Ferguson, Missouri
Ferguson is a city in St. Louis County, Missouri, United States.[1] It is part of the Greater St. Louis metropolitan area. The population was 21,203 at the 2010 census.[6]
Ferguson, Missouri | |
|---|---|
City | |
| City of Ferguson | |
 Ferguson's Church Street in 2012, the Wildwood House in 2012, the Ferguson Municipal Library in 2014, and the Ferguson City Hall in 2012. | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Etymology: William B. Ferguson | |
| Nickname(s): "Community of Choice" | |
| Motto(s): "Proud Past. Promising Future!" | |
 Location within St. Louis County (left) and Missouri (right) | |
| Coordinates: 38°44′39″N 90°18′19″W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Missouri |
| County | St. Louis |
| Incorporated | 1894 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ella Jones (D) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6.18 sq mi (16.01 km2) |
| • Land | 6.17 sq mi (15.99 km2) |
| • Water | 0.01 sq mi (0.02 km2) |
| Elevation | 502 ft (153 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 21,203 |
| • Estimate (2019)[4] | 20,525 |
| • Density | 3,325.50/sq mi (1,283.98/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Fergusonian[5] |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 63135 |
| Area code | 314 |
| FIPS code | 29-23986[1] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0756046[1] |
| Website | City of Ferguson |
History
What is now the city of Ferguson was founded in 1855, when William B. Ferguson deeded 10 acres (4.0 ha) of land to the Wabash Railroad in exchange for a new depot and naming rights.[7][8] The settlement that sprang up around the depot was called Ferguson Station.[9] Ferguson was the first railroad station connected directly to St. Louis.[10] The station is a focal point of the city's history and is depicted on the city flag, designed in 1994.[11][12]
Ferguson's first schoolhouse was built in 1878. Ferguson was incorporated as a city in 1894.[13]
Emerson Electric moved its headquarters to Ferguson during the 20th century.[9]
Until the 1960s, Ferguson was a sundown town where African Americans were not allowed to remain after nightfall.[14]
Ferguson made frequent worldwide headlines for months following the 2014 killing of Michael Brown Jr. by a police officer and the ensuing civil unrest. The United States Department of Justice investigation which followed resulted in large legal fees for the town, in excess of $300,000 a year. The city now has a higher sales tax, utility gross receipts tax, and franchise tax for 2017/2018 to generate more revenue.[15]
Ferguson elected its first black and first female mayor, Ella Jones, on June 2, 2020.[16]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 185 | — | |
| 1890 | 750 | 305.4% | |
| 1900 | 1,015 | 35.3% | |
| 1910 | 1,658 | 63.3% | |
| 1920 | 1,874 | 13.0% | |
| 1930 | 3,798 | 102.7% | |
| 1940 | 5,724 | 50.7% | |
| 1950 | 11,573 | 102.2% | |
| 1960 | 22,149 | 91.4% | |
| 1970 | 28,759 | 29.8% | |
| 1980 | 24,740 | −14.0% | |
| 1990 | 22,286 | −9.9% | |
| 2000 | 22,406 | 0.5% | |
| 2010 | 21,203 | −5.4% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 20,525 | [4] | −3.2% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[17] | |||
The population of Ferguson grew rapidly during the late nineteenth century. In 1880 the population of the then Ferguson Station was 185 people. By 1890 the population was recorded as being 750 and only four years later it had increased to 1200.[18]
The population of Ferguson continued to grow rapidly during the first six decades of the twentieth century, from 1,015 people in 1900 to 22,149 people in 1960, an average growth rate of 5% per year. Since 1960 the population has remained nearly constant.
The ethnic composition of Ferguson has shifted, however. In 1970, 99% of the population of Ferguson was white and 1% black. In 1980, the proportion of white residents went down to 85%, whereas the proportion of black residents rose to 14%. In 1990, residents of Ferguson who were identified in the U.S. Census as white comprised 73.8% of the total, while those identified as black made up 25.1%.[19] The remainder, 1.1%, identified with other racial categories. In the 2000 U.S. Census, 44.7% were white and 52.4% were African-American, now the majority ethnicity.[20]
2010 Census
As of the 2010 U.S. Census,[3] there were 21,203 people, 8,192 households, and 5,500 families residing in the city. The population density was 3,425.4 inhabitants per square mile (1,322.6/km2). There were 9,105 housing units at an average density of 1,470.9 per square mile (567.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 67.4% black, 29.3% white, 0.5% Asian, 0.4% Native American, 0.4% from other races, and 2.0% from two or more races. Hispanic and Latino of any race were 1.2% of the population.
