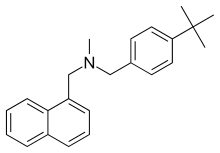
Butenafine
Butenafine, sold under the brand names Lotrimin Ultra, Mentax, and Butop (India), is a synthetic benzylamine antifungal. It is structurally related to synthetic allylamine antifungals such as terbinafine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mentax, Lotrimin Ultra |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Topical (cream) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 35–100 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H27N |
| Molar mass | 317.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Medical uses
Butenafine is indicated for the topical treatment of tinea (pityriasis) versicolor due to Malassezia furfur, as well as athlete's foot (Tinea pedis), ringworm (Tinea corporis) and jock itch (Tinea cruris) due to Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, and Trichophyton tonsurans.
It also displays superior activity against Candida albicans than terbinafine and naftifine. Butenafine demonstrates low minimum inhibitory concentrations against Cryptococcus and Aspergillus.
There is some evidence that it is effective against dermatophyte infections of the toenails, but needs to be applied daily for prolonged periods (at least one year).[1]
Typical usage
For 1% cream:
- for adults and children 12 years and older:
- wash the affected skin with soap and water and dry completely before applying
- apply once a day to affected skin for 2 weeks or as directed by a doctor
- wash hands after each use
- children under 12 years: ask a doctor
Available forms
Butenafine is typically available as a 1% topical cream.
Pharmacology
Like the allylamine antifungals, butenafine works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol by inhibiting squalene epoxidase, an enzyme responsible for the creation of sterols needed in fungal cell membranes. Lacking ergosterol, the cell membranes increase in permeability, allowing their contents to leak out. Furthermore, inhibition of squalene epoxidase leads to a toxic buildup of squalene. This double action of butenafine (increased membrane permeability and toxic buildup of squalene) makes butenafine fungicidal rather than merely fungistatic.
In addition to being an antifungal, butenafine is an anti inflammatory. Because fungal skin infections are often accompanied by significant inflammation, this is a desirable property. The fact that butenafine has intrinsic anti inflammatory properties is also desirable since it is not necessary to add cortical steroids (which decrease the ability to fight infection) to reduce inflammation.
Chemistry
Butenafine hydrochloride is an odorless white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in methanol, ethanol, and chloroform, and slightly soluble in water.
References
- Crawford F, Hollis S (July 2007). "Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD001434. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001434.pub2. PMC 7073424. PMID 17636672.