Aleutian for storms between the International Date Line and 140°W. However, for convenience, all information is listed by Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) first with the respective local time included in parentheses. This timeline includes information that was not operationally released, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center is included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
Timeline of events
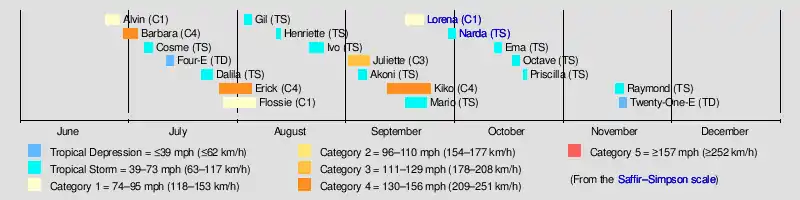
June
June 1
- The 2019 Central Pacific hurricane season officially begins.[1]
June 25
- 21:00 UTC (4:00 p.m. CDT) at 15.2°N 105.7°W – Tropical Depression One-E forms about 280 mi (450 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico.[2]
June 26
- 15:00 UTC (9:00 a.m. MDT) at 14.7°N 109.4°W – Tropical Depression One-E intensifies into Tropical Storm Alvin roughly 450 mi (725 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico.[3]
June 28
- 03:00 UTC (8:00 p.m. PDT June 27) at 17.4°N 115.4°W – Tropical Storm Alvin strengthens into a Category 1 hurricane roughly 520 mi (840 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Simultaneously, Alvin achieves peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 992 mbar (29.29 inHg).[4]
- 09:00 UTC (2:00 a.m. PDT) at 18.0°N 116.3°W – Hurricane Alvin weakens back to a tropical storm about 535 mi (860 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[5]
June 29
- 09:00 UTC (2:00 a.m. PDT) at 20.3°N 119.9°W – Tropical Storm Alvin weakens further to a tropical depression about 665 mi (1,075 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[6]
- 15:00 UTC (8:00 a.m. PDT) at 20.7°N 120.5°W – Tropical Depression Alvin degenerates into a post-tropical cyclone about 695 mi (1,120 km) west of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[7]
June 30
- 15:00 UTC (9:00 a.m. MDT) at 10.6°N 110.4°W – Tropical Storm Barbara forms from a tropical wave roughly 850 mi (1,370 km) south of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula.[8]
July
July 1
- 21:00 UTC (2:00 p.m. PDT) at 11.5°N 118.5°W – Tropical Storm Barbara strengthens into a Category 1 hurricane roughly 970 mi (1,560 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[9]
July 2
- 03:00 UTC (8:00 p.m. PDT July 1) at 11.7°N 119.8°W – Hurricane Barbara rapidly strengthens into a Category 2 hurricane roughly 1,010 mi (1,625 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[10]
- 12:30 UTC (2:30 a.m. HST) at 12.3°N 121.6°W – Hurricane Barbara rapidly strengthens into a Category 4 hurricane roughly 1,060 mi (1,705 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, bypassing Category 3 status entirely.[11]
See also
References
- Neal Dorst (June 2, 2016). "TCFAQ G1) When is hurricane season?". Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2009-05-05. Retrieved July 24, 2018.
- Daniel P. Brown (June 25, 2019). Tropical Depression One-E Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2019.
- Andrew S. Latto; Michael J. Brennan (June 26, 2019). Tropical Storm Alvin Advisory Number 4 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2019.
- Richard J. Pasch (June 28, 2019). Hurricane Alvin Advisory Number 10 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- Daniel P. Brown (June 28, 2019). Tropical Storm Alvin Advisory Number 11 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- Daniel P. Brown (June 29, 2019). Tropical Depression Alvin Advisory Number 15 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
- Andrew S. Latto; Jack L. Beven (June 29, 2019). Post-Tropical Cyclone Alvin Advisory Number 16 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
- Andrew S. Latto; Jack L. Beven (June 30, 2019). Tropical Storm Barbara Advisory Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- Andrew S. Latto; John P. Cangialosi (July 1, 2019). Hurricane Barbara Advisory Number 6 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- Stacy R. Stewart (July 1, 2019). Hurricane Barbara Advisory Number 7 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- Lixion A. Avila (July 2, 2019). Hurricane Barbara Tropical Cyclone Update (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2019 Pacific hurricane season. |
| Preceded by 2018 |
Pacific hurricane season timelines 2019 |
Succeeded by 2020 |