There were 8,192 households, of which 39.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 29.6% were married couples living together, 31.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 6.1% had a male householder with no wife present, and 32.9% were non-families. 28.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.4% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.56 and the average family size was 3.12.
The median age in the city was 33.1 years. 28.7% of residents were under the age of 18; 10.4% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 25.2% were from 25 to 44; 25.3% were from 45 to 64; and 10.3% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 44.8% male and 55.2% female.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 6.20 square miles (16.06 km2), of which 6.19 square miles (16.03 km2) is land and 0.01 square miles (0.03 km2) is water.[21]
Climate
Ferguson has a humid subtropical-continental climate. Winters are cold, while summers are hot and humid. The record high is 115 °F, and the record low is −19 °F.
| Climate data for Ferguson, MO | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 77 (25) |
85 (29) |
92 (33) |
93 (34) |
98 (37) |
105 (41) |
115 (46) |
110 (43) |
104 (40) |
94 (34) |
86 (30) |
79 (26) |
115 (46) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 38 (3) |
44 (7) |
55 (13) |
67 (19) |
76 (24) |
85 (29) |
90 (32) |
88 (31) |
80 (27) |
68 (20) |
54 (12) |
42 (6) |
66 (19) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 21 (−6) |
27 (−3) |
36 (2) |
47 (8) |
57 (14) |
66 (19) |
71 (22) |
69 (21) |
60 (16) |
48 (9) |
37 (3) |
26 (−3) |
47 (8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −19 (−28) |
−18 (−28) |
−5 (−21) |
20 (−7) |
31 (−1) |
43 (6) |
51 (11) |
47 (8) |
32 (0) |
21 (−6) |
1 (−17) |
−16 (−27) |
−19 (−28) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.14 (54) |
2.28 (58) |
3.60 (91) |
3.69 (94) |
4.11 (104) |
3.76 (96) |
3.00 (76) |
2.98 (76) |
2.96 (75) |
2.76 (70) |
3.71 (94) |
2.86 (73) |
37.85 (961) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 7.4 (19) |
4.8 (12) |
3.3 (8.4) |
0.6 (1.5) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1.5 (3.8) |
4.9 (12) |
22.9 (58) |
| Source: [22] | |||||||||||||
Economy
The city is home to the headquarters of Emerson Electric.[23][24]
Government

The Mayor of Ferguson is directly elected for a three-year term.[25] The Ferguson city council is composed of six members.[26]
James Knowles III was elected mayor for a three-year term in April 2011 and ran unopposed in April 2014.[27] Voter turnout in the April 2014 mayoral election was approximately 12%.[26][27] In June 2020, Ella Jones (D) became the first African American and first woman to be elected mayor of Ferguson.[28]
The Ferguson Police Department is involved with the following public programs: Business Watch, Community Emergency Response Team (CERT), D.A.R.E. Program, Neighborhood Watch, School Resource Officers, and Riot Patrol.[26]
Ferguson also operates a two-station firehouse with a complement of 18 full-time firefighters as well as nine senior management officials.[29] The fire stations operate 24 hours a day.[29]
Ferguson Police Department
On March 4, 2015, the Ferguson Police Department was criticized by the United States Department of Justice for civil rights violations. The Department of Justice argued that the Ferguson Police Department and the City of Ferguson relied on unconstitutional practices in order to balance the city's budget through racially motivated excessive fines and punishments.[30]
On March 11, 2015, Ferguson Police Chief Thomas Jackson stated he was willing to resign, likely later that day (though no timeframe was confirmed) if he could get assurances that the Ferguson Police Department would be left in place and would not be dissolved; Fox News said he was not pushed out or fired. His resignation followed City Manager John Shaw who resigned March 10, and Municipal Judge Ronald Brockmeyer, who resigned March 9. Shaw had ultimate oversight over the Police Department and other city departments and was the most powerful civic official in Ferguson. He faced criticism for not doing enough to ameliorate the situation. The week before, three Ferguson Police Department employees were fired for offensive emails mentioned in the Justice Department report.[31]
