Geography of the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, together with Guam to the south, compose the Mariana Islands. The southern islands are limestone, with level terraces and fringing coral reefs. The northern islands are volcanic, with active volcanoes on Anatahan, Pagan and Agrihan. The volcano on Agrihan has the highest elevation at 3,166 feet (965 m). About one-fifth of the land is arable; another tenth is pasture. The primary natural resource is fish, some of which are endangered species, which leads to conflict. Also, development has created landfills which have contaminated the groundwater on Saipan, which could lead to disease.
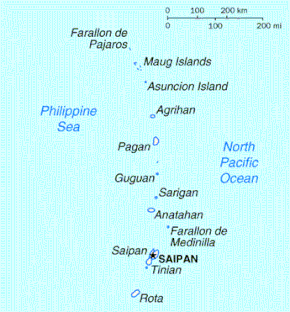
Anatahan Volcano is a small volcanic island 80 miles (130 km) north of Saipan. It is about 6 miles (10 km) long and 2 miles (3 km) wide. Anatahan began erupting suddenly from its east crater on May 10, 2003, at about 6 p.m. (0800 UTC). It has since alternated between eruptive and calm periods. On April 6, 2005, approximately 50,000 cubic meters (1,800,000 cu ft) of ash and rock were ejected, causing a large, black cloud to drift south over Saipan and Tinian.
Climate
The islands have a tropical marine climate moderated by seasonal northeast trade winds. There is little seasonal temperature variation. The dry season runs from December to June, and the rainy season from July to November and can include typhoons. The Guinness Book of World Records has cited Saipan as having the most equable climate in the world.[1] From 1927 to 1935, the temperature ranged from 19.6 degrees Celsius or 67.3 degrees Fahrenheit at the lowest to 31.4 degrees Celsius or 88.5 degrees Fahrenheit at the highest.[1]
References
- "Most equable temp-short period". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2019-09-20.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Geography of the Northern Mariana Islands. |
