1979 Pacific hurricane season
The 1979 Pacific hurricane season was an inactive Pacific hurricane season. It officially started on May 15, 1979, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1979, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1979. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeast Pacific Ocean.
| 1979 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
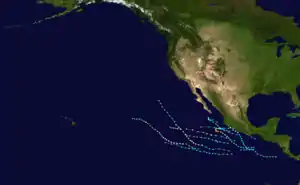 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 29, 1979 |
| Last system dissipated | November 18, 1979 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Ignacio |
| • Maximum winds | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 938 mbar (hPa; 27.7 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 13 |
| Total storms | 10 |
| Hurricanes | 6 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 4 |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
With ten storms, less than two-thirds of the average of seventeen, this season was very inactive. There were six hurricanes, also below average. Of those hurricanes, four were major by reaching Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. As of the 2018 Pacific hurricane season, 1979 remains the most recent year without any tropical cyclones active in the Central Pacific.[1]
Systems
Tropical Depression One-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | May 29 – May 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) |
A tropical disturbance formed on May 29 south of Manzanillo, Mexico and moved slowly southwestward. On May 31, the storm was upgraded to tropical depression status based on satellite data. Shortly after becoming a depression, the storm turned northward over cooler waters where it rapidly weakened and dissipated 370 mi (600 km) southwest of Manzanillo. The only effects from the tropical depression was from a ship which reported heavy rainfall.[2]
Hurricane Andres
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | May 31 – June 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 992 mbar (hPa) |
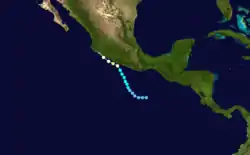
A depression formed on May 31, In early June, it became a hurricane, subsequently named Andres, and approached the Mexican coast as a large hurricane. The hurricane disintegrated rapidly as it approached the coast, and eventually made landfall as a weak depression on June 4.[2] Initial reports indicated that the storm made landfall with winds of 60 mph (95 km/h);[3] however, according to the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Database, the storm crossed the shore with winds of 75 mph (120 km/h).
Around Acapulco, airlines canceled flights in and out of the region on June 3 and resumed the following day after the passage of Andres. Torrential rainfall triggered widespread flooding which inundated homes and floated cars left on streets.[4] High winds also downed power lines, leaving many residents without electricity.[5] Offshore, two fishermen were killed by the storm after their boat capsized amidst rough seas.[4]
Tropical Storm Blanca
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | June 21 – June 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
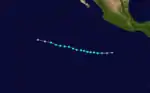
A westward moving tropical disturbance from the Atlantic crossed into the Pacific Ocean over Costa Rica and Panama on June 17. Continuing westward, the disturbance developed into the third tropical depression of the season on June 21. It further intensified and became Tropical Storm Blanca, eventually peaking as a relatively weak 50 mph (85 km/h) tropical storm. As Blanca was heading west-northwestward, it began to slowly weaken after peak intensity, and later dissipated on June 25. Blanca remained out at sea for the entire duration, and no fatalities or damage was reported as a result.[2]
Tropical Storm Carlos
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 14 – July 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) |
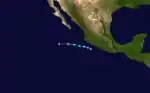
A tropical disturbance formed in the Gulf of Tehuantepec on July 11. The system moved across the Gulf of Tehuantepec 9 mph (14 km/h) and gradually intensified. By late on July 14, satellites indicated a cyclonic circulation; the disturbance was promptly classified as Tropical Depression Four while 253 mi (407 km) west of Acapulco, Guerrero, Mexico. As the depression moved over sea surface temperatures (SST's) of 86 °F (30 °C), it rapidly intensified into Tropical Storm Carlos early on July 15. As Carlos headed westward at 23 mph (37 km/h), it continued to strengthen. By midday on July 15, Carlos attained its peak intensity with winds of 50 mph (85 km/h). Shortly thereafter, Carlos moved over slightly colder SST's, and a weakened trend began as a result. Early on July 16, Carlos was downgraded to a tropical depression and dissipated later that day.[2]