Michael Brown shooting
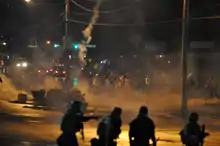
On August 9, 2014, an 18-year-old black man, Michael Brown, was fatally shot by Darren Wilson with the Ferguson Police Department.[32][33] The incident sparked protests and acts of vandalism in Ferguson as well as widespread calls for an investigation into the incident.[34] On August 10, after a day of vigils, there were looting of businesses, arson, vandalism of vehicles, shots fired at firemen and violent clashes between protestors and police.[35][36][37] On August 18, soldiers from the Missouri National Guard arrived in Ferguson at the request of the Governor of Missouri Jay Nixon, who also ended midnight to 5:00 a.m. curfews that had been imposed.[38] On November 24, a grand jury decided that it would not indict Wilson in the shooting death of Brown.[39] Following the announcement of the grand jury's decision, there were peaceful protests as well as rioting.[40][41]
Education
St. Louis Community College-Florissant Valley, which has about 8,000 students, is located in Ferguson.
Much of the community is within the Ferguson-Florissant School District (FFSD).[42] Primary schools (grades K-2) serving sections of Ferguson include Central, Bermuda, Holman, and Walnut Grove. Intermediate schools (grade 3-5) serving sections of Ferguson include Lee-Hamilton, Griffith, and Berkeley. Zoned secondary schools with attendance boundaries that coincide with Ferguson include Johnson-Wabash 6th Grade Center, Ferguson Middle School, and McCluer High School.[43] A portion of Ferguson is instead in the Riverview Gardens School District,[44] and another is in the Hazelwood School District.[45]
The following FFSD public schools are located within the city of Ferguson:
- STEAM Academy at McCluer South-Berkeley (a magnet school for grades 9-12), formerly McCluer South-Berkeley High School
- Ferguson Middle School (7-8)
- Johnson-Wabash 6th Grade Center (formerly Elementary School)
- Griffith Elementary School (3-5)
- Lee-Hamilton Elementary School (3-5)
- Central Elementary School (K-2)
Vogt Elementary School closed in 2019.[46]
The following private schools are located within the city of Ferguson:
- Blessed Teresa of Calcutta School
- Our Lady of Guadalupe School
- Zion Lutheran School
Ferguson is also home to the Challenger Learning Center – St. Louis, which provides a space education program.
The Ferguson Municipal Public Library is one of several independent community libraries in St. Louis County and is a member of the Municipal Library Consortium of St. Louis County.
Notable people
This list may include persons born in the community, past residents, and current residents.
- General Ralph Eberhart, USAF, Commander of the North American Aerospace Defense Command during the September 11 attacks[47]
- Michael McDonald, Grammy Award-winning singer[48]
- Henry Miller, also known as Sentoryu, mixed martial artist and former sumo wrestler[49]
- Delrish Moss, Miami law enforcement veteran sworn in on May 9, 2016 as the first permanent African-American Police Chief of Ferguson[50]
- Susan Notorangelo, long-distance cyclist[51]
- Enos Slaughter, Hall of Fame-winning St. Louis Cardinals baseball player[48]
- Maury Travis, serial killer[52]
- Harry Tuthill, cartoonist of the syndicated comic strip, The Bungle Family[53]
- Tyron Woodley, American mixed martial artist, former UFC welterweight champion[54]
See also
References
- "Feature Detail Report for: Ferguson". Geographic Names Information System. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 26, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-07-08.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- https://www.cnn.com/interactive/2017/politics/state/ferguson-police-shooting/
- "Race, Hispanic or Latino, Age, and Housing Occupancy: 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File (QT-PL), Ferguson city, Missouri". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- Fox, Tim (1995). Where We Live: A Guide to St. Louis Communities. Missouri History Museum. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-883982-12-6.
