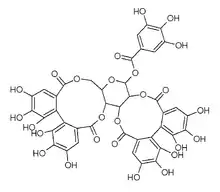
Casuarictin
Casuarictin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sanguiin H 11 Sanguiin H-11 1(beta)-O-Galloylpedunculagin 1(.beta.)-O-Galloylpedunculagin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C41H28O26 | |
| Molar mass | 936.64 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is formed from two hexahydroxydiphenic acid and one gallic acid units linked to a glucose molecule.
The molecule is formed from tellimagrandin II, itself formed from pentagalloyl glucose via oxidation. Casuarictin is transformed into pedunculagin via loss of a gallate group, and further into castalagin via glucose pyranose ring opening.
Oligomers
Sanguiin H-6 is a dimer, Lambertianin C is trimer and lambertianin D is a tetramer of casuarictin.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.