Chandigarh Airport
Chandigarh Airport (IATA: IXC, ICAO: VICG) is a custom airport which is the second busiest airport of Indian state of Punjab after Sri Guru Ram Dass Jee International Airport in Amritsar and serves the Union Territory of Chandigarh, and the cities of Mohali and Panchkula in the Indian states of Punjab and Haryana. The airport runway is located in the union territory of Chandigarh while the international terminal is located on the south side of the runway in the village of Jhiurheri, Mohali, Punjab.[5] The airport caters to six domestic airlines and connects Chandigarh to 2 international and 15 domestic destinations.
Chandigarh Airport | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Military/civil | ||||||||||
| Operator | Indian Air Force/Airports Authority of India/Chandigarh International Airport Limited | ||||||||||
| Serves | Chandigarh, Mohali, Panchkula | ||||||||||
| Location | Mohali, Punjab, India | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 314 m / 1,030 ft | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 30°40′29″N 76°47′26″E | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
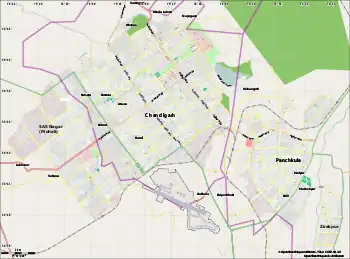 IXC  IXC | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics (April 2019 - March 2020) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
Chandigarh airport operated all its civil and commercial operations from the civil enclave of the Indian Air Force Station. Indian Airlines started operating flights from Chandigarh to Delhi in the 1970s. A new airport building was constructed in the civil enclave and was opened on 14 April 2011.[6] This air terminal was declared a customs airport on 19 August 2011, making it eligible for international flights, but no international flight ever operated from this terminal.[7]
In 2008, the Government of Punjab acquired 304.04 acres of land on the south side of the existing runway in Jheurheri village at a cost of ₹452 crore to build the new international terminal. This new terminal was completed in 2015 at a cost of ₹939 crore.[8][9][10] The Government of Punjab and the Government of Haryana each have a 24.5% stake and the Airports Authority of India holds the rest, a 51% stake, in the new terminal building.[11]
On 24 December 2015 the Mohali Industries Association filed a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the Punjab and Haryana High Court for non-operation of international flights after an amount of ₹1400 crores was spent on the airport.[12][13] After numerous hearings at Punjab and Haryana High Court and a long wait, IndiGo and Air India Express commenced flights to Dubai and Sharjah respectively from September 2016.[14][15]
Facilities
Terminal

The new terminal was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 11 September 2015.[16] This new eco-friendly terminal is one of its kind in India and was built by Larsen and Toubro.[17] The interior of the airport has plants, for a feeling of a botanical garden. It is located at the village of Jhiurheri in Punjab[18] and became operational on 19 October 2015.
The old domestic terminal will now be used for VIPs and a flying club. Construction of the new terminal included two link taxiways to the terminal and cargo complex. The terminal has four aero bridges apron for parking four in contact and eight remote parking stands for aircraft. The departures are on the first floor and arrivals on the ground floor. The first phase of the terminal covering 53,000 sq metre has a capacity of 1,600 passengers at a time and a parking space for 150 vehicles. This is not a greenfield airport but uses the runway of the present Indian air force base.[19]
There is one ATM located in the parking area, wifi inside the terminal and one duty-free shop in the departures area.[20][21] The airport facilities are operated by CHIAL (Chandigarh International Airport Limited) but the airport does not have an official website of its own.
