Tropical Storm Felice
Tropical Storm Felice was a modest tropical cyclone that lightly affected parts of the Gulf Coast of the United States in mid-September 1970. Spawned by an upper-level trough over the Bahamas, the system crossed the Florida Keys and entered the Gulf of Mexico, where it gradually began to strengthen. Felice was a disorganized storm for its entire duration, plagued by dry air, a lack of deep thunderstorm activity, and an ill-defined center of circulation, but nevertheless managed to peak as a high-end tropical storm with winds just below Category 1 hurricane strength. Tracking northwestward, the storm brushed southern Louisiana on September 15 before making landfall northeast of Galveston, Texas, late that same day. Once ashore, Felice quickly deteriorated as it recurved into the central United States. While over southeastern Oklahoma, however, its remnants still closely resembled a formidable tropical cyclone.
| Tropical storm (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Felice near peak intensity on September 15 | |
| Formed | September 12, 1970 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 17, 1970 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 70 mph (110 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 997 mbar (hPa); 29.44 inHg |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | |
| Part of the 1970 Atlantic hurricane season | |
In advance of the cyclone, officials prompted residents in vulnerable communities to leave their homes, and temporary storm shelters were established. However, the effects from Felice were generally light. Beneficial rains fell over parts of southern Florida, while sections of coastal Louisiana experienced minimal gale-force winds and above-normal tides. Winds gusting to 55 mph (89 km/h) at Galveston—and estimated near 70 mph (110 km/h) elsewhere—caused scattered power outages and minor tree damage, while heavy rainfall totaling over 6 in (150 mm) triggered some street flooding. Felice delayed the local rice harvest and damaged some hay that had been cut before the storm. Significant precipitation and gusty winds accompanied the system into northern Texas and Oklahoma. Overall, the storm left no fatalities or widespread property damage anywhere along its path.
Meteorological history
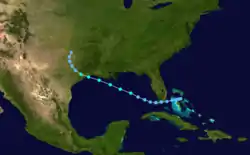
Developing as a tropical depression near Nassau in the Bahamas on September 12, Felice had its origins in a persistent upper-level trough over the area. The nascent depression tracked slowly toward the west-southwest without much intensification, ultimately passing just north of Key West, Florida as it entered the Gulf of Mexico.[1][2] Over the open waters of the Gulf, the system accelerated toward the west-northwest along the southern periphery of a large ridge of high pressure to the north.[2][3][4] While reconnaissance aircraft data on the storm suggested that the depression strengthened into a tropical storm midday on September 14,[5] the official Atlantic tropical cyclone database known as HURDAT indicates the disturbance attained tropical storm status at 0000 UTC on September 15.[2]
Despite continued gradual intensification, Felice remained disorganized as it approached the northern Gulf Coast at forward speeds of up to 20 mph (32 km/h).[1][5] The storm's center came within range of the weather radar site at New Orleans, Louisiana, resulting in close observation of the storm's progress. Felice suffered from restricted outflow and a nebulous circulation, marked by the appearance of two centers.[5][6] Near daybreak on September 15, a more distinct center had apparently formed 100 mi (160 km) to the west-northwest of the storm's initial core, which reportedly dissipated.[7] Operationally, forecasters at the National Hurricane Center believed a surge of southerly inflow transported a significant amount of atmospheric vorticity away from the old center of low pressure, allowing for a new surface-based circulation to form.[8] Indeed, a special off-hour advisory was issued to identify the storm's new location.[9] However, post-season analysis of Felice determined that due to the cyclone's disheveled nature, as well as technical problems at the time of observation, the center relocation could not be conclusively proven; as a result, the official storm path does not reflect any significant jogs.[1]
Felice moved nearly parallel to the southern coast of Louisiana as it began to show signs of improved structure.[1][10] It reached its peak intensity as a high-end tropical storm with winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) at 0000 UTC on September 16, while located about 100 mi south of Lafayette.[2] Dry continental air from the north likely prevented Felice from reaching Category 1 hurricane strength.[10] Even as a strong tropical storm, Felice lacked deep convection typical of mature tropical cyclones.[4] Shortly after peaking, Felice moved ashore at High Island, Texas—about 30 mi (48 km) to the northeast of Galveston—during the evening hours of September 15 local time.[11] The storm rapidly deteriorated once over land and slowed in forward speed.[10] Curving toward the northwest, Felice passed near Houston and weakened into a tropical depression.[2][11] The diminishing system turned northward through north-central Texas late on September 16 and entered southeastern Oklahoma by September 17.[12]
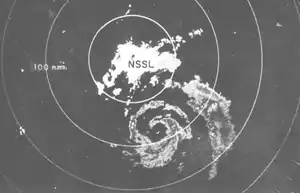
