Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile.[1]
Nomenclature
A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound 1,2-epoxyheptane, which can also be called 1,2-heptene oxide.
A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an epoxy, but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy groups that remain unreacted in the formation of the resin).
Synthesis
The dominant epoxides industrially are ethylene oxide and propylene oxide, which are produced respectively on the scales of approximately 15 and 3 million tonnes/year.[2]
Heterogeneously catalyzed oxidation of alkenes
The epoxidation of ethylene involves its reaction of oxygen according to the following stoichiometry:
- 7 H2C=CH2 + 6 O2 → 6 C2H4O + 2 CO2 + 2 H2O
The direct reaction of oxygen with alkenes is useful only for this epoxide. Modified heterogeneous silver catalysts are typically employed.[3] Other alkenes fail to react usefully, even propylene, though TS-1 supported Au catalysts can perform propylene epoxidation selectively.[4]
Olefin (alkene) oxidation using organic peroxides and metal catalysts
Aside from ethylene oxide, most epoxides are generated by treating alkenes with peroxide-containing reagents, which donate a single oxygen atom. Safety considerations weigh on these reactions because organic peroxides are prone to spontaneous decomposition or even combustion.
Metal complexes are useful catalysts for epoxidations involving hydrogen peroxide and alkyl hydroperoxides. Peroxycarboxylic acids, which are more electrophilic, convert alkenes to epoxides without the intervention of metal catalysts. In specialized applications, other peroxide-containing reagents are employed, such as dimethyldioxirane. Depending on the mechanism of the reaction and the geometry of the alkene starting material, cis and/or trans epoxide diastereomers may be formed. In addition, if there are other stereocenters present in the starting material, they can influence the stereochemistry of the epoxidation. Metal-catalyzed epoxidations were first explored using tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP).[5] Association of TBHP with the metal (M) generates the active metal peroxy complex containing the MOOR group, which then transfers an O center to the alkene.[6]
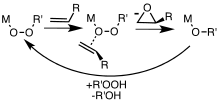 Simplified mechanism for metal-catalyzed epoxidation of alkenes with peroxide (ROOH) reagents.
Simplified mechanism for metal-catalyzed epoxidation of alkenes with peroxide (ROOH) reagents.
Organic peroxides are used for the production of propylene oxide from propylene. Catalysts are required as well. Both t-butyl hydroperoxide and ethylbenzene hydroperoxide can be used as oxygen sources.[7]
Olefin peroxidation using peroxycarboxylic acids
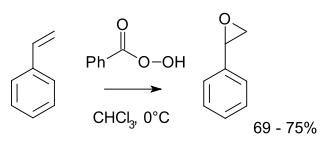
More typically for laboratory operations, the Prilezhaev reaction is employed.[8][9] This approach involves the oxidation of the alkene with a peroxyacid such as m-CPBA. Illustrative is the epoxidation of styrene with perbenzoic acid to styrene oxide:[10]
The reaction proceeds via what is commonly known as the "Butterfly Mechanism".[11] The peroxide is viewed as an electrophile, and the alkene a nucleophile. The reaction is considered to be concerted (the numbers in the mechanism below are for simplification). The butterfly mechanism allows ideal positioning of the O-O sigma star orbital for C-C Pi electrons to attack.[12] Because two bonds are broken and formed to the epoxide oxygen, this is formally an example of a coarctate transition state.
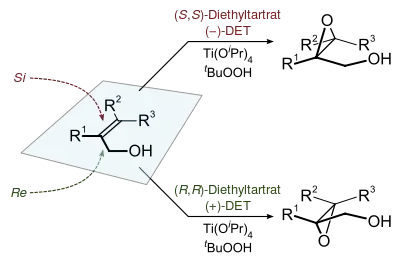
Hydroperoxides are also employed in catalytic enantioselective epoxidations, such as the Sharpless epoxidation and the Jacobsen epoxidation. Together with the Shi epoxidation, these reactions are useful for the enantioselective synthesis of chiral epoxides. Oxaziridine reagents may also be used to generate epoxides from alkenes.
