Elongated square pyramid
In geometry, the elongated square pyramid is one of the Johnson solids (J8). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by elongating a square pyramid (J1) by attaching a cube to its square base. Like any elongated pyramid, it is topologically (but not geometrically) self-dual.
| Elongated square pyramid | |
|---|---|
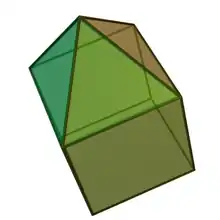 | |
| Type | Johnson J7 - J8 - J9 |
| Faces | 4 triangles 1+4 squares |
| Edges | 16 |
| Vertices | 9 |
| Vertex configuration | 4(43) 1(34) 4(32.42) |
| Symmetry group | C4v, [4], (*44) |
| Rotation group | C4, [4]+, (44) |
| Dual polyhedron | self |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |

A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.[1]
Formulae
The following formulae for the height (), surface area () and volume () can be used if all faces are regular, with edge length :[2]
Dual polyhedron
The dual of the elongated square pyramid has 9 faces: 4 triangular, 1 square and 4 trapezoidal.
| Dual elongated square pyramid | Net of dual |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
The elongated square pyramid can form a tessellation of space with tetrahedra,[3] similar to a modified tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb.
See also
References
- Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
- Sapiña, R. "Area and volume of the Johnson solid J8". Problemas y ecuaciones (in Spanish). ISSN 2659-9899. Retrieved 2020-08-28.
- http://woodenpolyhedra.web.fc2.com/J8.html