1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad (Italian: Giochi della XVII Olimpiade), were an international multi-sport event held from 25 August to 11 September 1960 in Rome, Italy. Rome had previously been awarded the administration of the 1908 Summer Olympics, but following the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 1906, the city had no choice but to decline and pass the honour to London. The Soviet Union won the most gold and overall medals at the 1960 Games.
 | |||
| Host city | Rome, Italy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nations | 83 | ||
| Athletes | 5,338 (4,727 men, 611 women) | ||
| Events | 150 in 17 sports (23 disciplines) | ||
| Opening | 25 August | ||
| Closing | 11 September | ||
| Opened by | |||
| Cauldron | |||
| Stadium | Stadio Olimpico | ||
| Summer | |||
| |||
| Winter | |||
| |||
Host city selection
On June 15, 1955, at the 50th IOC Session in Paris, France, Rome won the rights to host the 1960 Games, having beaten Brussels, Mexico City, Tokyo, Detroit, Budapest and finally Lausanne. Tokyo and Mexico City would subsequently host the proceeding 1964 and 1968 Summer Olympics respectively.[2]
Toronto was initially interested in the bidding, but appears to have dropped out during the final phase of the bid process.[3] This was the first of five unsuccessful attempts by Toronto to secure the Summer Olympics from then until the 2008 games.
| 1960 Summer Olympics bidding results[4] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Country | Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 3 | ||
| Rome | 15 | 26 | 35 | |||
| Lausanne | 14 | 21 | 24 | |||
| Detroit | 6 | 11 | — | |||
| Budapest | 8 | 1 | — | |||
| Brussels | 6 | — | — | |||
| Mexico City | 6 | — | — | |||
| Tokyo | 4 | — | — | |||
Highlights

- Swedish sprint canoeist Gert Fredriksson won his sixth Olympic title.
- Fencer Aladár Gerevich of Hungary won his sixth consecutive gold medal in the team sabre event.
- The Japanese men's gymnastics team won the first of five successive golds (see 1976 Summer Olympics).
- The United States men's national basketball team—led by promising college players Walt Bellamy, Jerry Lucas, Oscar Robertson and Jerry West—captured its fifth straight Olympic gold medal.
- Danish sailor Paul Elvstrøm won his fourth straight gold medal in the Finn class. Others to emulate his performance in an individual event are Al Oerter, Carl Lewis, Michael Phelps, Kaori Icho and, if the Intercalated (Interspaced) Games of 1906 are included, Ray Ewry.
- German Armin Hary won the 100 metres in an Olympic record time of 10.2 seconds.
- Wilma Rudolph, a former polio patient, won three gold medals in sprint events on the track. She was acclaimed as "the fastest woman in the world".
- Jeff Farrell won two gold medals in swimming. He underwent an emergency appendectomy six days before the Olympic Trials.[5]

- Abebe Bikila of Ethiopia won the marathon barefooted to become the first black African Olympic champion.
- Cassius Clay, later known as Muhammad Ali, won boxing's light-heavyweight gold medal. Ramon "Buddy" Carr was one of the coaches that led this team to winning gold.[6]
- Herb Elliott, AUS, won the men's 1500 meters in one of the most dominating performances in Olympic history.
- Rafer Johnson defeated his rival, fellow U.C.L.A. Bruin and friend C.K. Yang in one of the greatest Decathlon events in Olympic history.[7]
- Lance Larson, US, was controversially denied a 100 metres freestyle swimming gold, despite showing the best time.
- 16-years-old phenom Chris von Saltza won four medals in women's swimming, three of them gold.
- The future Constantine II, last King of Greece (abdicated and ended hybrid monarchy, 1973) won his country a gold in sailing: dragon class.
- The Pakistani Men's Field Hockey team broke a run of Indian team victories since 1928, defeating India in the final and winning Pakistan's first Olympic gold medal.
- Wrestlers Shelby Wilson, and Doug Blubaugh, who wrestled together growing up, won gold medals in their respective weight classes.
