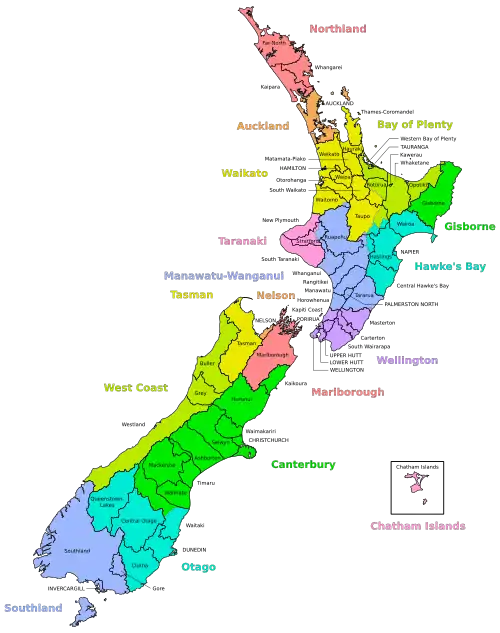
Districts of New Zealand
A district in New Zealand is a territorial authority area governed by a district council as a second-tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. They were formed as a result of local government reforms in 1989. There are 53 districts in New Zealand, and they do not include the 12 city councils, Auckland Council, or Chatham Islands Council. District councils serve a combination of rural and urban communities, while city councils administer the larger urban areas. Three districts (Gisborne, Tasman and Marlborough) are unitary authorities also performing the functions of a regional council.
Districts are not subdivisions of regions, and some of them fall within more than one region. Taupo District has the distinction of straddling the boundaries of four different regions. Regional council areas are based on water catchment areas, whereas district council areas are based on community of interest and road access. Regional councils are responsible for the administration of many environmental and public transport matters, while the district councils administer local roads and reserves, sewerage, building consents, the land use and subdivision aspects of resource management, and other local matters. Some activities are delegated to council-controlled organisations.
Districts
There are currently 53 districts:[1]
Bay of Plenty Region (4)
Hawke's Bay Region (3)
Manawatū-Whanganui Region (4)
Northland Region (3)
Taranaki Region (2)
Waikato Region (7)
Wellington Region (4)
Mixed (6)
- Rangitikei District (Manawatū-Whanganui: 86.37%; Hawke's Bay: 13.63%)
- Rotorua Lakes (Bay of Plenty: 61.52%; Waikato: 38.48%)
- Stratford District (Taranaki: 68.13%; Manawatū-Whanganui: 31.87%)
- Tararua District (Manawatū-Whanganui: 98.42%; Wellington: 1.58%)
- Taupo District (Waikato: 73.74%; Bay of Plenty: 14.31%; Hawke's Bay: 11.26%; Manawatū-Whanganui: 0.69%)
- Waitomo District (Waikato: 94.87%; Manawatū-Whanganui: 5.13%)
Unitary authority (1)
Canterbury Region (8)
Otago Region (3)
Southland Region (2)
West Coast Region (3)
Mixed (1)
- Waitaki District (Canterbury: 59.61%; Otago: 40.39%)
Unitary authorities (2)
Notes:
- Kaikoura District was transferred from the Nelson-Marlborough Region to the Canterbury Region in 1992.
- The Banks Peninsula District became a part of Christchurch as a result of 2005 referendum.
- Franklin District, Papakura District, and Rodney District no longer exist as of 2010. They became part of other districts and the Auckland Region.
See also
References
- "Districts". Department of Internal Affairs. Retrieved 2 June 2011.