Although Felice officially dissipated as a tropical cyclone at 1200 UTC on September 17,[2] its remnants exhibited a structure very similar to that of a healthy tropical cyclone, as depicted by radar imagery from the National Severe Storms Laboratory in Norman. Curved rainbands surrounded a distinct eye feature, which passed about 90 mi (140 km) southeast of Norman. Two aircraft flew into the area to collect data on the unique storm; notably, they discovered that the system retained a deep warm core relative to its environment. Throughout the day on September 17, the remnants of Felice continued to weaken.[13] The residual surface low recurved toward the east-northeast over Oklahoma and Arkansas before fully dissipating after September 19.[14]
Preparations and impact
As Felice neared the coast, gale warnings were hoisted from Morgan City, Louisiana, to Galveston, while a hurricane watch extended from Morgan City to Port O'Connor, Texas.[15] Small craft advisories were also posted, cautioning light vessels to remain in port.[16] All coastal advisories were discontinued by the early hours of September 16.[17] Residents in the path of the storm generally evacuated in a timely manner.[11] Over 3,000 fled the storm in Cameron Parish, Louisiana;[18] around half of the residents in the low-lying southern part of the parish had already left before the mandatory evacuation was ordered.[19] Farther west, one of two evacuation routes out of Sabine Pass, Texas had been rendered unusable a few days before the storm when a bridge was damaged in a maritime accident. As the remaining highway was considered susceptible to coastal flooding, officials quickly worked to evacuate 1,300 people in Sabine Pass before the storm's approach. The American Red Cross converted nine public schools into temporary storm shelters in and around Beaumont.[11] Shelters were also set up in Houston and Baton Rouge, Louisiana, though they went mostly unused.[20] The post offices in Sabine Pass, Gilchrist, and Port Bolivar transferred money orders, first-class parcels and postage stamps to the Beaumont office as a safety precaution.[21]
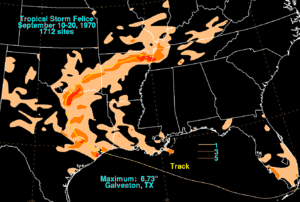
While crossing the Florida Keys on September 13, the depression dropped modest but beneficial rainfall of around 1 to 3 in (25 to 75 mm) over the southern Florida Peninsula.[14][22] The highest tides associated with Felice ran 3.9 ft (1.2 m) above normal at Cameron, Louisiana.[10] Rainfall in Louisiana was light, peaking near 2.5 in (65 mm) in areas closest to the storm's path. Coastal locations experienced gusty winds, occasionally blowing gale-force;[18] an anemometer at Grand Chenier recorded northeasterly gusts up to 42 mph (68 km/h) on the evening of September 15.[23] Though the winds may have affected the quality of sugar cane crops in extreme southern areas of the state, no flooding or property damage was reported.[18]
The storm's landfall was accompanied by significant rainfall, gusty winds, and heightened tides. At Crystal Beach, near where Felice crossed the coast, a distinct lull in the wind and rain coincided with the passage of the storm's poorly defined eye.[24] Weather observers in Gilchrist and Humble estimated gusts at 70 mph (110 km/h) from the east and southwest, respectively.[21] Galveston endured sustained winds of 43 mph (69 km/h) and gusts as high as 55 mph (89 km/h).[21] The storm uprooted some newly planted palm trees, one of which landed on a parked car. Isolated power outages affected parts of the area, including the east side of Galveston after a transformer was hit by lightning.[24] Elsewhere, Felice brought down numerous tree limbs and power lines.[21] In Washington County to the north, the storm damaged vegetation,[25] and winds gusted to 46 mph (74 km/h) in Houston.[11]
Heavy rains, accumulating to 6.73 in (171 mm), triggered minor urban flooding in downtown Galveston.[14][22] Moderate to heavy rainfall affected a broad area along the storm's path, with multiple reports of 5 in (130 mm) or more. The precipitation resulted in a few instances of inconsequential flooding, but more commonly proved beneficial as it helped to relieve dry conditions throughout eastern Texas.[11][21] Rice and hay crops sustained minor damage, with the harvest of the former delayed by about a week. Along the coast, storm tides peaked at 3.0 ft (0.9 m) above normal.[21] As the weakening storm progressed inland, it continued to drop heavy rainfall. Over 6 in (150 mm) of rain fell over Denton County in northern Texas.[21] In southeastern Oklahoma, the remnants of Felice produced rainfall rates up to 2 in (50 mm) per hour, contributing to totals over 4 in (100 mm). Relatively strong winds, peaking around 50 mph (80 km/h), occurred near the remnant center of circulation.[13] The system continued to generate showers and thunderstorms over the central Mississippi River Valley,[26] producing a swath of 3 inch or greater rainfall totals across northern Arkansas.[14]
See also
- List of Texas hurricanes
- Tropical Storm Danielle (1980) – weak tropical storm that brought widespread rainfall to portions of Texas and Louisiana
- Hurricane Barry (1983) – crossed the Florida peninsula before striking the border between Texas and Mexico, causing minimal damage
- Tropical Storm Edouard (2008) – strong, albeit short-lived, tropical storm that brought rainfall to east Texas
- Tropical Storm Erin (2007) - Another Tropical system that became unusually organized over Oklahoma.