Tropical Depression Five-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | July 16 – July 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) |
On July 16, Tropical Depression Five formed approximately 190 mi (310 km) west-southwest of Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico. The depression tracked northwestward and did not intensify into a tropical storm. Instead, the depression dissipated later that day.[2]
Hurricane Dolores
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 17 – July 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) |
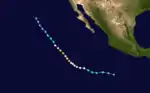
Dolores began as a tropical disturbance that developed 350 n mi south of the Guatemalan coast on July 14. Moving west at 11 mph (17 km/h) the disturbance began to intensify. By July 17, a circulation had developed in the center and the disturbance was upgraded to a tropical depression near 10.5N 103.7W. Winds increased to 40 mph (65 km/h) by 1800 UTC and the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Dolores. Dolores intensified over 85.F water as it moved around a high pressure area over the west coast of Baja California. It then was upgraded to a hurricane on July 18 at 1800 UTC. On July 19 at 0600 UTC, Dolores turned to the northwest and intensified rapidly. Satellite imagery showed Dolores with a well defined eye by 1800 UTC July 19. Winds increased near the center to 115 mph (185 km/h) by July 20 and Dolores reached its maximum intensity of 120 mph (195 km/h) on July 21. Moving 690 mi (1110 km) offshore and parallel to the Baja California coast, the cyclone began to weaken over cooler 78.F water. By July 22 it was downgraded from a hurricane to a tropical storm. The next day it was downgraded to a tropical depression near 23.3 N 127.0W. The final advisory on the cyclone was issued at 1800 UTC 23 July.[2]
Hurricane Enrique
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 17 – August 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min) |
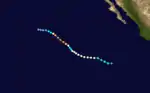
Enrique began as a tropical disturbance that developed over the open Pacific on August 17. Moving west at 10 mph (16 km/h), the disturbance began to intensify over 86.F water. By August 17 at 1800 UTC a circulation had developed about in the center, and the disturbance was upgraded to a tropical depression. The next day, the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Enrique. On the 19th of August the storm was upgraded to hurricane status, it then moved over cooler water and began to weaken to a tropical storm. By August 21, winds increased to 80 mph (130 km/h) and the storm was upgraded again to a hurricane near 16.4N, 126.7W. Enrique intensified rapidly on August 22 and reached its peak intensity of 145 mph (230 km/h) at 1200 UTC. The storm then moved over cooler waters and weakened. Enrique was downgraded to a tropical storm near 20.4N, 132.0W. By August 24 it was downgraded to a tropical depression near 21.3N 135.8W. Enrique then dissipated several hours later. The final advisory on the cyclone was issued at 1800 UTC.[2]
Hurricane Fefa
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | August 21 – August 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) |
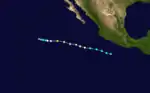
Fefa began as a tropical disturbance south-southeast of Acapulco on August 19. It then was upgraded to a tropical depression on August 21 and a tropical storm a few hours later. As Fefa moved west-northwest, winds increased to 75 mph (120 km/h) and on August 22 at 0600 UTC, Fefa was upgraded to a hurricane.[2] Fefa then started to rapidly intensify, reaching its peak intensity of 115 mph (185 km/h) on August 23 at 1200 UTC.[6] Moving to the west, Fefa accelerated to 22 mph (35 km/h) and slowed down as it started to weaken over cooler water. By August 24, winds in the center of Fefa had decreased to 75 mph (120 km/h) and the hurricane was downgraded to a tropical storm six hours later. Continuing to weaken, Fefa was downgraded to a tropical depression near 18.N, 122.7 W. The final advisory on the cyclone was issued the next day as Fefa dissipated.[2]
Tropical Depression Nine-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | September 4 – September 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) |
This depression existed on September 4.[2]
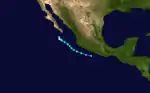
Hurricane Guillermo
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 8 – September 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min) 994 mbar (hPa) |
Guillermo originated from a tropical disturbance that formed in the Gulf of Tehuantepec on September 7. The system moved northwestward at 17 mph (27 km/h), and was upgraded to Tropical Depression Ten on September 8. The depression quickly intensified, and became a tropical storm on September 9. Guillermo was a short-lived hurricane which did not have direct impacts on land.