Homogeneously catalysed asymmetric epoxidations
Arene oxides are intermediates in the oxidation of arenes by cytochrome P450. For prochiral arenes (naphthalene, toluene, benzoates, benzopyrene), the epoxides are often obtained in high enantioselectivity.
Chiral epoxides can often be derived enantioselectively from prochiral alkenes. Many metal complexes give active catalysts, but the most important involve titanium, vanadium, and molybdenum.[13][14]
The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is one of the premier enantioselective chemical reactions. It is used to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols.[15][16]
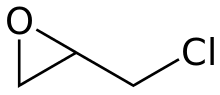
Intramolecular SN2 substitution
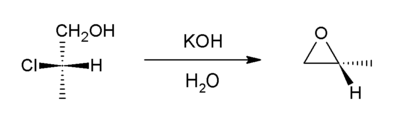
This method involves dehydrohalogenation. It is a variant of the Williamson ether synthesis. In this case, an alkoxide ion intramolecularly displaces chloride. The precursor compounds are called halohydrins and can be generated through halohydration of an alkene. [18] Starting with propylene chlorohydrin, most of the world's supply of propylene oxide arises via this route.[7]
An intramolecular epoxide formation reaction is one of the key steps in the Darzens reaction.
In the Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction epoxides are generated from carbonyl groups and sulfonium ylides. In this reaction, a sulfonium is the leaving group instead of chloride.
Nucleophilic epoxidation
Electron-deficient olefins, such as enones and acryl derivatives can be epoxidized using nucleophilic oxygen compounds such as peroxides. The reaction is a two-step mechanism. First the oxygen performs a nucleophilic conjugate addition to give a stabilized carbanion. This carbanion then attacks the same oxygen atom, displacing a leaving group from it, to close the epoxide ring.
Biosynthesis
Epoxides are uncommon in nature. They arise usually via oxygenation of alkenes by the action of cytochrome P450.[19] (but see also the short-lived Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids which act as signalling molecules.[20] and similar Epoxydocosapentaenoic acids, and Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids.)
Reactions
Ring-opening reactions dominate the reactivity of epoxides.
Hydrolysis and addition of nucleophiles
 Two pathways for the hydrolysis of an epoxide.
Two pathways for the hydrolysis of an epoxide.
Alcohols, water, amines, thiols and many other reagents add to epoxides. This reaction is the basis of two commercial applications, the formation of epoxy glues and the production of glycols.[17] Under acidic conditions, nucleophilic addition is affected by steric effects, as normally seen for SN2 reactions, as well as the stability of emerging carbocation (as normally seen for SN1 reactions). Hydrolysis of an epoxide in presence of an acid catalyst generates the glycol.
Polymerization and oligomerization
Polymerization of epoxides gives polyethers. For example ethylene oxide polymerizes to give polyethylene glycol, also known as polyethylene oxide. The reaction of an alcohol or a phenol with ethylene oxide, ethoxylation, is widely used to produce surfactants:[21]
- ROH + n C2H4O → R(OC2H4)nOH
With anhydrides, epoxides give polyesters.[22]
Deoxygenation
Epoxides can be deoxygenated using oxophilic reagents. This reaction can proceed with loss or retention of configuration.[23] The combination of tungsten hexachloride and n-butyllithium gives the alkene.[24]
Other reactions
- Reduction of an epoxide with lithium aluminium hydride or aluminium hydride produces the corresponding alcohol.[25] This reduction process results from the nucleophilic addition of hydride (H−).
- Reductive cleavage of epoxides gives β-lithioalkoxides.[26]
- Reduction with tungsten hexachloride and n-butyllithium generates the alkene[27]
- Epoxides undergo ring expansion reactions, illustrated by the insertion of carbon dioxide to give cyclic carbonates.
- When treated with thiourea, epoxides convert to the episulfide, which are called thiiranes.
