Tarn (lake)
A tarn (or corrie loch) is a proglacial mountain lake, pond or pool, formed in a cirque excavated by a glacier. A moraine may form a natural dam below a tarn.[1]
Etymology

The word is derived from the Old Norse word tjörn ("a small mountain lake without tributaries") meaning pond. In parts of Northern England - predominantly Cumbria but also areas of North Lancashire and North Yorkshire - 'tarn' is widely used as the name for small lakes or ponds, regardless of their location and origin (e.g. Talkin Tarn, Urswick Tarn, Malham Tarn).[2] Similarly, in Scandinavian languages, a tjern or tjärn, tärn or tjørn is a small natural lake, often in a forest or with vegetation closely surrounding it or growing into the tarn.
The specific technical use for a body of water in a glacial corrie comes from high number of tarns found in corries in the Lake District, an upland area in Cumbria.[3] Nonetheless, there are many more bodies of water called 'tarn' in the Lake District than actually fit this technical use.
Formation
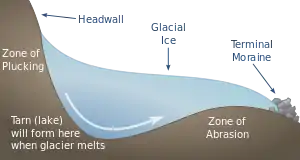
Tarns are the result of small glaciers called cirques, also known as corries. Cirques form in hollows on mountainsides near the firn line. Eventually, the hollow in which a cirque forms may become a large bowl shape in the side of the mountain, caused by weathering by ice segregation, and as well as being eroded by plucking. The basin will become deeper as it continues to be eroded by ice segregation and abrasion.[4][5] A cirque typically will be partially surrounded on three sides by steep cliffs, with a fourth side a form of morraine constructed from glacial till, which forms the lip, threshold or sill,[6] from which either a stream or glacier will flow away from the cirque.
Tarns form from the melting of the cirque glacier. They may either be seasonal features as supraglacial lakes, or permanent features which form in the hollows left by cirques in formerly glaciated areas. [3]
Gallery

 Veľké Hincovo, the largest and deepest tarn in Slovakia
Veľké Hincovo, the largest and deepest tarn in Slovakia_N._Cascades_Nat._Park%252C_Pickett_Range_WA.jpg.webp) Lousy Lake (tarn) in North Cascades National Park, Picket Range, Washington, USA
Lousy Lake (tarn) in North Cascades National Park, Picket Range, Washington, USA


 The Dreadful Lake (tarn), Rila Mountain, Bulgaria
The Dreadful Lake (tarn), Rila Mountain, Bulgaria
 Marichini lakes (tarns), the origin of the Maritsa river seen from Musala peak, Rila Mountain, Bulgaria
Marichini lakes (tarns), the origin of the Maritsa river seen from Musala peak, Rila Mountain, Bulgaria Sea Lion Tarn on Livingston Island in Antarctica
Sea Lion Tarn on Livingston Island in Antarctica
See also
References
- "Illustrated Glossary of Alpine Glacial Landforms". Archived from the original on 2007-08-11. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- "Fresh Water Tarns". Cumbria Wildlife Trust. Archived from the original on 2007-06-27. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Evans, Ian; Cox, Nick (1995). "The form of glacial cirques in the English Lake District, Cumbria". Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie. 2 (39): 175-202.
- Johnny W. Sanders; Kurt M. Cuffey; Jeffrey R. Moore; Kelly R. MacGregor; Jeffrey L. Kavanaugh (2012). "Periglacial weathering and headwall erosion in cirque glacier bergschrunds". Geology. 40 (9): 779–782. Bibcode:2012Geo....40..779S. doi:10.1130/G33330.1. S2CID 128580365.
- Rempel, A.W.; Wettlaufer, J.S.; Worster, M.G. (2001). "Interfacial Premelting and the Thermomolecular Force: Thermodynamic Buoyancy". Physical Review Letters. 87 (8): 088501. Bibcode:2001PhRvL..87h8501R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.088501. PMID 11497990. S2CID 10308635.
- Evans, I.S. (1971). "8.11(i) The geomorphology and Morphometry of Glacial and Nival Areas". In Chorley R.J. & Carson M.A. (ed.). Introduction to fluvial processes. University paperbacks. 407. Routledge. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-416-68820-7. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
External links
 Media related to Tarn (lake) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tarn (lake) at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of tarn at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of tarn at Wiktionary
