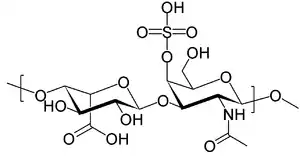
Dermatan sulfate
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.305 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H21NO15S |
| Molar mass | 475.37 g·mol−1 |
| | |
It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B,[1] although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C14H21NO15S.
Function
Dermatan sulfate may have roles in coagulation, cardiovascular disease, carcinogenesis, infection, wound repair, maintains the shape of galactosamine 4-sulfate skin and fibrosis.[1]
Pathology
Dermatan sulfate accumulates abnormally in several of the mucopolysaccharidosis disorders.
An excess of dermatan sulfate in the mitral valve is characteristic of myxomatous degeneration of the leaflets leading to redundancy of valve tissue and ultimately, mitral valve prolapse (into the left atrium) and insufficiency. This chronic prolapse occurs mainly in women over the age of 60, and can predispose the patient to mitral annular calcification. Mitral valve insufficiency can lead to eccentric (volume dependent or dilated) hypertrophy and eventually left heart failure if untreated.
See also
References
- Trowbridge JM, Gallo RL (September 2002). "Dermatan sulfate: new functions from an old glycosaminoglycan". Glycobiology. 12 (9): 117R–25R. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwf066. PMID 12213784.
External links
- Dermatan+sulfate at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)