Uses
- Illustrative epoxides
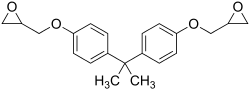 Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether is a component in common household "epoxy".
Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether is a component in common household "epoxy".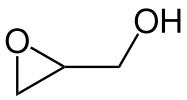 The chemical structure of the epoxide glycidol, a common chemical intermediate.
The chemical structure of the epoxide glycidol, a common chemical intermediate.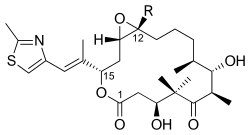 Epothilones are naturally occurring epoxides.
Epothilones are naturally occurring epoxides.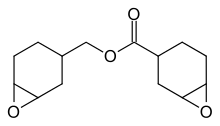 3,4-Epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3’,4’-epoxycyclohexane carboxylate, precursor to coatings.[28]
3,4-Epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3’,4’-epoxycyclohexane carboxylate, precursor to coatings.[28]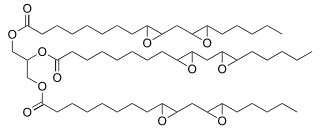 Epoxidized linolein, a major component of epoxidized soybean oil (ESBO), a commercially important plasticizer.
Epoxidized linolein, a major component of epoxidized soybean oil (ESBO), a commercially important plasticizer. Benzene oxide exists in equilibrium with the oxepin isomer.
Benzene oxide exists in equilibrium with the oxepin isomer.
Ethylene oxide is widely used to generate detergents and surfactants by ethoxylation. Its hydrolysis affords ethylene glycol. It is also used for sterilisation of medical instruments and materials.
The reaction of epoxides with amines is the basis for the formation of epoxy glues and structural materials. A typical amine-hardener is triethylenetetramine (TETA).
Safety
Epoxides are alkylating agents, making many of them highly toxic.[29]
References
- Guenter Sienel; Robert Rieth; Kenneth T. Rowbottom. "Epoxides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_531.
- Siegfried Rebsdat, Dieter Mayer "Ethylene Oxide" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_117 Article Online Posting Date: March 15, 2001.
- Sajkowski, D. J.; Boudart, M. (1987). "Structure Sensitivity of the Catalytic Oxidation of Ethene by Silver". Catalysis Reviews. 29 (4): 325–360. doi:10.1080/01614948708078611.
- Nijhuis, T. Alexander; Makkee, Michiel; Moulijn, Jacob A.; Weckhuysen, Bert M. (1 May 2006). "The Production of Propene Oxide: Catalytic Processes and Recent Developments". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 45 (10): 3447–3459. doi:10.1021/ie0513090. hdl:1874/20149.
- Indictor N., Brill W. F. (1965). "Metal Acetylacetonate Catalyzed Epoxidation of Olefins with t-Butyl Hydroperoxide". J. Org. Chem. 30 (6): 2074. doi:10.1021/jo01017a520.
- Thiel W. R. (1997). "Metal catalyzed oxidations. Part 5. Catalytic olefin epoxidation with seven-coordinate oxobisperoxo molybdenum complexes: a mechanistic study". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 117: 449–454. doi:10.1016/S1381-1169(96)00291-9.
- Dietmar Kahlich, Uwe Wiechern, Jörg Lindner “Propylene Oxide” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002 by Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_239
- March, Jerry. 1985. Advanced Organic Chemistry, Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-85472-7.
- Nikolaus Prileschajew (1909). "Oxydation ungesättigter Verbindungen mittels organischer Superoxyde" [Oxidation of unsaturated compounds by means of organic peroxides]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 42 (4): 4811–4815. doi:10.1002/cber.190904204100.
- Harold Hibbert and Pauline Burt (1941). "Styrene Oxide". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 494
- Paul D. Bartlett (1950). "Recent work on the mechanisms of peroxide reactions". Record of Chemical Progress. 11: 47–51.
