Veterinary medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, control, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it also deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutrition and product development. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both domesticated and wild, with a wide range of conditions which can affect different species.

Veterinary medicine is widely practiced, both with and without professional supervision. Professional care is most often led by a veterinary physician (also known as a vet, veterinary surgeon or veterinarian), but also by paraveterinary workers such as veterinary nurses or technicians. This can be augmented by other paraprofessionals with specific specialisms such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species relevant roles such as farriers.
Veterinary science helps human health through the monitoring and control of zoonotic disease (infectious disease transmitted from non-human animals to humans), food safety, and indirectly through human applications from basic medical research. They also help to maintain food supply through livestock health monitoring and treatment, and mental health by keeping pets healthy and long-living. Veterinary scientists often collaborate with epidemiologists and other health or natural scientists, depending on type of work. Ethically, veterinarians are usually obliged to look after animal welfare. Veterinarians diagnose, treat, and help keep animals safe and healthy.
History
Premodern era
Archeological evidence, in the form of a cow skull upon which trepanation had been performed, shows that people were performing veterinary procedures in the Neolithic (3400–3000 BCE).[1]

The Egyptian Papyrus of Kahun (Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt) is the first extant record of veterinary medicine.[2] The Shalihotra Samhita, dating from the time of Ashoka, is an early Indian veterinary treatise. The edicts of Asoka read: "Everywhere King Piyadasi (Asoka) made two kinds of medicine (चिकित्सा) available, medicine for people and medicine for animals. Where there were no healing herbs for people and animals, he ordered that they be bought and planted."[3] Hippiatrica is a Byzantine compilation of hippiatrics, dated to the 5th or 6th century.[4]
The first attempts to organize and regulate the practice of treating animals tended to focus on horses because of their economic significance. In the Middle Ages, farriers combined their work in horseshoeing with the more general task of "horse doctoring". The Arabic tradition of Bayṭara, or Shiyāt al-Khayl, originates with the treatise of Ibn Akhī Hizām (fl. late 9th century).
In 1356, the Lord Mayor of London, concerned at the poor standard of care given to horses in the city, requested that all farriers operating within a seven-mile (11.3 km) radius of the City of London form a "fellowship" to regulate and improve their practices. This ultimately led to the establishment of the Worshipful Company of Farriers in 1674.[5]
Meanwhile, Carlo Ruini's book Anatomia del Cavallo, (Anatomy of the Horse) was published in 1598. It was the first comprehensive treatise on the anatomy of a non-human species.[6]
Establishment of profession

The first veterinary school was founded in Lyon, France, in 1762 by Claude Bourgelat.[7] According to Lupton,[8] after observing the devastation being caused by cattle plague to the French herds, Bourgelat devoted his time to seeking out a remedy. This resulted in his founding a veterinary school in Lyon in 1761, from which establishment he dispatched students to combat the disease; in a short time, the plague was stayed and the health of stock restored, through the assistance rendered to agriculture by veterinary science and art."[8] The school received immediate international recognition in the eighteenth century and its pedagogical model drew on the existing fields of human medicine, natural history, and comparative anatomy.[9]
The Odiham Agricultural Society was founded in 1783 in England to promote agriculture and industry,[10] and played an important role in the foundation of the veterinary profession in Britain. A founding member, Thomas Burgess, began to take up the cause of animal welfare and campaign for the more humane treatment of sick animals.[11] A 1785 Society meeting resolved to "promote the study of Farriery upon rational scientific principles."
The physician James Clark wrote a treatise entitled Prevention of Disease in which he argued for the professionalization of the veterinary trade, and the establishment of veterinary colleges. This was finally achieved in 1790, through the campaigning of Granville Penn, who persuaded the Frenchman, Benoit Vial de St. Bel to accept the professorship of the newly established Veterinary College in London.[10] The Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons was established by royal charter in 1844. Veterinary science came of age in the late 19th century, with notable contributions from Sir John McFadyean, credited by many as having been the founder of modern Veterinary research.[12]
In the United States, the first schools were established in the early 19th century in Boston, New York and Philadelphia. In 1879, Iowa Agricultural College became the first land grant college to establish a school of veterinary medicine.[13]
Veterinary workers
Veterinary physicians
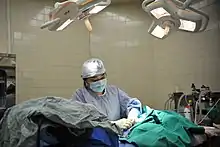
Veterinary care and management is usually led by a veterinary physician (usually called a vet, veterinary surgeon or veterinarian). This role is the equivalent of a doctor in human medicine, and usually involves post-graduate study and qualification.
