Great Eastern Main Line
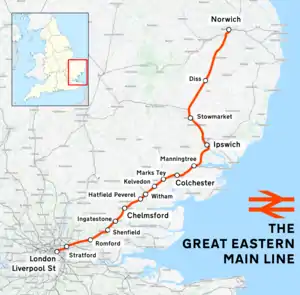
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a 114.5-mile (184.3 km) major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and the East of England, including Shenfield, Chelmsford, Colchester, Ipswich and Norwich. Its numerous branches also connect the main line to Southminster, Braintree, Sudbury, Harwich and a number of coastal towns including Southend-on-Sea, Clacton-on-Sea, Walton-on-the-Naze and Lowestoft.[1]
| Great Eastern Main Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Class 745 at Colchester in 2020 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | Greater London East of England | ||
| Termini | London Liverpool Street 51.5188°N 0.0815°W Norwich 52.6267°N 1.3067°E | ||
| Stations | 27 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Intercity, commuter rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Operator(s) | Greater Anglia TfL Rail c2c (limited services) | ||
| Depot(s) | Norwich Crown Point Clacton-on-Sea Ilford Colchester | ||
| Rolling stock | |||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1862 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 114 miles 40 chains (184.3 km) | ||
| Number of tracks | 1–6 | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Old gauge | 5 ft (1,524 mm) until 1844 | ||
| Electrification | Mk1 and GEFF 25 kV 50 Hz AC OHLE | ||
| Operating speed | 100 mph (160 km/h) | ||
| |||
Great Eastern main line | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Its main users are commuters travelling to and from London, particularly the City of London, which is served by Liverpool Street, and areas in east London, including the Docklands financial district via the London Underground and Docklands Light Railway connections at Stratford. The line is also heavily used by leisure travellers, as it and its branches serve a number of seaside resorts, shopping areas and countryside destinations. The route also provides the main artery for substantial freight traffic to and from Felixstowe and Harwich, via their respective branch lines. Trains from Southend Airport also run into London via the GEML.[2]
History
Eastern Counties and Eastern Union Railways (1839–1862)
The first section of the line, built by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR), opened in June 1839 between a short-lived temporary terminus at Devonshire Street in the East End of London and Romford, then in the Havering Liberty in Essex. The London terminus was moved in July 1840 to Shoreditch (later renamed Bishopsgate), after 1900 in the Metropolitan Borough of Bethnal Green, and at the eastern end the line was extended 6 miles (9.7 km) out to Brentwood in the same year. A further 34 miles (55 km) of track was added out to Colchester by 1843.[3] The original gauge for the line was 5 ft (1,524 mm), but this was converted to 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge in 1844.
The section of line between Colchester and Ipswich was built by the Eastern Union Railway (EUR) to standard gauge and opened to passenger traffic in June 1846. Its sister company, the Ipswich and Bury Railway, built a line to Bury St Edmunds and this was completed in November 1846. Both companies shared the same office, many directors and key staff, and started operating as a unified company with the EUR name from 1 January 1847. An extension from a new junction at Haughley to Norwich Victoria opened in December 1849, although the position of the latter station was poor and a spur to allow some trains to operate into Norwich (Thorpe) station was opened to regular traffic in November 1851.[4]
In the late 19th century the double-track main line was expanded with additional tracks being added to cope with more traffic. In 1854 a third track was added between Bow Junction and Stratford to help accommodate London, Tilbury and Southend Railway services which at that time were operating via Stratford.
Until 1860 trains serving the town of Ipswich used a station called Ipswich Stoke Hill which was located south of the Stoke tunnel. The town's current station is located to the north of the tunnel.
The ECR had leased the EUR from 1854 but by the 1860s the railways in East Anglia were in financial trouble and most were leased to the ECR; they wished to amalgamate formally, but could not obtain government agreement for this until 1862, when the Great Eastern Railway (GER) was formed out of the consolidation.[5]
Great Eastern Railway (1862–1922)
From November 1872 Bishopsgate (Low Level) became a temporary terminus to relieve the main high level Bishopsgate station while the GER was building its new permanent terminus at Liverpool Street. The latter opened in stages from February 1874, beginning with the first four platforms, until it was fully open from November 1875. At that time the original 1840 Bishopsgate station closed to passengers and was converted into a goods yard.
