Béjar
Béjar (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈbexaɾ]) is a town and municipality in the province of Salamanca, western Spain, part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. As of 2017, it had a population of 15,016.

Béjar | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
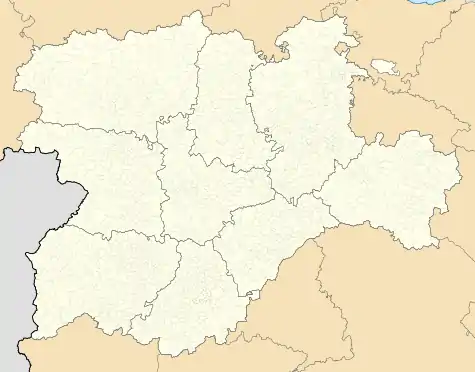 Béjar Location in Spain 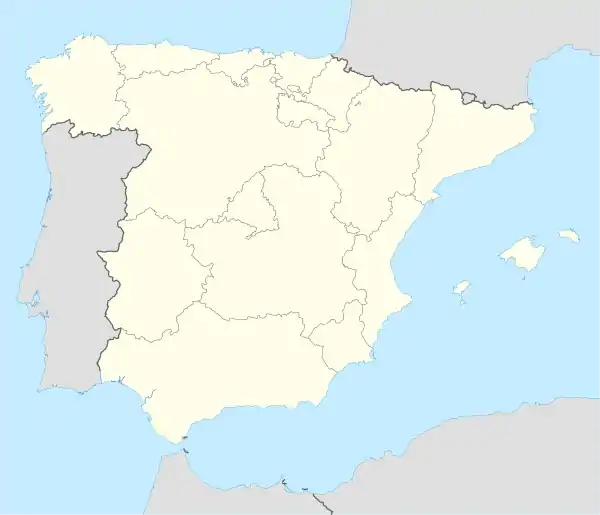 Béjar Béjar (Spain) | |
| Coordinates: 40°23′N 5°46′W | |
| Country | |
| Autonomous community | |
| Province | Salamanca |
| Comarca | Sierra de Béjar |
| Judicial district | Béjar |
| Founded | 400 BC |
| Government | |
| • Alcalde | Alejo Riñones Rico (2011) (PP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 46 km2 (18 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 959 m (3,146 ft) |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 12,961 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (730/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | bejarano |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 37700 |
| Dialing code | 923 |
| Website | www |
History
The first inhabitants of what is now Béjar were the Vettones, who settled an area to the south of the city now known as La Antigua around 400 BC. The city formed part of Roman Hispania in the beginning of the 1st century BC. In AD 713, the city was taken by Muslim Berbers (Moors) from the Visigoths and in the 11th century, it was conquered by King Alfonso VI of Castile. Following this, the walls, parts of which still stand, were constructed to repel frequent Arab incursions that took place until the end of the Reconquista.
The city was later the center of the Duchy of Béjar ruled by the powerful House of Zúñiga.
- Semana Santa's feast day 2009

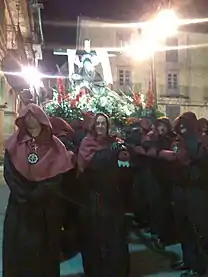
Name
The name Béjar is of pre-Roman origin. Spanish historians and archeologists do not have evidence of the name's origin, but there are documents with the forms Biclara and Biclaro,[3] of uncertain meaning. An older spelling of the city's name is Béxar, and in medieval documents, Vexar is also found. Despite the similarity between Béxar and the Spanish abeja (bee), these two words are not related.
Bexar County in the U.S. state of Texas acquired its name indirectly from this city.
Monuments
Béjar has many remarkable monuments and historical buildings:[4]
- City walls: well-preserved medieval fort
- Church of Saint James (Santiago): built in XII century, now serves as a Museum of Religious Art
- Church of Saint Mary the Great (Santa María la Mayor): built between the 12th and 17th centuries, in several different architectural styles (from Mudejar to Baroque)
- Jewish Museum David Melul: shows Béjar's Hebrew past
- Ducal Palace and Camera Obscura: an ancient fortress transformed into a palace for the Duke and Duchess of Béjar in the 16th century.
See also
References
- "Municipio:Béjar". www.lasalina.es (in Spanish). Retrieved 2017-10-28.
- Municipal Register of Spain 2018. National Statistics Institute.
- García Sánchez, Jairo Javier (12 de julio de 2004). Castilla y León y sus toponimos (II). Rinconete (Centro Virtual Cervantes).
- "Conoce Béjar – Excmo. Ayuntamiento de Béjar" (in Spanish). Retrieved 2019-01-22.
External links
- i-Béjar web portal (in Spanish)