Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether
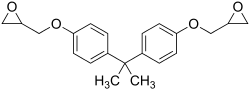
Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (commonly abbreviated BADGE or DGEBA) is an organic compound used as constituent of epoxy resins. The compound is a colorless solid (commercial samples can appear yellow) that melts slightly above room temperature.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[[4-[2-[4-(Oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)phenyl]propan-2-yl]phenoxy]methyl]oxirane | |
| Other names
Diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A; 2,2-Bis(4-glycidyloxyphenyl)propane; Epoxide A | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | BADGE; DGEBA |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.294 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | C019273 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24O4 | |
| Molar mass | 340.419 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation and reactions
It is prepared by O-alkylation of bisphenol A with epichlorohydrin. This reaction mainly affords bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, as well as some oligomer. The degree of polymerization may be as low as 0.1.[2] The epoxide content of such epoxy resins is of interest. This parameter is commonly expressed as the epoxide number, which is the number of epoxide equivalents in 1 kg of resin (Eq./kg), or as the equivalent weight, which is the weight in grams of resin containing 1 mole equivalent of epoxide (g/mol). Since unsymmetrical epoxides are chiral, the bis epoxide consists of three stereoisomers, although these are not separated.
Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether slowly hydrolyzes to 2,2-bis[4(2,3-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl)propane (bis-HPPP).
Similarly, DGEBA reacts with acrylic acid to give vinyl ester resins. The reaction results in opening of the epoxide ring, generating unsaturated esters at each terminus of the molecule. Such materials are often diluted with styrene and converted to resin.
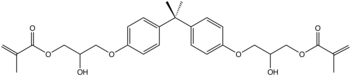
Epoxy resins are thermosetting polymers, which are crosslinked using hardeners (curing agents). The most common curing agents for epoxy resins are polyamines, aminoamides, and phenolic compounds.[3]
Safety
Bisphenol A has attracted much attention as a potential endocrine disruptor.[4][5] It has antiandrogen and PPARγ-modulating properties.
BADGE is listed as an IARC Group 3 carcinogen, meaning it is "not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans".[6] From the 1990s onward, concern has been raised over this possible carcinogenicity because BADGE is also used in epoxy resins in the lining of some tin cans for foodstuffs, and unreacted BADGE may end up in the contents of those cans.[4]
See also
- Bisphenol AF (BPAF)
- Bisphenol S (BPS)
- EPI-001
References
- Pham, Ha Q.; Marks, Maurice J. (2012). "Epoxy Resins". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_547.pub2.
- Mark, Herman (16 October 2013). "Epoxy Resins". Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology. ISBN 9780470073698.
- Forrest, M.J.: Coatings and Inks for Food Contact Materials, in RAPRA review reports, vol. 16, no. 6 (2005), p.8
- Walfried Rauter, Gerald Dickinger, Rudolf Zihlarz and Josef Lintschinger, “Determination of Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) and its hydrolysis products in canned oily foods from the Austrian market”, Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. A 208 (1999) 208–211
- "Leitlinie zur hygienischen Beurteilung von organischen Beschichtungen im Kontakt mit Trinkwasser (Beschichtungsleitlinie)" [Guideline for public health evaluation of organic chemical coatings in contact with drinking water (coating guideline)] (PDF). www.umweltbundesamt.de (in German). 16 March 2016.
- Group 3: Not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans Archived November 28, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, International Agency for Research on Cancer