Dumont d'Urville Station
The Dumont d'Urville Station (French: Base antarctique Dumont-d'Urville) is a French scientific station in Antarctica on Île des Pétrels, archipelago of Pointe-Géologie in Adélie Land. It is named after explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville, whose expedition landed on Débarquement Rock in the Dumoulin Islands at the northeast end of the archipelago on January 21, 1840. It is operated by the "French Polar Institute Paul-Émile Victor", a joint operation of French public and para-public agencies. It is the capital of Adélie Land.
Dumont d'Urville Station | |
|---|---|
| Base antarctique Dumont-d'Urville | |
 Dumont d'Urville Station | |
 Flag | |
 Dumont d'Urville Station Location of Dumont d'Urville Station in Antarctica | |
| Coordinates: 66°39′46″S 140°00′07″E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Archipelago of Pointe-Géologie |
| Location in Antarcticia | Adélie Land |
| Administered by | French Polar Institute Paul-Émile Victor |
| Established | 12 January 1956 |
| Named for | Jules Dumont d'Urville |
| Type | All-year round |
| Period | Annual |
| Status | Operational |
| Website | www.institut-polaire.fr (in French) |
D10 Skiway | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Private | ||||||||||
| Location | Dumont d'Urville Station | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 662 ft / 202 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 66°42′01″S 139°49′41″E | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 D10 Skiway Location of airfield in Antarctica | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History

A pioneering French Antarctic research station, Port Martin, located 62 kilometres (39 mi) east of D'Urville, was destroyed by fire on the night of January 23, 1952, without death or injury. In 1952, a small base was built on Île des Pétrels to study a rookery of emperor penguins. This base was called Base Marret. As the main base Port Martin was a total loss, Base Marret was chosen as overwintering site for 1952/1953. The new main base, Dumont D'Urville station, was built on the same island and opened on January 12, 1956, to serve as the centre for French scientific research during the Antarctic International Geophysical Year 1957/1958. The station has remained in active use ever since.
The station allows 30-40 people to come ashore at one time. Ice and strong katabatic winds often prevent landings, either by boat or by helicopter. The station can accommodate about 30 winter-overs and 120 during the summer. The icebreaker ship L'Astrolabe carries supplies and personnel to the station from the port of Hobart, Tasmania. It does 5 round-trips between November and March.
The Academy Award-winning documentary film La Marche de l'empereur, released in English as March of the Penguins, was filmed in the region around this base.
Wildlife
One of the main interests of the base is the study of wildlife, notably the emperor penguins. In the summer, the rocks near the base serve as a refuge for the Adélie penguin, which comes here to reproduce. Skua, snow petrel, giant petrel, Cape petrel also spend the summer near the base. In the winter, only emperor penguins stay to reproduce. However, around August, giant petrels return to feed on emperor penguin chicks.
Some marine animals are equally present despite the negative temperature of the water. Among rare visitors to the archipelago, there are other species of penguins, orcas, and rorquals.
Activity
The base Dumont d'Urville is first and foremost a scientific base, even if nowadays the transportation of supplies to the Concordia Station (operated together with Italian researchers) represents an important part of the activity of the base.
Chemistry of the atmosphere
The laboratory in atmospheric chemistry of the base is used to analyse, among other things, sulfur compounds present in the atmosphere.
Geophysics
Nowadays, the study of geophysics is less present in the base. Nonetheless, several tools are still in use, notably a tide gauge, a cosmic rays detector, a GPS to measure the dip of the Antarctica into the upper mantle, and a lidar, which allows the analysis of the ozone depletion and the ozone holes.
Logistic
The proper functioning of the base and supplying Concordia require an important logistic, especially in the summer. Technicians, including electricians, plumbers, mechanics for the electric plant and auto mechanics are essential for the good functioning of the base all along the year.
Climate
Dumont d'Urville Station has a polar ice cap climate (EF) with year round wintry weather conditions.
| Climate data for Dumont d'Urville Station (extremes 1950–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
6.4 (43.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.7 (47.7) |
0.0 (32.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
0.5 (32.9) |
0.3 (32.5) |
0.3 (32.5) |
1.7 (35.1) |
4.7 (40.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
11.0 (51.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.0 (33.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−14.5 (5.9) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.3 (29.7) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
−15.2 (4.6) |
−17.3 (0.9) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−17.4 (0.7) |
−16.2 (2.8) |
−13.2 (8.2) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−11.1 (12.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.6 (25.5) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−11.3 (11.7) |
−14.8 (5.4) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−20.0 (−4.0) |
−20.0 (−4.0) |
−20.3 (−4.5) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −10.8 (12.6) |
−17.3 (0.9) |
−25.0 (−13.0) |
−26.1 (−15.0) |
−32.5 (−26.5) |
−34.9 (−30.8) |
−34.4 (−29.9) |
−37.4 (−35.3) |
−36.1 (−33.0) |
−37.2 (−35.0) |
−21.0 (−5.8) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−37.4 (−35.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 9 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 102 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67 | 63 | 65 | 66 | 65 | 61 | 65 | 66 | 63 | 56 | 54 | 63 | 63 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 282.1 | 206.2 | 155.0 | 105.0 | 40.3 | 12.0 | 15.5 | 68.2 | 150.0 | 251.1 | 315.0 | 359.6 | 1,960 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.1 | 7.3 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 5.0 | 8.1 | 10.5 | 11.6 | 5.4 |
| Source 1: Deutscher Wetterdienst[2] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[3] | |||||||||||||
Gallery
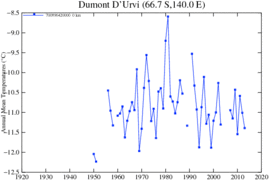 Climate graph of 1950-2012 air average temperatures at D'Urville Station
Climate graph of 1950-2012 air average temperatures at D'Urville Station A colony of Adélie penguins
A colony of Adélie penguins
See also
References
- "S10 Skiway". Airport Nav Finder. Retrieved October 15, 2018.
- "Klimatafel von Dumont d'Urville / Adélie-Land (Frankreich) / Antarktis" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- "Station Dumont d'Urville" (in French). Météo Climat. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dumont d'Urville Station. |
- (in French) Official website IPEV Institut Polaire Français Paul Emilie Victor
- (in French) Terre Adélie - Dumont d'Urville Station, site of Samuel Blanc
- (in French) Base Dumont d'Urville site from Ifremer
- (in French) l'Astrolabe
- A winter at the station
- COMNAP Antarctic Facilities
- COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map
.svg.png.webp)