By the 1870s suburbia in the Forest Gate area was developing quickly and in 1872 suburban trains (this was the first distinctive suburban service on the main line as previously main line trains had performed this duty) terminated at a bay platform at Forest Gate. These were followed by trains from Fenchurch Street[Note 1] in 1877. By 1882 these services had been extended and were terminating at Ilford, Romford or Brentwood.
In 1877 a fourth track was added between Bow Junction and Stratford and two goods-only tracks were added between Stratford and Maryland Point. The four-track Bow Junction to Stratford section was extended back to James Street Junction (near Globe Road station which opened the same year) in 1884 but Bethnal Green to James Street did not follow until 1891. It was also in this year that two extra tracks were added between Bethnal Green and Liverpool Street which were for the use of West Anglia Main Line services. These tracks were built through the basement warehousing associated with Bishopsgate station located above.
The line was quadrupled to Ilford in 1895 and in 1899 out to Seven Kings.
In 1902 the quadruple track was extended from Seven Kings to Romford, but it wasn't until 1913 that four-tracking out to Shenfield was suggested and the First World War caused delay to this plan.[6] In 1903 the Fairlop Loop opened and a number of services that had previously terminated at Ilford were extended onto it. These services generally looped round and back to the GEML at Stratford (on the Cambridge line platforms).
London and North Eastern Railway (1923–1947)
The GER was grouped in 1923 into the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER). In 1931/32 the LNER quadrupled the tracks to Shenfield which became the terminus for inner-suburban operation.
In the 1930s a flyover was constructed just west of Ilford to switch the main and electric lines over, to enable main line trains to utilise Liverpool Street's longer west side platforms without having to cross east side suburban traffic in the station throat. The new arrangement also facilitated cross-platform interchange with the Central line at Stratford, with services commencing in 1946. Either side of the Ilford flyover there are single-track connections between each pair of lines, with the westbound track extending to Manor Park and just beyond. The eastbound track extends as far as Ilford station. It was also envisaged that a flyover would be built at the country-end of the carriage sidings at Gidea Park to allow trains bound for the Southend line to change from the main line to the electric line, instead of at the London-end of Shenfield as they do now.
Plans were drawn up in the 1930s to electrify the suburban lines from Liverpool Street to Shenfield at 1,500 V DC and work was started on implementing this. However, the outbreak of the Second World War brought the project to a temporary halt and it was not until 1949 that the scheme was completed with electrification being extended to Chelmsford in 1956.[7]
During World War II the long-distance named trains were withdrawn, and these returned after the war with the reintroduction of the "Hook Continental" and "Scandinavian" boat trains to Harwich Parkeston Quay in 1945. The East Anglian (Liverpool street – Norwich) was restored in October 1946 and in 1947 the "Day Continental" which pre-war had operated as the "Flushing Continental", recommenced operation.[8]
British Railways (1948–1994)
After nationalisation in 1948, the GEML formed part of the Eastern Region of British Railways.
The Summer 1950 timetable saw the introduction of a regular interval service between Liverpool Street and Clacton, which left Liverpool Street on the half-hour and Clacton on the hour. Summer Saturdays in 1950 also saw the introduction of the "Holiday Camps Express" workings to Gorleston, near Lowestoft. The latter half of 1950 and early 1951 saw the testing of new EM1 electric locomotives for use over the Woodhead Line between Manchester and Sheffield.[9]
January 1951 saw the introduction of the Britannia class 4-6-2 express locomotives and saw a speeding up of services on the GEML. However, not every one was a fan; British Railways chairman Sir Michael Barrington Ward exclaimed "What? Send the first British Railways standard engines to that tramline? No!"
