Cahul County (Romania)
Cahul County was a county of the Kingdom of Romania, in the historical region of Bessarabia, the successor of Cahul County.
Județul Cahul | |
|---|---|
County (Județ) | |
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Historic region | Bessarabia |
| Capital city (Reședință de județ) | Cahul |
| Established | 1925 |
| Ceased to exist | Administrative and Constitutional Reform in 1938 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,442 km2 (1,715 sq mi) |
| Population (1930) | |
| • Total | 196,693 |
| • Density | 44/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
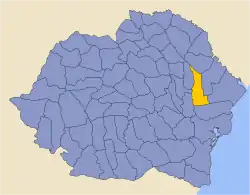
The county was located in the eastern part of Greater Romania, in the southwestern part of Bessarabia. Cahul County was bordered by the counties of Cetatea Albă and Tighina to the east, Lăpușna to the north, County, Tutova and Covurlui to the west, and Ismail to the south.
Its territory underwent changes in the north, where one third of Plasa Cantemir was for some time part of Fălciu County, and in the south, where the communes of Brînza, Colibași, Văleni, and Vulcănești were left in Cahul County, while the communes of Valea-Stejarului, Grecenii-Burlăcenilor, and Bulgărica were part of Ismail County. Plasa Dragoş-Voda, headquartered at Albota was renamed Plasa Mihai Viteazu.
Its territory is currently part of the Republic of Moldova, corresponding roughly to the districts Cahul, Cantemir, Leova, Taraclia and the Vulcănești district (dolay) from Gagauzia.
History
At the end of the Crimean War, by the Treaty of Paris (1856), Southern Bessarabia was returned by the Russian Empire to Moldavia. Southern Bessarabia was administratively organized into 3 counties: Cahul, Bolgrad and Ismail, and it was part of Moldavia and, after 1859, part of the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia (called Romania after 1866) until 1878, when by the Treaty of Berlin (1878) all three counties were ceded back to the Russian Empire in exchange for Northern Dobruja.
With the Union of Bessarabia with Romania in 1918, Cahul County returned to Romania, being formally re-established in 1925.
After the 1938 Administrative and Constitutional Reform, this county merged with the counties of Brăila, Covurlui, Fălciu, Ismail, Putna, Râmnicu Sărat, Tecuci, Tulcea and Tutova to form Ținutul Dunării.
The area of the county was occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940 and became part of the Moldavian SSR. The area returned to Romanian administration following the Axis Powers' invasion of the Soviet Union in July 1941. A military administration was established and the region's Jewish population was either executed on the spot or deported to Transnistria, where further numbers were killed.[2] As the Soviet Union's offensive pushed the Axis powers back, the area again was under Soviet control. On September 12, 1944, Romania signed the Moscow Armistice with the Allies. The Armistice, as well as the subsequent peace treaty of 1947, confirmed the Soviet-Romanian border as it was on January 1, 1941.[3][4] The area of the county, along with the rest of the Moldavian SSR, became part of the independent country of Moldova.
Population
According to the census data of 1930, the county's population was 196,693, of which 51.2% were ethnic Romanians, 17.9% Gagauz, 14.5% Bulgarians, 7.5% Russians, 4.4% Germans, 2.3% Jews, as well as other minorities.[5] From the religious point of view 92.1% of the population was Eastern Orthodox, 4.3% Lutheran, 2.3% Jewish, as well as other minorities.
Urban population
In the year 1930, the county's urban population was 17,909, of which 50.5% were ethnic Romanians, 19.6% Russians, 17.5% Jews, 1.3% Ukrainians, 1.3% Bulgarians, as well as other minorities.[5] From a religious point of view, the urban population consisted of 76.5% Eastern Orthodox, 17.5% Jewish, 4.7% Old-Style Orthodox, 0.7% Roman Catholic, as well as other minorities.
Gallery
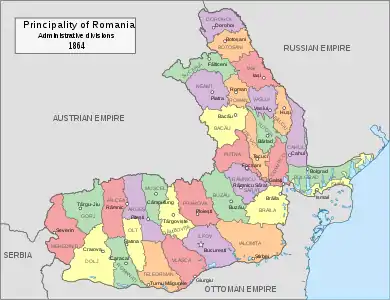 Cahul County as part of the Principality of Romania (1864–1878)
Cahul County as part of the Principality of Romania (1864–1878).jpg.webp) Cahul County as constituted in 1925
Cahul County as constituted in 1925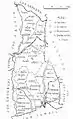 Map of Cahul County as of 1938
Map of Cahul County as of 1938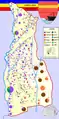 Ethnic make up of Cahul County per census of 1930
Ethnic make up of Cahul County per census of 1930
References
- Portretul României Interbelice - Județul Cahul
- James Stuart Olson; Lee Brigance Pappas; Nicholas Charles Pappas (1994). An Ethnohistorical dictionary of the Russian and Soviet empires. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 484. ISBN 9780313274978.
- "The Avalon Project : The Armistice Agreement with Rumania; September 12, 1944". avalon.law.yale.edu. Retrieved 17 March 2018.
- United States Department of State. Foreign relations of the United States, 1946. Paris Peace Conference: documents Volume IV (1946)
- Recensământul general al populației României din 29 decemvrie 1930, Vol. II, pag. 100
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Interwar Cahul County. |