Lowlights
- Danish cyclist Knud Enemark Jensen collapsed during the 100km team race because of heat stroke and later died in the hospital. It was the second time an athlete died in competition at the Olympics, after the death of Portuguese marathon runner Francisco Lázaro at the 1912 Summer Olympics.[8]
Historical landmarks
- South Africa appeared in the Olympic arena for the last time under its apartheid regime. It would not be allowed to return until 1992, by when apartheid in sport was being abolished.
- Singapore competed for the first time under its own flag, which was to become its national flag after independence, as the British had granted it self-government a year earlier. Tan Howe Liang won silver in the Weightlifting lightweight category, which was the first time (and the only time until 2008) that an athlete from Singapore won an Olympic medal.
Non-medal winners
- Finnish Vilho Ylönen, a field shooter, shot a bullseye to a wrong target, and in so doing he dropped from second place to fourth.
- Peter Camejo, a 2004 American vice-presidential candidate for the Green Party, competed in yachting for Venezuela.
- The future Queen Sofía of Spain represented her native Greece in sailing events.
Broadcasting
- CBS paid US$394,000 (equivalent to $3,405,064 in 2019) for the exclusive right to broadcast the Games in the United States. This was the first Summer Olympic games to be telecast in North America. In addition to CBS in the United States, the Olympics were telecast for the first time in Canada (on CBC Television) and in Mexico (through the networks of Telesistema Mexicano). Since television broadcast satellites were still two years into the future, CBS, CBC, and TSM shot and edited videotapes in Rome, fed the tapes to Paris where they were re-recorded onto other tapes which were then loaded onto jet planes to North America. Planes carrying the tapes landed at Idlewild Airport in New York City, where mobile units fed the tapes to CBS, to Toronto for the CBC, and to Mexico City for TSM. Despite this arrangement, many daytime events were broadcast in North America, especially on CBS and CBC, the same day they took place.[9]
Venues

- Olympic Stadium2 (Stadio Olimpico) - opening/closing ceremonies, athletics, equestrian events
- Flaminio Stadium1 (Stadio Flaminio) - football finals
- Swimming Stadium1 - swimming, diving, water polo, modern pentathlon (swimming)
- Sports Palace1 (Palazzo dello sport) - basketball, boxing
- Olympic Velodrome1 - cycling (track), field hockey
- Small Sports Palace1 (Palazzetto dello Sport) - basketball, weightlifting
- Marble Stadium2 (Stadio dei Marmi) - field hockey preliminaries
- Baths of Caracalla - gymnastics
- Basilica of Maxentius - wrestling
- Palazzo dei Congressi - fencing
- Umberto I Shooting Range1 - modern pentathlon (shooting), shooting (pistol/ rifle)
- Roses Swimming Pool1 (Piscina delle Rose) - water polo
- Lake Albano, Castelgandolfo - rowing, canoeing
- Piazza di Siena, Villa Borghese gardens - equestrian (dressage, eventing - jumping, jumping - individual)
- Pratoni del Vivaro, Rocca di Papa - equestrian (eventing)
- Gulf of Naples, Naples - yachting
- Communal Stadium, Florence - football/soccer preliminaries
- Communal Stadium, Grosseto - football/soccer preliminaries
- Communal Stadium, L'Aquila - football/soccer preliminaries
- Ardenza Stadium, Livorno - football/soccer preliminaries
- Adriatico Stadium, Pescara - football/soccer preliminaries
- Saint Paul's Stadium, Naples - football/soccer preliminaries
- Campo Tre Fontane - field hockey preliminaries
- Acqua Santa Golf Club Course - modern pentathlon (running)
- Arch of Constantine - athletics (marathon finish)
- Cesano Infantry School Range - shooting (300 m free rifle)
- Lazio Pigeon Shooting Stand - shooting (trap shotgun)
- Passo Corese - modern pentathlon (riding)
- Grande Raccordo Anulare - athletics (marathon)
- Via Appian Antica - athletics (marathon)
- Via Cassia - cycling (individual road race)
- Via Flaminia - cycling (individual road race)
- Via Cristoforo Colombo - athletics (marathon), cycling (road team time trial)
- Via di Grottarossa - cycling (individual road race)
1 New facilities constructed in preparation for the Olympic Games. 2 Existing facilities modified or refurbished in preparation for the Olympic Games.