23 Britannias were allocated to the GE section and, in summer 1951, the Liverpool Street–Norwich service went over to an hourly clockface interval service.[10][11]
The British Railways 1955 Modernisation Plan called for overhead line systems in Great Britain to be standardised at 25 kV AC. However, due to low clearances under bridges, the route was electrified at 6.25 kV AC. The section between Liverpool Street and Southend Victoria was completed in November 1960. Extensive testing showed that smaller electrical clearances could be tolerated for the 25 kV system than originally thought necessary. As a result, it was now possible to increase the voltage without having to either raise bridges or lower the tracks along the route to obtain larger clearances. The route between Liverpool Street and Southend Victoria was converted to 25 kV AC between 1976 and 1980.[12]
By the late 1970s, the costs of running the dated mechanical signalling systems north of Colchester was recognised and, in 1978, a scheme for track rationalisation and re-signalling was duly submitted to the Department of Transport. This was followed by a proposal, in 1980, to electrify the Great Eastern Main Line.[13]
The early 1980s saw track rationalisation and signalling work carried out in the Ipswich area and, on 9 April 1985, the first electric train consisting of two Class 305 electric multiple units (EMU) worked into Ipswich station. The previous year, another member of the class had been dragged to Ipswich by a diesel locomotive and was used for crew training. The first passenger carrying train was formed of British Rail Class 309 EMUs, which ran on 17 April 1985. The plan was for Inter-City trains to be hauled by British Rail Class 86 locomotives which, until the line beyond Ipswich to Norwich was electrified, would changeover with the Class 47s at Ipswich; this arrangement commenced from 1 May 1985.
During 1985-87, the line to Norwich was electrified and through electric working commenced in May 1987.[14]
In 1986, the line as far as Manningtree became part of Network SouthEast, although some NSE services actually terminated at Ipswich, whilst longer-distance Norwich services were operated by InterCity. Local services operating from the Ipswich and Norwich areas were operated by Regional Railways.
The privatisation era (1994 onwards)
Between 1997 and 2004, services into Essex and some into Suffolk were operated by First Great Eastern, whilst services into Norfolk and other Suffolk services were operated by Anglia Railways. Between 2004 and 2012, services out of Liverpool Street, except for a limited number of c2c trains, were all operated by National Express East Anglia. Since 2012, the franchise has been operated by Abellio Greater Anglia; in May 2015, the Shenfield "metro" stopping service transferred to TfL Rail, as a precursor to Crossrail.
Liverpool Street IECC replaced signal boxes at Bethnal Green (closed 1997), Bow (closed 1996), Stratford (GE panel closed 1997), Ilford (closed 1996), Romford (closed 1998), Gidea Park (closed 1998), Shenfield (closed 1992) and Chelmsford (closed 1994). The system uses BR Mark 3 solid state interlockings, predominantly four-aspect signals and a combination of Smiths clamp-lock and GEC-Alsthom HW2000 point machines.
The first signal box to be closed and transferred to Liverpool Street IECC was Shenfield in 1992, which had only opened 10 years earlier. The last boxes to be transferred were at Romford and Gidea Park in 1998; these were the oldest of those being transferred, having been opened under the GER/LNER 1924 resignalling scheme.
Accidents and incidents
A number of fatal accidents have occurred on the line throughout its history:
- 1840: Brentwood; four killed[15]
- 1872: Kelvedon; one killed and 16 injured in a derailment[16]
- 1905: Witham; 11 killed and 71 injured in a derailment[17]
- 1913: Colchester; three killed and 14 injured in a collision and derailment[18][19]
- 1915: Ilford; 10 killed and 500 injured in a collision between two trains[20]
- 1941: Brentwood; seven killed in a collision between two trains[21]
- 1944: Ilford; nine killed and 38 injured in a collision between two trains[22]
- 1944: Romford; one killed and three injured in a collision between two trains[23]
Infrastructure
The line is owned and maintained by Network Rail.[2] It is part of Network Rail Strategic Route 7, which is composed of SRSs 07.01, 07.02 and 07.03, and is classified as a primary line. The GEML has a loading gauge of W10 between Liverpool Street and Haughley Junction (approximately 13 miles 63 chains north of Ipswich[24]) and from there is W9 to Norwich. The maximum line speed is 100 mph (160 km/h).[25]
The main line is electrified at 25 kV AC using overhead wires and comes under the control of Romford Electrical Control Room. The branches to Upminster, Southend Victoria, Southminster, Braintree, Clacton-on-Sea, Walton-on-the-Naze and Harwich Town are also electrified.