References
- Simpson, R. H. & Pelissier, Joseph M. (April 1971). "Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1970" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. American Meteorological Society. 99 (4): 276. Bibcode:1971MWRv...99..269S. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1971)099<0269:ahso>2.3.co;2.
- National Hurricane Center Hurricane Research Division (2012). "Easy-to-Read HURDAT". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Weather Bureau Miami (September 15, 1970). "Tropospheric mean circulation—1000–400 mb layer". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Forecaster Simpson (September 15, 2015). "Tropical Cyclone Discussion Storm Felice, 15/2100z". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- United States Weather Bureau (September 30, 1970). "Tropical Storm Felice, September 15, 1970: page 2". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Forecaster Sugg (September 15, 1970). "Tropical Cyclone Discussion Storm Felice, 15/0900z". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- New Orleans Weather Bureau (September 15, 1970). "Tropical Storm Special Advisory Number 5". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Forecaster Simpson (September 15, 1970). "Tropical Cyclone Discussion Storm Felice, 15/1500z". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Forecaster Sugg (September 15, 1970). "Tropical Cyclone Discussion Storm Felice, 15/1130z". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- United States Weather Bureau (September 30, 1970). "Tropical Storm Felice, September 15, 1970: page 3". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Orton, Robert. "Tropical Storm Felice: September 14–17, 1970". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- R.H. Simpson & Joseph M. Pelisser (1971). "Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1970" (PDF). NOAA. Retrieved 2008-01-11.
- Jessup, Edward A (April 1971). "Picture of the Month: Tropical Storm Felice in Oklahoma" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. American Meteorological Society. 99 (4): 278–280. Bibcode:1971MWRv...99..278J. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1971)099<0278:tsfio>2.3.co;2. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Roth, David. "Tropical Storm Felice – September 13–20, 1970". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Weather Bureau New Orleans (September 15, 1970). "Tropical Storm Advisory Number 7". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- United Press International (September 15, 1970). "Storm Felice Menaces Louisiana–Texas Coast". The Palm Beach Post. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Weather Bureau New Orleans (September 16, 1970). "Tropical Storm Felice Bulletin". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Cry, George W (1970). Climatological Data: Louisiana – September 1970 Special Weather Summary. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. p. 99. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- "Tropical Storm Nears Louisiana". The Toledo Blade. Associated Press. September 14, 1970. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- United Press International (September 16, 1970). "Felice Fizzles Out". Beaver County Times. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Orton, Robert. "Tropical Storm Felice: September 14–17, 1970: page 2". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Condon, Charles R (1970). Climatological data: National summary; Tropical Storm Felice, Sept. 11–17, 1970. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. p. 469. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- "Wind Direction and Speed for Rockefeller Refuge, Grand Chenier, Louisiana Taken from Bendix Friez Wind Recorded". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- Graham, Brian (September 16, 1970). "Storm Goes Ashore at High Island". The Galveston Daily News.
- "Tropical Cyclone Data Felice, Damage Report: page 3". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
- "Felice Has Hangover". Schenectady Gazette. Associated Press. September 18, 1970. Retrieved June 13, 2014.