Games
Participating National Olympic Committees
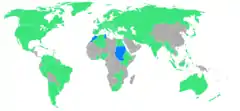
A total of 83 nations participated at the Rome Games. Athletes from Morocco, San Marino, Sudan, and Tunisia competed at the Olympic Games for the first time. Athletes from Barbados, Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago would represent the new (British) West Indies Federation, competing as "Antilles", but this nation would only exist for this single Olympiad. Athletes from Northern Rhodesia and Southern Rhodesia competed under the Rhodesia name while representing the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. Athletes from East Germany and West Germany would compete as the United Team of Germany from 1956 to 1964. The number in parentheses indicates the number of participants that each country contributed.
.svg.png.webp) Suriname also made its first Olympic appearance, but its lone athlete (Wim Esajas) withdrew from competition due to a scheduling error.[10]
Suriname also made its first Olympic appearance, but its lone athlete (Wim Esajas) withdrew from competition due to a scheduling error.[10]
Sports
The 1960 Summer Olympics featured 17 different sports encompassing 23 disciplines, and medals were awarded in 150 events. In the list below, the number of events in each discipline is noted in parentheses.
- Aquatics
 Diving (4)
Diving (4) Swimming (15)
Swimming (15) Water polo (1)
Water polo (1)
 Athletics (34)
Athletics (34) Basketball (1)
Basketball (1) Boxing (10)
Boxing (10)_pictogram.svg.png.webp) Canoeing (7)
Canoeing (7)_pictogram.svg.png.webp) Cycling
Cycling
- Road (2)
- Track (4)
 Equestrian
Equestrian
- Dressage (1)
- Eventing (2)
- Jumping (2)
 Fencing (8)
Fencing (8) Field hockey (1)
Field hockey (1) Football (1)
Football (1)_pictogram.svg.png.webp) Gymnastics (14)
Gymnastics (14) Modern pentathlon (2)
Modern pentathlon (2) Rowing (7)
Rowing (7) Sailing (5)
Sailing (5) Shooting (6)
Shooting (6) Weightlifting (7)
Weightlifting (7) Wrestling
Wrestling
- Freestyle (8)
- Greco-Roman (8)
Calendar
- All dates are in Central European Time (UTC+1)
| OC | Opening ceremony | ● | Event competitions | 1 | Gold medal events | CC | Closing ceremony |
| August / September | 25 Thu |
26 Fri |
27 Sat |
28 Sun |
29 Mon |
30 Tue |
31 Wed |
1 Thu |
2 Fri |
3 Sat |
4 Sun |
5 Mon |
6 Tue |
7 Wed |
8 Thu |
9 Fri |
10 Sat |
11 Sun |
Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | CC | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 34 | ||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 10 | 10 | |||||||||
| ● | ● | 7 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | |||||||||||||||
| ● | 1 | 1 | 1 | ● | ● | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Equestrian | ● | 1 | 1 | ● | ● | 2 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||
| ● | 1 | ● | 1 | 1 | 1 | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | |||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | ● | ● | 1 | |||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | 2 | 5 | 7 | 14 | |||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | 7 | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 5 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| ● | 1 | 1 | ● | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | ||||||||||||
| ● | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 15 | |||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 7 | |||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | 8 | ● | ● | ● | ● | 8 | 16 | |||||||||
| Daily medal events | 2 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 5 | 14 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 0 | 14 | 15 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 15 | 1 | 150 | |
| Cumulative total | 2 | 6 | 6 | 17 | 22 | 36 | 44 | 55 | 70 | 70 | 84 | 99 | 111 | 123 | 134 | 149 | 150 | ||
