Ethyl cyanoacetate
Ethyl cyanoacetate is an organic compound that contains a carboxylate ester and a nitrile. It is a colourless[1] liquid with a pleasant odor. This material is useful as a starting material for synthesis due to its variety of functional groups and chemical reactivity.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.009 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3276 2666 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 113.116 g·mol−1 |
| -67.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H319, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P322, P330, P337+313, P363, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
Ethyl cyanoacetate may be prepared in various ways:
- Kolbe nitrile synthesis using ethyl chloroacetate and sodium cyanide.[2]
- Fischer esterification of cyanoacetic acid with ethanol in the presence of a strong mineral acids (e.g. concentrated sulfuric acid). The cyanoacetic acid can be prepared via Kolbe nitrile synthesis using sodium chloroacetate and sodium cyanide.[2]
- Reaction of the sodium cyanoacetate with ethyl bromide in an aqueous–organic two-phase system in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst.[3]
- Oxidation of 3-ethoxypropionitrile, an ether, with oxygen under pressure in the presence of cobalt(II) acetate tetrahydrate as catalyst and N-hydroxyphthalimide as a radical generator.[4]
Properties
Physical properties
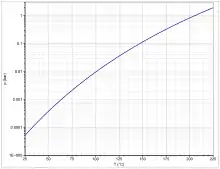
Ethyl cyanoacetate is a colorless liquid, it boils at atmospheric pressure at 209 °C.[5] The vapor pressure follows the Antoine equation log10(P) = A−(B/(T+C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 7.46724, B = 3693.663 and C = 16.138 in the temperature range from 341 to 479 K[6] In solid phase, two polymorphic forms can occur.[7] Below -111 °C, the crystal form II is dominant.[7] Above this temperature, the crystal form I is formed which melts at -22 °C.[5] The heat capacity at 25 °C is 220.22 J K−1 mol−1.[7]
Chemical properties
With its three different reactive centers—nitrile, ester, acidic methylene site—ethyl cyanoacetate is a versatile synthetic building block for a variety of functional and pharmacologically active substances. It contains an acidic methylene group, flanked by both the nitrile and carbonyl, and so can be used in condensation reactions like the Knoevenagel condensation or the Michael addition. This reactivity is similar to that of esters of malonic acid. As an example of reactivity at the nitrile, diethyl malonate is obtained from cyanoacetic acid ethyl ester by reaction with ethanol in the presence of strong acids.[2] Heating in the presence of sodium ethoxide forms the dimeric 3-amino-2-cyano-2-pentendiaciddiethylester.[8]
Use
Due to its functionality cyanoacetate reacts:
- At the nitrile group in various ways:
- Nucleophilic attack at the ester group, as part of acyl substitution: reaction with ammonia leads to cyanoacetamide, which can be converted by dehydration with PCl5 or POCl3 to malononitrile.[10]
- Via the acidic methylene group as a nucleophile
Ethyl cyanoacetate is a building block for the synthesis of heterocycles which are used for example as drugs:
- Allopurinol, used for the treatment of chronic gout, can be synthesized starting with a Knoevenagel condensation with triethyl orthoformate; the condensation product is cyclized with hydrazine to give a substituted pyrazole and subsequently with formamide to allopurinol, a substituted pyrazolo-pyrimidine.[11]
- The purine derivatives theophylline, caffeine and uric acid are synthetically accessible from ethyl cyanoacetate and N,N'-dimethylurea.[12]
- The pteridine derivative folic acid is assigned to the vitamin B complex; ethyl cyanoacetate and guanidine can be used as starting material in a multi-stage convergent synthesis.
- The pyrrole ethosuximide is used to treat epilepsy, it can be obtained from ethyl cyanoacetate and butanone in a multistep synthesis.
- The pyrimidine derivative trimethoprim is used as co-trimoxazole in fixed combination with sulfamethoxazole used as bacteriostatic agent and is synthesized from ethyl cyanoacetate and 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde or its benzyl chloride.
Also many other functional heterocycles are in good yields accessible from ethyl cyanoacetate, such as 3-substituted coumarin derivatives.[13]
Non-cyclic products from this starting material include:
- The anticonvulsant valproic acid
- Ethyl cyanoacrylate, used as superglue, via reaction with formaldehyde
Ethyl cyanoacetate is also used to prepare 3,3-diphenylpropan-1-amine, which is the precursor used in the synthesis of Prenylamine & Droprenilamine.
References
- Entry on Cyanessigsäureester. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 2016-06-15.
- J. K. H. Inglis. "Ethyl Cyanoacetate". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.008.0074.
- EP application 1028105, Hanselmann, Paul & Hildebrand, Stefan, "Process for the preparation of cyanoacetic esters", published 2000-08-16, assigned to Lonza AG
- EP patent 1208081, Hanselmann, Paul & Hildebrand, Stefan, "Method for producing cyanoacetic acid esters", issued 2004-04-14, assigned to Lonza AG
- Record of CAS RN 105-56-6 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 3. März 2011.
- Stull, D.R. (1947). "Vapor Pressure of Pure Substances Organic Compounds". Ind. Eng. Chem. 39 (4): 517–540. doi:10.1021/ie50448a022.
- Khodzhaeva, M.G.; Bugakov, Yu.V.; Ismailov, T.S.: Heat capacity and thermodynamic functions of ethyl cyanoacetate in Khim.-Farm. Zhur. 21 (1987) 760-762, DOI:10.1007/BF00872889.
- Dorokhov, V. A.; Baranin, S. V.; Dib, A.; Bogdanov, V. S. (1992). "'Codimers' of N-(pyrid-2-yl) amides and ethyl cyanoacetate". Russ. Chem. Bulletin. 41 (2): 287–291. doi:10.1007/bf00869516.
- Zheng, Shuyan; Yu, Chunhui; Shen, Zhengwu (2012). "Ethyl Cyanoacetate: A New Cyanating Agent for the Palladium-Catalyzed Cyanation of Aryl Halides". Org. Lett. 14 (14): 3644–3647. doi:10.1021/ol3014914.
- Mary Eagleson: Concise encyclopedia chemistry, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin - New York 1994, ISBN 3-11-011451-8.
- Axel Kleemann, Jürgen Engel: "Pharmazeutische Wirkstoffe", 2. Aufl., Georg Thieme, Stuttgart - New York 1982, ISBN 3-13-558402-X.
- Beyer-Walter: "Lehrbuch der Organischen Chemie", 24. Aufl., S. Hirzel, Stuttgart - Leipzig 2004.
- Avetisyan, A. A.; Vanyan, É. V.; Dangyan, M. T. (1980). "Synthesis of functionally substituted coumarins". Chem. Heterocycl. Compounds. 15 (9): 959–960. doi:10.1007/BF00473834.
- Harald Strittmatter, Stefan Hildbrand and Peter Pollak "Malonic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a16_063.pub2