Between Romford and Chadwell Heath, there is a Network Rail maintenance depot adjacent to the Jutsums Lane overbridge. In addition, at the London-end of the depot, is Network Rail's Electrical Control Room that controls the supply and switching of the overhead line system for the whole of the former Anglia Region.
Signalling is controlled by two main signalling centres: Liverpool Street IECC (opened in 1992) and Colchester PSB (opened in December 1983). Liverpool Street IECC controls signalling up to Marks Tey, where it fringes with Colchester PSB, which has control to Norwich. There are also several small signal boxes that control local infrastructure, such as Ingatestone box, which has jurisdiction over several local level crossings.
Line-side train monitoring equipment includes hot axle box detectors (HABD) on the down main and down electric lines near Brentwood (17 miles 35 chains from Liverpool Street) and on the up main near Margaretting (25 miles 78 chains). Other equipment includes wheel impact load detectors (WILD) ‘Wheelchex’ on the down main and up main west of Church Lane level crossing (24 miles 75 chains).[26][27]
Track layout
On leaving Liverpool Street, the route comprises two pairs of tracks, known as the mains and the electrics, with a further pair of tracks, the suburbans, which carry the West Anglia Main Line alongside the GEML to Bethnal Green.
From Bethnal Green, the GEML has four lines to Bow junction, where there is a complex set of switches and crossings. A line from the LTS (Fenchurch Street) route joins the "up" (London-bound) electric and there are a further two lines, the "up" and "down" Temple Mills, giving access to the North London Line and Temple Mills. The GEML has six tracks up to the London-end of Stratford and the junction to Temple Mills; there are five lines through the station, dropping to four at the country end.
At Shenfield, the line to Southend Victoria diverges and the main line route drops from four lines to two; this arrangement continues for the vast majority of the way to Norwich. There are several locations where the route has more than two lines, predominantly through stations such as Colchester and Ipswich, along with goods loops, such as at the London end of Ingatestone.
Tunnel and viaducts
Major civil engineering structures on the Great Eastern Main Line include the following:[26]
| Railway Structure | Length | Distance from London Liverpool Street Station | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trowse Swing Bridge (River Wensum) | 123 miles 37 chains (via Cambridge) | Norwich | |
| Lakenham Viaduct (including River Yare) | 8 chains (c. 160 metres) | 112 miles 33 chains – 112 miles 25 chains (via Ipswich) | Between Norwich and Diss stations |
| Thraston Viaduct (River Tas) | 105 miles 62 chains (via Ipswich) | ||
| River Waveney Viaduct | 94 miles 54 chains (via Ipswich) | South of Diss station | |
| Badley Viaduct (River Gipping) | 2 chains (c. 40 metres) | 79 miles 09 chains – 79 miles 07 chains (via Ipswich) | Between Stowmarket and Needham Market stations |
| Ipswich or Stoke Tunnel (see note below) | 361 yards (330 metres) | 68 miles 47 chains – 68 miles 31 chains | South of Ipswich station |
| Cattawade Viaduct | 4 chains (c. 80 metres) | 60 miles 10 chains – 60 miles 06 chains | East of Manningtree station |
| River Stour Viaduct | 4 chains (c. 80 metres) | 59 miles 75 chains – 59 miles 71 chains | |
| Lexden Viaduct (River Colne) | 6 chains (c. 120 metres) | 49 miles 69 chains – 49 miles 63 chains | West of Colchester (North) station |
| River Ter Viaduct | 35 miles 22 chains | Between Hatfield Peverel and Chelmsford stations | |
| Boreham Viaduct | 3 chains (c. 60 metres) | 32 miles 72 chains – 32 miles 69 chains | |
| River Chelmer Viaduct | 30 miles 25 chains | East of Chelmsford station | |
| Chelmsford Viaduct | 24 chains (c. 480 metres) | 29 miles 64 chains – 29 miles 40 chains | West of Chelmsford station |
| River Can Viaduct | 3 chains (c. 60 metres) | 29 miles 36 chains – 29 miles 26 chains | |
| Ilford or Aldersbrook Flyover | 6 miles 78 chains | West of Ilford station | |
| Bethnal Green Viaduct | 1 mile 6 chains (c. 1730 metres) | 1 miles 58 chains – 0 mile 52 chains | Bethnal Green |
Stoke tunnel
The only tunnel on the line is just south of Ipswich. The 361-yard (330 m) long tunnel was built by Peter Bruff as part of the Ipswich & Bury Railway. It was completed in 1846 and it is thought to be the earliest driven on a sharp continuous curve.[28] During the excavation of the tunnel, many important fossils were discovered, including rhinoceros, lion and mammoth; the site was known as the "Stoke Bone Beds".[29] The finds are considered important in understanding climate change during the Ice Age.[30] This tunnel had the trackbed lowered so the line could accommodate taller freight trains.