In many countries, the local nomenclature for a vet is a protected term, meaning that people without the prerequisite qualifications and/or registration are not able to use the title, and in many cases, the activities that may be undertaken by a vet (such as animal treatment or surgery) are restricted only to those people who are registered as vet. For instance, in the United Kingdom, as in other jurisdictions, animal treatment may be performed only by registered vets (with a few designated exceptions, such as para-veterinary workers), and it is illegal for any person who is not registered to call themselves a vet or perform any treatment.
Most vets work in clinical settings, treating animals directly. These vets may be involved in a general practice, treating animals of all types; may be specialized in a specific group of animals such as companion animals, livestock, laboratory animals, zoo animals or horses; or may specialize in a narrow medical discipline such as surgery, dermatology, laboratory animal medicine, or internal medicine.
As with healthcare professionals, vets face ethical decisions about the care of their patients. Current debates within the profession include the ethics of purely cosmetic procedures on animals, such as declawing of cats, docking of tails, cropping of ears and debarking on dogs.
A wide range of surgeries and operations are performed on various types of animals, but not all of them are carried out by vets. In a case in Iran, for instance, an eye surgeon managed to perform a successful cataract surgery on a rooster for the first time in the world.[14]
Paraveterinary workers
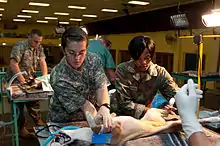
Paraveterinary workers, including veterinary nurses, technicians and assistants, either assist vets in their work, or may work within their own scope of practice, depending on skills and qualifications, including in some cases, performing minor surgery.
The role of paraveterinary workers is less homogeneous globally than that of a vet, and qualification levels, and the associated skill mix, vary widely.
Allied professions
A number of professions exist within the scope of veterinary medicine, but which may not necessarily be performed by vets or veterinary nurses. This includes those performing roles which are also found in human medicine, such as practitioners dealing with musculoskeletal disorders, including osteopaths, chiropractors and physiotherapists.
There are also roles which are specific to animals, but which have parallels in human society, such as animal grooming and animal massage.
Some roles are specific to a species or group of animals, such as farriers, who are involved in the shoeing of horses, and in many cases have a major role to play in ensuring the medical fitness of the horse.
Veterinary research

Veterinary research includes research on prevention, control, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases of animals and on the basic biology, welfare, and care of animals. Veterinary research transcends species boundaries and includes the study of spontaneously occurring and experimentally induced models of both human and animal disease and research at human-animal interfaces, such as food safety, wildlife and ecosystem health, zoonotic diseases, and public policy.[15]
Clinical veterinary research
As in medicine, randomized controlled trials are fundamental also in veterinary medicine to establish the effectiveness of a treatment.[16] However, clinical veterinary research is far behind human medical research, with fewer randomized controlled trials, that have a lower quality and that are mostly focused on research animals.[17] Possible improvement consists in creation of network for inclusion of private veterinary practices in randomized controlled trials.
There are no studies on the effect of community animal health services on improving household wealth and the health status of low-income farmers.[18]
See also
Notes
- Ramirez Rozzi, Fernando; Froment, Alain (19 April 2018). "Earliest Animal Cranial Surgery: from Cow to Man in the Neolithic". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 5536. Bibcode:2018NatSR...8.5536R. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-23914-1. PMC 5908843. PMID 29674628.
- Thrusfield 2007, p. 2.
- Finger 2001, p. 12.
- Scarborough, John; Cutler, Anthony (1 January 2005), "Hippiatrica", The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780195046526.001.0001, ISBN 9780195046526, retrieved 27 September 2019
- Hunter, Pamela (2004). Veterinary Medicine: A Guide to Historical Sources, p. 1. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.
