Vistula Spit canal
The Vistula Spit canal (official name Nowy Świat ship canal, Polish: Kanał żeglugowy Nowy Świat[1]) is a planned canal across the Polish section of the Vistula Spit that will create a second connection between the Vistula Lagoon and Gdańsk Bay. It will allow ships to enter the Vistula Lagoon and the port of Elbląg without having to rely on the Russian Strait of Baltiysk, saving a 100 km journey. The works started in February 2019. It is planned to be 1305 m in length and will allow ships of draft up to 4 m, length up to 100 m, and beam up to 20 m.[2] It is planned to be completed in 2022. [3]
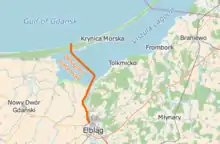
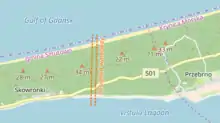
The planned canal location is between the villages of Skowronki and Przebrno.
Works
The major works include:[4]
- Construction of the breakwater harbor on the Gdańsk Bay side.
- Construction of the shipping channel together with all its infrastructure
- New roads and bridges
- Construction of an artificial island in the Vistula Lagoon.
The works started in February 2020 with tree cutting, which was finished during February 15 - 20, 2020. Logging and branch removal was to be finished by the end of March.[2]
The beginning of the construction of the artificial island was announced on May 30, 2020. It area is planned to be about 180 hectares and it is expected to be a bird habitat.[3]
Costs
A contract was signed with a Polish-Belgium consortium in October 2019 to build the canal at a cost of PLN 992m (EUR230m). the total cost of the project is expected to be PLN 2 billion.[5]
Concerns
Environmental concerns had been expressed by environmental activists in Europe and Poland which did not stop the project. The Russian Federation strongly objected to the canal on both environmental and security grounds, claiming that the canal will allow NATO warships to enter the Vistula lagoon without passing close by the Russian military facilities at Baltiysk, claiming that the canal presented a direct threat to the security of Kaliningrad and the Russian Federation as a whole.[6]
References
- GABO -, Agencja Reklamowa (April 7, 2016). "Przekop Mierzei do 2022 r.? Minister Gróbarczyk: Ten termin wydaje się jak najbardziej możliwy". info.elblag.pl.
- "RDLP: wycinka na Mierzei Wiślanej jest zakończona". Onet Wiadomości. February 20, 2019.
- "Przekop Mierzei Wiślanej. Rozpoczęła się budowa sztucznej wyspy". NIEZALEZNA.PL. May 30, 2020.
- Zobacz jak wygląda budowa przekopu Mierzei Wiślanej, Wprost, May 14, 2020
- "Polish gov't agrees huge deal for strategic canal to Baltic Sea". PolskieRadio.pl. 4 October 2019.
- "New Polish shipping canal viewed as threat in Moscow: analysis". PolskieRadio.pl. 2 July 2020.
External links
YouTube videos of the progress of the construction:
- Przekop Mierzei Wiślanej 23.01.2020 [The Dig on the Vistula Spit 23.01.2020], Żuławy TV
- Youtube search for "Przekop Mierzei Wiślanej "