- Bryan, William Smith; Rose, Robert; Elwang, William Wilson (1876). A History of the Pioneer Families of Missouri: With Numerous Sketches, Anecdotes, Adventures, Etc., Relating to Early Days in Missouri. Also the Lives of Daniel Boone and the Celebrated Indian Chief Black Hawk, with Numerous Biographies and Histories of Primitive Institutions. Lucas brothers. p. 167.
- "City History". City of Ferguson. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
The city boomed during the post-World War II era. Commuter trains were replaced by automobile traffic. Plentiful employment was provided by new industries, including the relocated headquarters of Emerson Electric Company. Scores of new homes were built and the city's population continued to expand. In 1954, Ferguson became a charter city, one of the first in St. Louis County to adopt the council-manager form of government.
- Montesi, Al; Deposki, Richard (2002). St. Louis Union Station. Arcadia Publishing. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7385-1983-8.
- Shapiro, Mary. "Oh, so proudly we hail". stltoday.com.
- "Ferguson, Missouri (U.S.)". crwflags.com.
- "Ferguson Missouri". AboutStLouis.com. Retrieved 13 August 2014.
- Pearce, Matt (April 5, 2017). "Ferguson's white mayor wins reelection in his first race since 2014 unrest". Los Angeles Times. Los Angeles. p. A11.
By a margin of 56% to 44%, Knowles defeated his lone challenger, Councilwoman Ella Jones, who is black. If Jones had won, she would have made history as the first black mayor of a city that was once an overwhelmingly white 'sundown town' where, until the 1960s, African Americans were banned after dark.
- https://www.moodys.com/research/Moodys-Affirms-Ba3-on-Ferguson-MOs-GO-Bonds-Outlook-Positive--PR_904022483.
- "US: Ferguson, Missouri elects first Black mayor". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved June 3, 2020.
- United States Census Bureau. "Census of Population and Housing". Retrieved November 26, 2014.
- Null, J. (June 2007). American Educational History Journal. ISBN 9781593117689.
- "Bureau of Census, 1990 Census of Population: General Population Characteristics, Missouri" (PDF). Census.gov. p. 56. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 March 2003. Retrieved 1 December 2014.
- Daniel Fowler (July 28, 2015). "With Racial Segregation Declining Between Neighborhoods, Segregation Now Taking New Form" (News release). asanet.org. American Sociological Association. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
The racial composition of Ferguson went from about 25 percent black to 67 percent black in a 20 year period.
- "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2012-07-02. Retrieved 2012-07-08.
- "Intellicast - Ferguson Historic Weather Averages in Missouri (63135)". www.intellicast.com. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- "A closer look at Ferguson, Missouri, the St. Louis suburb where Michael Brown was killed". Fox News. Associated Press. November 24, 2014. Retrieved November 25, 2014.
- Snyder, Benjamin (August 18, 2014). "Amid unrest, it's business as usual for Ferguson's Emerson Electric". Fortune. Retrieved November 25, 2014.
- Howard, Shannon (2014-04-06). "Election Day brings new leadership to NoCo". NOCO. Archived from the original on 2014-08-20. Retrieved 2014-08-19.
- Vega, Tanzina (2014-08-14). "Deep Tensions Rise to Surface After Ferguson Shooting". The New York Times. Retrieved 2014-08-19.
- "St. Louis County Election Results April 2014". stlouisco.com. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- https://www.stltoday.com/news/local/govt-and-politics/ella-jones-becomes-the-first-african-american-and-first-woman-elected-mayor-of-ferguson/article_4fcddeed-9586-571c-b88a-bbcae3c71f70.html
- "Fire Department - Ferguson, MO - Official Website". www.fergusoncity.com. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- Apuzzo, Matt (3 March 2015). "Ferguson Police Routinely Violate Rights of Blacks, Justice Dept. Finds". The New York Times. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- "Ferguson police chief resigns after scathing Justice Dept. report". msn.com.
