Glossary of vexillology
Flag terminology is the nomenclature, or system of terms, used in vexillology, the study of flags, to describe precisely the parts, patterns, and other attributes of flags and their display.
Flag types
- Banderole or bannerol
A small flag or streamer carried on the lance of a knight, or a long narrow flag flown from the mast-head of a ship.
- Banner
Generically, a synonym for a flag of any kind, and in heraldry specifically, a square or rectangular flag whose design is identical to the shield of a coat of arms; also denominated a banner of arms.
- Burgee
A distinguishing flag of a recreational boating organisation, which commonly has the shape of a pennant.
- Civil ensign, merchant flag, or merchant ensign
A version of a national flag that is flown on civil ships to denote their nationality.
- Civil flag
A version of a national flag that is flown on civil installations or craft.
- Colour or color
The flag of a military unit.
- Corner flag
A small flag flown at each of the corners of a football pitch or other sports field.
- Courtesy flag or courtesy ensign
A flag that is flown on a visiting ship in foreign waters as a sign of respect for the foreign nation.
- Ensign
The flag of any ship or military unit, or, generically, a synonym for any kind of flag. On ships, an ensign is normally flown at the stern.
- Fanion
A small flag that the French military uses.
- Gonfalon, gonfanon, or gonfalone
A heraldic flag that is suspended and pendent from a crossbar.
- Guidon
A small flag that a military unit flies; in Scottish heraldry, a smaller version of the standard (see below).
- Jack
A flag flown from a short jackstaff at the bow of a ship.
- Pennon or pennant
A flag that is wider at the hoist than at the fly.
- Pipe banner
A decorative flag for Scottish Highland bagpipes.
- Prayer flag
A kind of flag that is flown along mountain ridges and peaks in the Himalayas in order to bless the surrounding land.
- Rank flag or distinguishing flag
A flag that a superior naval officer flies on his flagship or headquarters.
- Signal flag
A flag or pennant that communicates or signals information that is not heraldic.
- Standard
In heraldry, a long tapering flag that bears heraldic badges and the motto of the armiger; it may also refer to a military colour that cavalry units fly or a royal standard of a monarch or member of a royal family.
- State flag or governmental flag
A version of a national flag that represents and may be restricted in use only to the national government and agencies thereof; the design of many state flags consists of the civil flag (see above) defaced with a coat of arms or other heraldic charge.
- Vexilloid
A flag-like object that is used in a similar symbolic manner as a flag, but that differs from a conventional flag in some way.
- Vexillum
A flag-like object that is suspended from a horizontal crossbar; the Ancient Roman army used it as its military standard.
- War flag, military flag, or battle flag
A variant of a national flag that a nation's military forces use on land.
- Windsock
A conical textile tube that is used to indicate the direction and strength of wind.
Flag elements
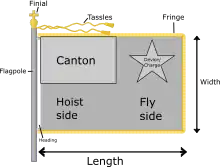
Parts of a flag
- Badge
- A coat of arms or simple heraldic symbol.
- Canton
- Any quarter of a flag, but commonly means the upper hoist quarter, such as the field of stars in the flag of the United States or the Union Jack in the Australian Flag.
- Charge
- A figure or symbol appearing in the field of a flag.
- Emblem
- A device often used as a charge on a flag. It may be heraldic in origin or modern, for example the maple leaf on the Canadian Flag.
- Field
- The background of a flag; the color behind the charges.
- Fimbriation
- A narrow edging or border, often in white or gold, on a flag to separate two other colors. For example the white and gold lines of the South African Flag.
- Finial
- A decorative or protective cap atop the flagpole. Often shaped like a sphere, but can also be a shape with heraldic significance, such as a spear or an eagle. Sometimes referred to as a capper.
- Fly
- The half or edge of a flag farthest away from the flagpole. This term also sometimes refers to the horizontal length of a flag.
- Hoist
- The half or edge of a flag nearest to the flagpole. This term also sometimes refers to the vertical dimension of a flag.
- Length
- The span of a flag along the side at right angles to the flagpole.
- Width or breadth
- The span of a flag down the side parallel to the flagpole.
Basic patterns
Flags often inherit traits seen in traditional European heraldry designs and as a result patterns often share names.
| Name | Illustration | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Border/bordure |  |
 Flag of Maldives Flag of Maldives |
| Canton |  |
 Flag of the United States of America Flag of the United States of America |
| Quadrisection |  |
 Flag of Panama Flag of Panama |
| Greek cross
(couped cross) |
 |
 Flag of Switzerland Flag of Switzerland |
| Symmetric cross |  |
 Flag of Georgia Flag of Georgia |
| Nordic cross |  |
 Flag of Iceland Flag of Iceland |
| Pale |  |
 Flag of Canada Flag of Canada |
| Fess |  |
 Flag of Austria Flag of Austria |
| Bend | 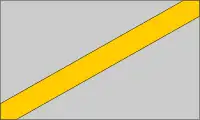 |
 Flag of Tanzania Flag of Tanzania |
| Chevron | 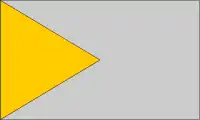 |
 Flag of Palestine Flag of Palestine |
| Pall | 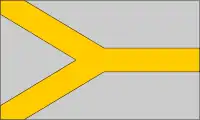 |
 Flag of South Africa Flag of South Africa |
| Saltire |  |
 Flag of Scotland Flag of Scotland |
Techniques in flag display
- Distress
- Flying the flag upside-down,[1] or tying it into a wheft.[2]
- Half-mast
A style of flag display where the flag is flown at least the width of the flag between the top of the flag and the top of the pole.
- Hoist
- The act or function of raising a flag, as on a rope.
- Lower
- The act or function of taking down a flag, as on a rope.
Illustrations
Flag illustrations generally depict flags flying from the observer's point of view from left to right, the view known as the obverse (or "front"); the other side is the reverse (or "back"). There are some exceptions, notably some Islamic flags inscribed in Arabic, which is written from right to left; for these the obverse is defined as the side with the hoist to the observer's right.
See also
References
- For example, 36 US Code §176 provides: “The flag should never be displayed with the union down, except as a signal of dire distress in instances of extreme danger to life or property.”
- "Flying flags upside down". fotw.net. 30 September 2006. Archived from the original on 19 May 2012.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.