Rolling stock
Electric locomotive powered inter-city trains operated the London-Norwich service from electrification of the line in the mid-1980s until March 2020.
Class 86 locomotives powered the service from 1985 until 2005, with rakes of Mark 2 coaches. Push-pull services were introduced during their tenure, initially using a DBSO coach at the Norwich end and latterly with Driving Van Trailers, cascaded from the West Coast Main Line.
From 2004, Class 90 locomotives replaced the ageing Class 86s and rolling stock was updated with refurbished former West Coast Main Line Mark 3 coaches, following the introduction of the Class 390 Pendolino stock on that route.
By March 2020, new Class 745 EMUs had fully replaced Class 90 and Mark 3 coaches; thereby ending locomotive operation on the inter-city services on the Great Eastern Main Line.[31][32] Class 90s are still operating Freightliner services along with Class 66 and Class 70 diesels and Class 86 electrics.
Electric multiple units are used for inner and outer suburban passenger trains and diesel multiple units are used on non-electrified branch lines. Electric and diesel hauled freight services also operate on the Great Eastern Main Line.[2] The main passenger units utilised are:
- Class 315: 318 seats across four cars per trainset. Maximum speed 75 mph (120 km/h).
- Class 321: 307 seats across four cars. Maximum speed 100 mph (160 km/h).
- Class 345: 450 seats across nine cars.[Note 2] Maximum speed 90 mph (140 km/h).
- Class 360: 280 seats across four cars. Maximum speed 100 mph (160 km/h).
- Class 745: 757 seats across twelve cars. Maximum speed 100 mph (160 km/h).
- Class 755: 167 seats across three cars (class 755/3) or 229 seats across four cars (class 755/4). Maximum speed 100 mph (160 km/h).
Current developments
Crossrail
In 2015 TfL Rail, the precursor of Crossrail, took over operation of the Shenfield stopping "metro" service and, from 2021, the full Crossrail service will run via a tunnel through central London and link up with the Great Western Main Line to Reading and Heathrow Airport.
The first new Class 345 rolling stock entered service on the service on 22 June 2017. The new trains, built at Bombardier's Derby factory, provide air conditioned walk-through carriages, intelligent lighting and temperature control, closed-circuit television and passenger information displays showing travel information, including about onward journeys. It is planned that by September 2017, half of the services between Shenfield and Liverpool Street will have switched to the new Class 345 trains. From May 2015, Crossrail services (re-branded as TfL Rail) will interchange with existing GEML services at Liverpool Street (via new underground platforms), Stratford, Romford and Shenfield.
Proposed developments
A new station is planned at Great Blakenham as part of the SnOasis development approximately halfway between Needham Market and Ipswich,[33][34] Another is planned at Beaulieu, 3 miles north-east of Chelmsford entailing a long section of extra tracks on viaduct/bridge.[35]
Crossrail will run to Shenfield from summer 2021.[36]
In November 2013 an upgrade of the GEML to enable London-Norwich express services to achieve an improved journey time of 90 minutes was announced.[37]
Services
The majority of trains are operated by Abellio Greater Anglia, with TfL Rail operating the Liverpool Street to Shenfield stopping "metro" trains. A limited number of weekend c2c services operate on part of the line between Stratford and Liverpool Street.[2]
Main line
Fast and semi-fast services utilise the main line between Liverpool Street and Shenfield. Branch lines diverge at Romford, Shenfield, Witham, Marks Tey, Colchester, Ipswich, Stowmarket and Norwich.