- Wernham, R. B. (1968). The New Cambridge Modern History: The Counter-Reformation and price revolution, 1559–1610, Volume 3, p. 472. Cambridge University Press.
- Marc Mammerickx, Claude Bourgelat: avocat des vétérinaires, Bruxelles 1971
- J.L.Lupton, "Modern Practical Farriery", 1879, in the section: "The Diseases of Cattle Sheep and Pigs" pp. 1
- Heintzman, Kit (2018). "A cabinet of the ordinary: domesticating veterinary education, 1766–1799". The British Journal for the History of Science. 51 (2): 239–260. doi:10.1017/S0007087418000274. PMID 29665887.
- Pugh, L.P (1962), From Farriery to Veterinary Medicine 1785–1795, Heffner, Cambridge (for RCVS), pp. 8–19
- Cotchen, Ernest (1990), The Royal Veterinary College London, A Bicentenary History, Barracuda Books Ltd, pp. 11–13
- Exacting researcher brought profession into modern age, American Veterinary Medical Association
- Widder, Keith R. (2005). Michigan Agricultural College: The Evolution Of A Land-Grant Philosophy, 1855–1925, p. 107. MSU Press
- "Rooster Undergoes World's First Cataract Surgery". IFPNews.com. 22 April 2018.
- National Research Council, (US) Committee on the National Needs for Research in Veterinary Science (2005). Critical Needs for Research in Veterinary Science. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
- Sargeant, JM (2010). "Quality of reporting of clinical trials of dogs and cats and associations with treatment effects". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 24 (1): 44–50. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2009.0386.x. PMID 19807866.
- Di Girolamo, N (2016). "Deficiencies of effectiveness of intervention studies in veterinary medicine: a cross-sectional survey of ten leading veterinary and medical journals". PeerJ. 4: e1649. doi:10.7717/peerj.1649. PMC 4734056. PMID 26835187.
- Martin Curran, Marina; MacLehose, Harriet (19 April 2006). Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group (ed.). "Community animal health services for improving household wealth and health status of low income farmers". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003049. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003049.pub2. PMC 6532712. PMID 16625568.
Further reading
Introductory textbooks and references
- Aspinall, Victoria; Cappello, Melanie; Bowden, Sally (2009), Introduction to Veterinary Anatomy and Physiology Textbook, Jeffery, Andrea (forward), Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7020-2938-7
- Boden, Edward; West, Geoffrey Philip (1998), Black's veterinary dictionary, Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 978-0-389-21017-7
- Done, Stanley H. (1996), Color atlas of veterinary anatomy: The dog & cat, Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7234-2441-3
- Dyce, Keith M.; Sack, Wolfgang O.; Wensing, Cornelis Johannes Gerardus (2010), Textbook of veterinary anatomy, Saunders, ISBN 978-1-4160-6607-1
- Fenner, William R. (2000), Quick reference to veterinary medicine, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-397-51608-7
- Lawhead, James B.; Baker, MeeCee (2009), Introduction to veterinary science, Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-1-4283-1225-8
- Pfeiffer, Dirk (2009), Veterinary Epidemiology: An Introduction, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 978-1-4051-7694-1
- Radostits, O. M.; Gay, C. C.; Blood, D. C.; Arundel, J. H.; Hinchcliff, Kenneth W (2000), Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Sheep, Pigs, Goats and Horses (9th ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences, p. 1877, ISBN 978-0-7020-2604-1
Monographs and other speciality texts
- Dunlop, Robert H.; Malbert, Charles-Henri (2004), Veterinary pathophysiology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-2826-8
- Eurell, Jo Ann Coers; Eurell, Jo Ann; Frappier, Brian L.; Dellman, Horst-Dieter (25 May 2006), Dellmann's textbook of veterinary histology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-7817-4148-4
- Foreyt, William J.; Foreyt, Bill (2001), Veterinary parasitology reference manual, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-2419-2
- Gupta, Ramesh Chandra (2007), Veterinary toxicology: basic and clinical principles, Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-370467-2
- Hirsh, Dwight C.; Maclachlan, Nigel James; Walker, Richard L. (2004), Veterinary microbiology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-0379-1
