Deadmond Glacier
Deadmond Glacier (72°1′S 96°27′W) is a glacier about 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing from the east side of Evans Peninsula on Thurston Island into Cadwalader Inlet. It was discovered by the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Commander Robert B. Deadmond, executive officer of USS Burton Island, forming part of this expedition.[1]
| Deadmond Glacier | |
|---|---|
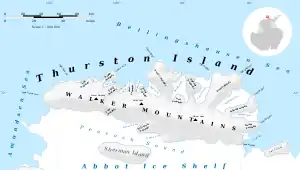 Map of Thurston Island | |
 Location of Deadmond Glacier in Antarctica | |
| Location | Ellsworth Land |
| Coordinates | 72°01′S 96°27′W |
| Length | 6 nautical miles (11 km; 6.9 mi) |
| Thickness | unknown |
| Terminus | Cadwalader Inlet |
| Status | unknown |

Satellite image of Thurston Island.
Maps
- Thurston Island – Jones Mountains. 1:500000 Antarctica Sketch Map. US Geological Survey, 1967.
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.
References
- "Deadmond Glacier". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
 This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Deadmond Glacier". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Deadmond Glacier". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
| Types | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomy | |||||||
| Processes | |||||||
| Measurements | |||||||
| Volcanic relations | |||||||
| Landforms |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.