Additionally, a very limited number of main line services call at Ilford, Seven Kings and Gidea Park during early mornings and late nights, often for the convenience of drivers who may be working at these locations.
| Station | Borough | Branch lines | Patronage, 2017/18 |
|---|---|---|---|
| London Liverpool Street | City of London | 66,966,512 | |
| Stratford | Newham | 40,077,086 | |
| Romford | Havering | Romford–Upminster line | 8,702,772 |
| Shenfield | Brentwood | Shenfield–Southend line | 3,872,486 |
| Ingatestone | Brentwood | 875,874 | |
| Chelmsford | Chelmsford | 8,619,956 | |
| Hatfield Peverel | Braintree | 419,264 | |
| Witham | Braintree | Braintree branch line | 2,331,630 |
| Kelvedon | Braintree | 844,570 | |
| Marks Tey | Colchester | Gainsborough line | 577,550 |
| Colchester | Colchester | Sunshine Coast line | 4,378,758 |
| Manningtree | Tendring | Mayflower line | 1,078,502 |
| Ipswich | Ipswich | East Suffolk line; Felixstowe branch line | 3,351,902 |
| Needham Market † | Mid Suffolk | 100,648 | |
| Stowmarket | Mid Suffolk | Ipswich–Ely line | 935,244 |
| Diss | South Norfolk | 689,962 | |
| Norwich | Norwich | Wherry lines; Bittern line; Breckland line | 4,156,302 |
† Needham Market is not served by main line trains.
Electric line
A high-frequency stopping service operates on the line, referred to as the Shenfield Metro, between Liverpool Street and Shenfield; it serves all stations and is currently operated by TfL Rail. The off-peak service consists of six trains per hour, with some additional services during peak times.[2] During peak times, some trains start or terminate at Gidea Park. The line is mostly within Greater London, with two stations in the Essex borough of Brentwood.
The electric line is also used by limited services extending to and from Southend Victoria.[2]
| Station | Travelcard zone | Borough | Patronage, 2017/18 |
|---|---|---|---|
| London Liverpool Street | 1 | City of London | 66,966,512 |
| Stratford | 2/3 | Newham | 40,077,086 |
| Maryland | 3 | Newham | 1,145,882 |
| Forest Gate | 3 | Newham | 2,834,734 |
| Manor Park | 3/4 | Newham | 1,601,080 |
| Ilford | 4 | Redbridge | 7,679,264 |
| Seven Kings | 4 | Redbridge | 2,959,784 |
| Goodmayes | 4 | Redbridge | 3,544,810 |
| Chadwell Heath | 5 | Redbridge | 3,755,174 |
| Romford | 6 | Havering | 8,702,772 |
| Gidea Park | 6 | Havering | 2,711,136 |
| Harold Wood | 6 | Havering | 2,929,720 |
| Brentwood | 9 | Brentwood | 2,992,072 |
| Shenfield | C | Brentwood | 3,872,486 |
Passenger volume
These are the passenger usage statistics from the year beginning April 2002 to the year beginning April 2013. Needham Market is the only station on the line that is not served by trains to/from London.