- Hunter, Pamela (2004), Veterinary Medicine: A Guide to Historical Sources, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., p. 611, ISBN 978-0-7546-4053-0
- Merck, Melinda D. (2007), Veterinary forensics: animal cruelty investigations, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-8138-1501-5
- Murphy, Frederick A. (1999), Veterinary virology, Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-511340-3
- Nicholas, Frank W. (2009), Introduction to Veterinary Genetics, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 978-1-4051-6832-8
- Robinson, Wayne F.; Huxtable, Clive R. R. (2004), Clinicopathologic Principles for Veterinary Medicine, Cambridge University Press, p. 452, ISBN 978-0-521-54813-7
- Slatter, Douglas H. (2002), Textbook of small animal surgery, Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7216-8607-3
- Kahn, Cynthia M., ed. (2010), The Merck Veterinary Manual, Whitehouse Station, N.J., Merck, ISBN 978-0-911910-93-3
- Thrusfield, Michael (2007), Veterinary epidemiology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-1-4051-5627-1
- Zajac, A.; Conboy, Gary A.; American Association of Veterinary Parasitologists (2006), Veterinary clinical parasitology, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-8138-1734-7
Veterinary nursing, ophthalmology, and pharmacology
- Adams, H. Richard (2001), Veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-1743-9
- Bryant, Susan (2010), Anesthesia for Veterinary Technicians, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 978-0-8138-0586-3
- Cannon, Marthaxcx; Hijfte, Myra Forster-van (2006), Feline medicine: a practical guide for veterinary nurses and technicians, Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7506-8827-7
- Crispin, Sheila M. (2005), Notes on veterinary ophthalmology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-632-06416-8
- Gelatt, Kirk N. (2000), Essentials of veterinary ophthalmology, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-683-30077-2
- Lane, D. R.; Cooper, B. (2003), Veterinary nursing, Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7506-5525-5
- Pattengale, Paula (2004), Tasks for the veterinary assistant, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-7817-4243-6
- Riviere, Jim E.; Papich, Mark G. (2009), Veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 978-0-8138-2061-3
Related fields
- Anthony, David; University of Pennsylvania. University Museum (1984), Man and animals: living, working, and changing together : in celebration of the 100th anniversary, the School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, UPenn Museum of Archaeology, ISBN 978-0-934718-68-4
- Catanzaro, Thomas E. (1998), Building the Successful Veterinary Practice: Innovation and creativity, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-2984-5
- Finger, Stanley (2001), Origins of neuroscience: a history of explorations into brain function, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-514694-3
- Rollin, Bernard E. (2006), An introduction to veterinary medical ethics: theory and cases, Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-8138-0399-9
- Sherman, David M. (2002), Tending animals in the global village: a guide to international veterinary medicine, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-683-18051-0
- Shilcock, Maggie; Stutchfield, Georgina (2003), Veterinary practice management: a practical guide, Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 978-0-7020-2696-6
- Smith, Gary; Kelly, Alan M., eds. (2008), Food Security in a Global Economy: Veterinary Medicine and Public Health, Phila.: University of Pennsylvania Press, p. 176, ISBN 978-0-8122-2044-5
- Swabe, Joanna (1999), Animals, Disease, and Human Society: Human-animal Relations and the Rise of Veterinary Medicine, Routledge, p. 243, ISBN 978-0-415-18193-8
- Swope, Robert E.; Rigby, Julie (2001), Opportunities in veterinary medicine careers, McGraw-Hill Professional, p. 151, ISBN 978-0-658-01055-2
- Swabe, Joanna (1999), Veterinary Courses and CE., p. 244, ISBN 978-0-415-18193-8
- Anthony, David; Zoetis (2014), VeritasDVM, Dr. Donal Smith, ISBN 978-0-934718-68-4
External links
 The dictionary definition of veterinary medicine at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of veterinary medicine at Wiktionary Media related to Veterinary medicine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Veterinary medicine at Wikimedia Commons