Runway
From 2017 to 2019, the runway went through a major upgrade and repair that was completed on 9 April 2019. The expanded runway is 12,400 ft (3,779 m) long with effective take-off length of runway 10,400 ft (3,170 m).[22] Since 10 April 2019, the airport is available for 24 hour operations with CAT IIB ILS.[23]
The first night flight was launched by GoAir on October 5, 2019.[24]
Airlines and destinations
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Air India | Delhi, Leh (resumes 30 March 2021) |
| Air India Express | Delhi, Sharjah |
| Air Taxi India | Hisar[25] |
| Alliance Air | Delhi, Dharamshala, Kullu[26] |
| GoAir | Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Delhi, Mumbai, Srinagar |
| IndiGo | Ahmedabad,[27] Bangalore, Chennai, Dehradun (begins 28 March 2021),[28] Delhi, Goa, Hyderabad, Indore (begins 28 March 2021),[28] Jaipur,[29] Jodhpur (begins 28 March 2021),[28] Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai, Patna, Pune, Srinagar[30][27] |
| Vistara | Delhi, Mumbai |
Location and surface transport connectivity

The new terminal is located 14 km (8.7 mi) from Chandigarh City centre in Sector 17. Chandigarh Transport Undertaking (CTU) Route 38 and 36 operates public AC bus to Sector 17, PGI, Panjab University and to Interstate Bus Terminal in Sector 43 from the airport. CTU has its own dedicated mobile app called CTU bus guide from which all the routes and time of buses to and from the airport can be obtained.[31] Chandigarh Interstate Bus terminal located 10 km from airport in Sector 43 operates direct bus services to all major cities in Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
Accidents and incidents
- On 20 September 2014, an Antonov 32 transport plane operated by the Indian Air Force was damaged beyond repair while landing at the Chandigarh International Airport. Upon landing the right wing broke off and the airplane rolled over and came to rest inverted, in the grass next to the runway. The left wing was also severed and the Number 1 propeller broke away from the engine. This led to a fire break out, but was quickly contained. A few people on board suffered minor burn injuries.[32]
See also
References
- "Chandigarh Airport Report" (PDF). Airport Authority of India. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 May 2018. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- https://www.aai.aero/sites/default/files/traffic-news/Mar2k20Annex3.pdf
- https://www.aai.aero/sites/default/files/traffic-news/Mar2k20Annex4.pdf
- https://www.aai.aero/sites/default/files/traffic-news/Mar2k20Annex2.pdf
- India (10 September 2015). "Land gone, Jheurheri villagers set up hotels near Chandigarh airport". The Indian Express. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Chandigarh Stories". Tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Chandigarh Stories". www.tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- "PM Narendra Modi inaugurates new terminal at Chandigarh airport - The Economic Times". indiatimes.com.
- http://gmada.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/RTIGMADA.pdf
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Main News". www.tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- "PM inaugurates new terminal at Chandigarh airport". Trinuneindia News Service. Retrieved 17 September 2016.
- The Tribune Chandigarh, Tribune News. "Mohali Industries Assn files PIL against Centre". tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- The Tribune Chandigarh, Tribune News. "Shut airport, if you can't make it operational: HC". tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- "Air India Express launches services to Dubai and Sharjah - Gulf Business". Gulf Business. 16 October 2016. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- "IndiGo to start Chandigarh-Dubai flights from September". www.businesstoday.in. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- "PM Modi inaugrates [sic] Chandigarh International Airport". The Times of India. 11 September 2015. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- "India Has a New Eco-Friendly Airport Terminal. And It Is More than Just Amazing! - The Better India". The Better India. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- "PM Narendra Modi inaugurates new terminal at Chandigarh airport". businesstoday.in.
- "Punjabnewsline.com". Punjabnewsline.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- NYOOOZ (25 June 2017). "Chandigarh International Airport: Two years after inauguration, new terminal to get Wi-Fi facility | CHANDIGARH NYOOOZ". Nyoooz.com. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- Balachandran, Vappala (19 July 2018). "Airport gets another duty-free shop". Tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- "ixc". Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- "IXC now 24*7". Tribune India. 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chandigarh/night-flight-from-october-5-in-chandigarh/articleshow/71162636.cms
- "Haryana Launches Air Taxi Services From Chandigarh To Hisar". NDTV. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- "Air India and Alliance Air schedule list". airindia.in. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- "New Flights Information, Status & Schedule | IndiGo". www.goindigo.in.
- "Chandigarh to have direct flights to Dehradun, Indore, Jodhpur, Jammu". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- "Jaipur to get new flights to Goa and Chandigarh". Times of India. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- "IndiGo flight schedules". goindigo.in.
- http://chdctu.gov.in/PDF/cturoutes.pdf
- "ASN Aircraft accident Antonov 32RE K2757 Chandigarh Airport (IXC)". Aviation-safety.net. 20 September 2014. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
