French cruiser Marseillaise (1935)
Marseillaise was a French light cruiser of the La Galissonnière class. During the Second World War, she remained with Vichy France.
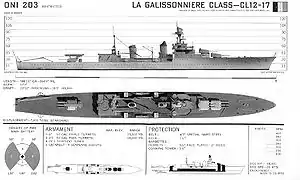 General layout of a La Galissonnière-class cruiser | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Marseillaise |
| Namesake: | La Marseillaise |
| Builder: | AC Loire, Nantes, France |
| Laid down: | 23 October 1933 |
| Launched: | 17 July 1935 |
| Commissioned: | 10 October 1937 |
| Fate: | Scuttled 1942, Scrapped 1946-1947 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | La Galissonnière-class cruiser |
| Displacement: |
|
| Length: | 179 m (587 ft) |
| Beam: | 17.5 m (57 ft) |
| Draught: | 5.35 m (17.6 ft) |
| Propulsion: | |
| Speed: | 31 knots (57 km/h; 36 mph) |
| Range: |
|
| Complement: | 540 |
| Armament: |
|
| Armour: |
|
| Aircraft carried: |
|
Design and description
The La Galissonnière class was designed as an enlarged and improved version of the preceding Emile Bertin. The ships had an overall length of 179.5 meters (588 ft 11 in), a beam of 17.48 meters (57 ft 4 in), and a draft of 5.28 meters (17 ft 4 in). They displaced 7,722 metric tons (7,600 long tons) at standard load and 9,460 t (9,310 long tons) at deep load. Their crew consisted of 557 men in peacetime and 612 in wartime.[1]
Construction and career
When commissioned, Marseillaise joined the French Mediterranean Squadron and became the flagship of Contre-Amiral Decoux in 1938. In January 1939 she joined the 3rd Cruiser Division at Casablanca, and she was at Toulon when war was declared, as flagship of the 4th Squadron, part of Force Z.
Marseillaise participated in the transport of gold to Canada in April 1940.
Concerns regarding Italian intentions prompted reorganisation of French naval forces. The 3rd Cruiser Division was sent to Bizerte as part of the Force de Raid, to protect French interests in North Africa, should Italy enter the war.
After the French surrender, on 4 July 1940, she returned to Toulon. As a result of the British attack on Mers-el-Kebir, the Germans suspended the disarming of the French fleet and Marseillaise became part of the newly formed High Seas force.
In the scuttling of the French fleet in Toulon, the ship was sabotaged by her crew and set on fire. The captain of Marseillaise was anxious that the Germans should not capture the ship. He ordered scuttling charges to be set and the sea valves opened only on one side, ignoring orders to sink his ship on an even keel. German commandos arrived at the gangplank but were refused permission to go aboard. They did not force the issue and stood on the dock and watched the ship slowly capsize. The last officers abandoned ship as explosions ripped the vessel apart and fires took hold. The ship's officers were taken prisoner, and the ship burned for seven days.
The burnt-out hulk of Marseillaise was scrapped in 1946–1947.
Citations
- Jordan & Moulin, p. 124
Bibliography
- Jordan, John & Moulin, Jean (2013). French Cruisers 1922–1956. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-133-5.