| August / September | 25 Thu |
26 Fri |
27 Sat |
28 Sun |
29 Mon |
30 Tue |
31 Wed |
1 Thu |
2 Fri |
3 Sat |
4 Sun |
5 Mon |
6 Tue |
7 Wed |
8 Thu |
9 Fri |
10 Sat |
11 Sun |
Total events |
Medal count
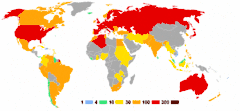
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1960 Games:[11]
| Rank | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43 | 29 | 31 | 103 | |
| 2 | 34 | 21 | 16 | 71 | |
| 3 | 13 | 10 | 13 | 36 | |
| 4 | 12 | 19 | 11 | 42 | |
| 5 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 22 | |
| 6 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 9 | |
| 7 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 21 | |
| 8 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 18 | |
| 9 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 21 | |
| 10 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | |
| Totals (10 nations) | 134 | 112 | 105 | 351 | |
See also
- 1960 Summer Paralympics
- 1960 Winter Olympics
- Olympic Games celebrated in Italy
- 1956 Winter Olympics – Cortina D'Ampezzo
- 1960 Summer Olympics – Rome
- 2006 Winter Olympics – Turin
- 2026 Winter Olympics – Milan and Cortina D'Ampezzo
- Summer Olympic Games
- Olympic Games
- International Olympic Committee
- List of IOC country codes
- Universiades celebrated in Italy
- 1959 Summer Universiade – Turin
- 1966 Winter Universiade – Sestriere
- 1970 Summer Universiade – Turin
- 1975 Winter Universiade – Livigno
- 1975 Summer Universiade – Rome
- 1985 Winter Universiade – Belluno
- 1997 Summer Universiade – Sicily
- 2003 Winter Universiade – Tarvisio
- 2007 Winter Universiade – Turin
- 2013 Winter Universiade – Trentino
- 2019 Summer Universiade – Naples
- Deaflympics celebrated in Italy
- 1957 Summer Deaflympics – Milan
- 1983 Winter Deaflympics – Madonna di Campiglio
- 2001 Summer Deaflympics – Rome
- 2019 Winter Deaflympics – Province of Sondrio
References
- "Factsheet - Opening Ceremony of the Games of the Olympiad" (PDF) (Press release). International Olympic Committee. 9 October 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- "IOC VOTE HISTORY".
- "Toronto has made 5 attempts to host the Olympics. Could the sixth be the winner?". thestar.com. 24 July 2015.
- "Past Olympic host city election results". GamesBids. Archived from the original on 24 January 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- Coplan, Joseph (July 19, 2000). "Profiling Jeff Farrell, 1968 ISHOF Honor Swimmer". USMS. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
- Zaborney, Mark (March 11, 2016). "Ramon 'Buddy' Carr (1926-2016): TPD officer coached gold-medalist boxer". Toledo Blade.
- Henderson, Jon (June 26, 2012). "Great Olympic Moments: UCLA friends Rafer Johnson and Yang Chuan-kwang make decathlon history in 1960". The Telegraph. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- Maraniss, David (2008). Rome 1960: The Olympics That Changed the World (1st ed.). New York City, NY: Simon & Schuster. p. 138. ISBN 978-1-4165-3407-5.
- "OLYMPICS AND TELEVISION - The Museum of Broadcast Communications". Museum.tv. Archived from the original on July 27, 2009. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
- Official Olympic Reports. Archived from the original on 2006-06-22.
- Byron, Lee; Cox, Amanda; Ericson, Matthew (August 4, 2008). "A Map of Olympic Medals". The New York Times. Retrieved February 26, 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1960 Summer Olympics. |
- "Rome 1960". Olympic.org. International Olympic Committee.
- Rome 1960: The Olympics That Changed the World, David Maraniss, New York, NY, U.S.: Simon & Schuster, 2008.
- The program of the 1960 Rome Olympics
- LIFE 12 Sep 1960
| Preceded by Melbourne/Stockholm |
Summer Olympic Games Rome XVII Olympiad (1960) |
Succeeded by Tokyo |