Tlacopan
Tlacopan (From Classical Nahuatl, tlacōtl, meaning stem or rod and -pan, meaning place in or on. This roughly translates to "place on the rods"),[1] also called Tacuba, was a Mexica altepetl situated on the western shore of Lake Texcoco, on the site of today's neighborhood of Tacuba in Mexico City.
Tlacopan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1428–1521 | |||||||
 Glyph
| |||||||
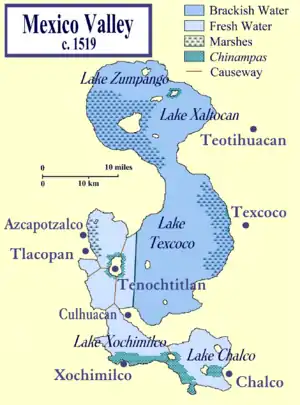 The Valley of Mexico at the time of the Spanish conquest, showing Tlacopan in relation to Tenochtitlan and other cities in the Valley of Mexico. | |||||||
| Common languages | Classical Nahuatl | ||||||
| Religion | Aztec religion | ||||||
| Historical era | Pre-Columbian | ||||||
• Formation of the Aztec Empire | 1428 | ||||||
| 1521 | |||||||
| |||||||
History
Tlacopan was a Tepanec subordinate city-state to nearby altepetl, Azcapotzalco.
In 1428, after its successful conquest of Azcapotzalco, Tlacopan allied with the neighbouring city-states of Tenochtitlan and Texcoco, thus becoming a member of the Aztec Triple Alliance and resulting in the subsequent birth of the Aztec Empire.[2]:xxxviii
Aculnahuacatl Tzaqualcatl, the son of the Tepanec ruler, Tezozomoc, was installed as tlatoani of Tlacopan until his death in c.1430. Throughout its existence, Tlacopan was to remain a minor polity within the Triple Alliance. It received only a fifth of tribute earnt from joint campaigns with its more powerful allies.
In 1521, The Aztec Empire collapsed as a result of the Spanish conquest of Mexico, led by Hernán Cortés and his native Tlaxcallan allies. Over the next few centuries, Tlacopan has been assimilated into the sprawling mega-metropolis of Mexico City. The archæological site of Tlacopan is located in Tacuba, within the present-day minicipality of Miguel Hidalgo.
References
- Siméon, R. (1977). Diccionario de la lengua náhuatl o mexicana. México: Siglo Veintiuno.
- León-Portilla, M. 1992, 'The Broken Spears: The Aztec Accounts of the Conquest of Mexico. Boston: Beacon Press, ISBN 978-0807055014
- Townsend, Richard F. (2000). The Aztecs (revised ed.). London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-28132-7.