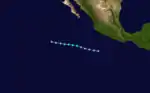
Tropical Storm Hilda
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | October 4 – October 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 994 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical disturbance developed south of Guatemala on October 1. The system intensified as it moved west over SST's of at least 82 °F (28 °C). By early on October 4, the system was classified as Tropical Depression Eleven. After forming, the depression continued west 15 mph (24 km/h) over SST's of 84 °F (29 °C). The depression eventually turned west-northwest, where it intensified into Tropical Storm Hilda on October 5. Hilda was a short-lived storm which did not affect land.
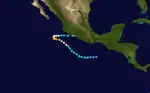
Hurricane Ignacio
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | October 23 – October 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min) 938 mbar (hPa) |
On October 22, a well-organized area of low pressure formed a few hundred miles of the coast of Guatemala. The next day, the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center upgraded the low into a depression. The system would strengthen into a tropical storm hours prior to formation. The system strengthened into a tropical storm, which was named Ignacio. On October 25, Tropical Storm Ignacio strengthened into a minimal hurricane on October 26. It quickly intensified, becoming a major hurricane a few hours later. On October 27, Ignacio reached its peak intensity with winds of up to 145 mph (230 km/h). On October 28, however, the storm began to weaken, and was downgraded into a Category 1 hurricane. On October 29, it weakened into a tropical storm. The system weakened to a depression on October 30. Ignacio made landfall on the coast of western Mexico as a tropical depression. The storm dissipated hours later after landfall, without causing any impact.[2]
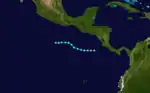
Tropical Storm Jimena
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | November 15 – November 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) |
The final tropical cyclone of the season developed from a tropical disturbance which formed 92 mi (148 km) south of Panama on November 13. The system headed west-northwest at 8 mph (13 km/h) until curving westward and speeding up to 11 mph (18 km/h) on the following day. As the disturbance intensified over SST's of 84 °F (29 °C), satellite imagery indicated that a cyclonic circulation existed. As a result, the disturbance was upgraded to Tropical Depression Thirteen while 210 mi (340 km) west-southwest of the Cabo Blanco Absolute Natural Reserve on November 15. The depression steadily intensified as it headed westward, and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Jimena later that day. On the following day, Jimena turned west-northwestward and continued to intensify. Later that day, Jimena peaked with maximum sustained winds of 65 mph (100 km/h). Also on November 16, Jimena curved briefly northwestward. After resuming its westward direction, Jimena began to weaken from SST's of 82 °F (28 °C) and cold, dry, and northerly winds from the Gulf of Tehuantepec. By early on November 18, Jimena weakened enough to be downgraded to a tropical depression. Shortly thereafter, Jimena was declared dissipated while centered 426 mi (686 km) south of Acapulco, Guerrero, Mexico.[2]
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms that formed in the eastern Pacific in 1979. This was the first time most of these names were used, except for Blanca and Dolores, which were previously used in the old four-year lists. Names that were not assigned are marked in gray.
|
|
|
The central Pacific used names and numbers from the west Pacific's typhoon list. No names were used.
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- 1979 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1979 Pacific typhoon season
- 1979 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons: 1978–79, 1979–80
References
- "Previous Tropical Systems in the Central Pacific". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2013-01-02.
- Gunther, Emil (1980). "Eastern North Pacific Tropical Cyclones of 1979". Monthly Weather Review. Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center. 108 (5): 631–641. Bibcode:1980MWRv..108..631G. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<0631:ENPTCO>2.0.CO;2.
- "Season's first 'cane hits land". The Miami News. Associated Press. June 5, 1979. p. 41. Retrieved July 3, 2010.
- United Press International (June 5, 1979). "Hurricane Andrew Hits". The Bryan Times. p. 2. Retrieved July 3, 2010.
- Staff Writer (June 5, 1979). "Hurricane Rips Mexico". Reading Eagle. p. 21. Retrieved July 3, 2010.
- "Hurricane-3 Fefa". Unisys Weather. Retrieved 2016-08-27.