- "Ferguson Chief Names Darren Wilson as Cop Who Shot Michael Brown". NBCNews.com. 15 August 2014. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- Berman, Mark; Lowery, Wesley (15 August 2014). "Ferguson police call Michael Brown a robbery suspect, identify Darren Wilson as officer who shot him". Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- Lind, Dara (12 August 2014). "Outrage in Ferguson after police shooting of unarmed teenager Michael Brown". Vox Media. Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- Yang, John (August 10, 2014). "Looting Erupts After Vigil for Slain Missouri Teen Michael Brown". NBC News. Retrieved August 11, 2014.
- Fantz, Ashley; Howell, George (August 11, 2014). "Protesters fill streets after Michael Brown shooting". CNN. Retrieved August 11, 2014.
- Scher Zagier, Alan. "Police, protesters again clash outside St. Louis". Star-telegram.com (Ft. Worth). Associated Press. Retrieved 2014-08-12.
- Davey, Monica; Eligon, John; Blinder, Alan (August 19, 2014). "National Guard Troops Fail to Quell Unrest in Ferguson". The New York Times. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
In a news conference on Monday, family members and Dr. Baden said that the autopsy he had performed confirmed witness accounts that Mr. Brown was trying to surrender when he was killed.
- Alcindor, Yamiche; Welch, William M. (24 November 2014). "No indictment in Ferguson case". USA Today. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- Moni Basu, Holly Yan and Dana Ford, CNN (November 24, 2014). "Ferguson: Fires and chaos erupts after no indictment - CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved November 25, 2014.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Darcy, Oliver (25 November 2014). "61 Arrested, At Least a Dozen Buildings Set Aflame Following Ferguson Grand Jury Decision". The Blaze. Archived from the original on 9 December 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- "City Map". City of Ferguson. Retrieved 2019-11-10. - Compare this map against school attendance maps.
- "Restructuring Information". Ferguson-Florissant School District. Retrieved 2019-11-10. - Includes school attendance maps of FFSD schools.
- "Map". Riverview Gardens School District. Retrieved 2019-11-10. - Indicates sections of Ferguson in the district.
- "Fast Facts". Hazelwood School District. Retrieved 2019-11-10.
- Benchaabane, Nassim (2018-10-11). "Ferguson-Florissant picks redistricting plan; McCluer South-Berkeley will be special academy, Vogt Elementary to close". St. Louis Post-Dispatch . Retrieved 2019-11-10.
- Levins, Harry (2001-04-03). "Air Force General, a Missourian, may be in line to become next Chairman of Joint Chiefs of Staff". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Lee Enterprises. p. A3. Archived from the original on 2014-08-19 – via HighBeam Research.
He is Gen. Ralph E. 'Ed' Eberhart, a native of Nevada, Mo., who grew up in Ferguson and graduated from McCluer in 1964.
- Leonard, Mary Delach (August 15, 2014). "This Is Ferguson: Residents And Business Owners Tell Us About Their City". St Louis Public Radio. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- Lefton, Brad (17 June 1997). "Sentoryu from Sen-to-Ru-I-Su Our Town's Henry Miller Is a Really Big Man as Sumo Wrestler in Japan". St Louis Post-Dispatch (MO). Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- New Ferguson Police Chief Sworn In The New York Times, May 9, 2016
- Johnson, Kevin C. (July 23, 2010). "Michael McDonald one of several Ferguson honorees". St. Louis Post Dispatch. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- Nagus, Chris (July 9, 2014). "Catrina McGhaw: St. Louis woman finds out on TV she's renting serial killer Maury Travis' home". KMOV. Archived from the original on October 26, 2014. Retrieved September 18, 2014.
- Heintjes, Tom (August 12, 2013). "When the Bungles Mixed It Up with Their Neighbors on the Battlegrounds of Sunken Heights" (13). Hogan's Alley. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "MUTIGERS.COM Tyron Woodley Bio – Official Athletic Site Official Athletic Site – Wrestling". Mutigers.com. Archived from the original on 6 December 2014. Retrieved 1 December 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ferguson, Missouri. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ferguson. |
- Official website
- City of Ferguson (fergusoncity.com) at the Wayback Machine (archived August 10, 2002)
- "Historic Ferguson". Archived from the original on 2002-06-01. Retrieved 2015-03-14.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- Podcast: Ferguson’s Untold Tragedy of School Segregation—ProPublica (December 22, 2014)