- John O. Edwards (1962). Peroxide Reaction Mechanisms. Interscience, New York. pp. 67–106.
- Berrisford D. J., Bolm C., Sharpless K. B. (2003). "Ligand-Accelerated Catalysis". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 95: 1059–1070. doi:10.1002/anie.199510591.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sheldon R. A. (1980). "Synthetic and mechanistic aspects of metal-catalysed epoxidations with hydroperoxides". Journal of Molecular Catalysis. 1: 107–206. doi:10.1016/0304-5102(80)85010-3.
- Katsuki, T.; Sharpless, K. B. (1980). "The first practical method for asymmetric epoxidation". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102 (18): 5974–5976. doi:10.1021/ja00538a077.
- Hill, J. G.; Sharpless, K. B.; Exon, C. M.; Regenye, R. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol. 7, p. 461 (1990); Vol. 63, p. 66 (1985). (Article Archived 2013-09-27 at the Wayback Machine)
- Pham, Ha Q.; Marks, Maurice J. (2005). "Epoxy Resins". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_547.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Koppenhoefer, B.; Schurig, V. (1993). "(R)-Alkyloxiranes of High Enantiomeric Purity from (S)-2-Chloroalkanoic Acids via (S)-2-Chloro-1-Alkanols: (R)-Methyloxirane". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 8, p. 434
- Thibodeaux C. J. (2012). "Enzymatic Chemistry of Cyclopropane, Epoxide, and Aziridine Biosynthesis". Chem. Rev. 112: 1681–1709. doi:10.1021/cr200073d. PMC 3288687.
- Boron WF (2003). Medical Physiology: A Cellular And Molecular Approach. Elsevier/Saunders. p. 108. ISBN 978-1-4160-2328-9.
- Kosswig, Kurt (2002). "Surfactants". In Elvers, Barbara; et al. (eds.). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim, GER: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_747. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Julie M. Longo; Maria J. Sanford; Geoffrey W. Coates (2016). "Ring-Opening Copolymerization of Epoxides and Cyclic Anhydrides with Discrete Metal Complexes: Structure–Property Relationships". Chem. Rev. 116 (24): 15167–15197. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00553. PMID 27936619.
- Takuya Nakagiri, Masahito Murai, and Kazuhiko Takai (2015). "Stereospecific Deoxygenation of Aliphatic Epoxides to Alkenes under Rhenium Catalysis". Org. Lett. 17: 3346–3349. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b01583.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- K. Barry Sharpless, Martha A. Umbreit (1981). "Deoxygenation of Epoxides with Lower Valent Tungsten Halides: trans-Cyclododecene". Org. Synth. 60: 29. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.060.0029.
- Bruce Rickborn and Wallace E. Lamke (1967). "Reduction of epoxides. II. The lithium aluminum hydride and mixed hydride reduction of 3-methylcyclohexene oxide". J. Org. Chem. 32 (3): 537–539. doi:10.1021/jo01278a005.
- B. Mudryk; T. Cohen (1995). "1,3-Diols From Lithium Β-lithioalkoxides Generated By The Reductive Lithiation Of Epoxides: 2,5-dimethyl-2,4-hexanediol". Org. Synth. 72: 173. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.072.0173.
- K. Barry Sharpless, Martha A. Umbreit, Marjorie T. Nieh, Thomas C. Flood (1972). "Lower valent tungsten halides. New class of reagents for deoxygenation of organic molecules". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (18): 6538–6540. doi:10.1021/ja00773a045.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sasaki, Hiroshi (February 2007). "Curing properties of cycloaliphatic epoxy derivatives". Progress in Organic Coatings. 58 (2–3): 227–230. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2006.09.030.
- Niederer, Christian; Behra, Renata; Harder, Angela; Schwarzenbach, René P.; Escher, Beate I. (2004). "Mechanistic approaches for evaluating the toxicity of reactive organochlorines and epoxides in green algae". Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 23 (3): 697–704. doi:10.1897/03-83. PMID 15285364.