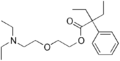
Butamirate
Butamirate (or brospamin) is a cough suppressant.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Excretion | 90% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.172 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 307.434 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
A study found it to bind to the cough center in the medulla oblongata, more specifically the dextromethorphan-binding site in guinea pig brain with high affinity.[2]
As a 2-(2-diethylaminoethoxy)ethyl ester, it is chemically related to oxeladin and pentoxyverine, which are in the same class. (Oxeladin has an additional ethyl group in its carboxylic acid, pentoxyverine has both ethyl groups of oxeladin replaced by one cyclopentyl in the same place.)
References
- Germouty J, Weibel MA (November 1990). "[Clinical comparison of butamirate citrate with a codeine-based antitussive agent]". Revue Médicale de la Suisse Romande. 110 (11): 983–6. PMID 1980027.
- Klein M, Musacchio JM (October 1989). "High affinity dextromethorphan binding sites in guinea pig brain. Effect of sigma ligands and other agents". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 251 (1): 207–15. PMID 2477524.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.