| Station usage | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station name | 2002–03 | 2004–05 | 2005–06 | 2006–07 | 2007–08 | 2008–09 | 2009–10 | 2010–11 | 2011–12 | 2012–13 | 2013–14 | 2014–15 | 2015–16 | 2016–17 | 2017–18 | 2018–19 | 2019–20 |
| Norwich | 2,351,236 | 2,421,607 | 2,527,760 | 2,711,910 | 3,449,930 | 3,568,618 | 3,496,082 | 3,749,474 | 3,911,508 | 4,126,012 | 4,139,820 | ||||||
| Diss | 328,606 | 314,136 | 325,553 | 417,857 | 551,781 | 559,544 | 539,234 | 600,904 | 621,728 | 646,158 | 675,527 | ||||||
| Stowmarket | 367,331 | 417,729 | 453,271 | 545,670 | 705,682 | 751,802 | 756,484 | 855,692 | 884,962 | 927,856 | 944,466 | ||||||
| Needham Market | 12,014 | 16,237 | 25,472 | 37,074 | 43,987 | 52,782 | 58,054 | 67,056 | 77,554 | 85,078 | 91,358 | ||||||
| Ipswich | 2,022,546 | 2,017,300 | 2,144,935 | 2,402,852 | 2,807,395 | 2,825,352 | 2,774,536 | 3,004,678 | 3,159,348 | 3,348,394 | 3,312,522 | ||||||
| Manningtree | 574,633 | 719,792 | 707,782 | 865,217 | 910,384 | 833,888 | 799,776 | 890,624 | 983,054 | 1,093,178 | 1,154,294 | ||||||
| Colchester | 4,005,869 | 4,305,315 | 4,287,601 | 4,337,926 | 4,516,616 | 4,502,739 | 4,218,622 | 4,362,914 | 4,584,110 | 4,291,055 | 4,402,045 | ||||||
| Marks Tey | 364,979 | 384,337 | 400,155 | 432,073 | 459,980 | 443,724 | 428,804 | 428,816 | 437,006 | 473,162 | 494,998 | ||||||
| Kelvedon | 789,487 | 774,972 | 759,680 | 787,033 | 799,439 | 797,236 | 763,240 | 791,312 | 827,358 | 812,610 | 837,236 | ||||||
| Witham | 2,173,543 | 2,261,186 | 2,307,269 | 2,342,618 | 2,341,123 | 2,277,436 | 2,076,532 | 2,159,09 | 2,251,940 | 2,244,774 | 2,349,736 | ||||||
| Hatfield Peverel | 419,144 | 418,145 | 412,523 | 416,083 | 398,255 | 394,420 | 357,382 | 357,458 | 389,284 | 399,602 | 408,896 | ||||||
| Chelmsford | 6,445,365 | 6,698,243 | 6,801,193 | 7,113,065 | 7,447,696 | 7,375,452 | 6,934,970 | 7,335,952 | 7,876,686 | 8,002,126 | 8,286,879 | ||||||
| Ingatestone | 554,235 | 606,007 | 628,220 | 630,362 | 649,324 | 637,918 | 596,310 | 636,170 | 694,754 | 715,974 | 750,746 | ||||||
| Shenfield | 2,701,210 | 2,861,253 | 2,907,917 | 2,965,886 | 3,024,519 | 3,008,422 | 2,825,598 | 2,936,428 | 2,991,100 | 3,131,298 | 3,314,120 | ||||||
| Brentwood | 2,361,639 | 2,475,272 | 2,535,139 | 2,479,150 | 2,520,143 | 2,557,092 | 2,322,842 | 2,420,930 | 2,495,480 | 2,701,998 | 2,809,578 | ||||||
| Harold Wood | 1,879,400 | 1,770,874 | 1,773,086 | 3,014,836 | 3,476,002 | 3,042,946 | 2,808,636 | 2,552,716 | 2,580,280 | 2,857,572 | 2,917,788 | ||||||
| Gidea Park | 1,838,172 | 1,689,192 | 1,670,663 | 2,703,604 | 3,172,538 | 2,587,398 | 2,401,226 | 2,467,414 | 2,524,448 | 2,587,142 | 2,810,806 | ||||||
| Romford | 5,208,851 | 5,118,900 | 4,823,860 | 7,363,378 | 8,372,672 | 7,310,172 | 6,736,060 | 6,817,246 | 6,998,872 | 7,445,556 | 8,265,442 | ||||||
| Chadwell Heath | 1,836,872 | 1,607,729 | 1,556,568 | 2,208,567 | 2,352,716 | 2,246,672 | 1,977,616 | 2,144,996 | 2,228,662 | 2,346,218 | 2,686,904 | ||||||
| Goodmayes | 1,472,318 | 1,155,770 | 1,070,419 | 1,961,690 | 2,092,464 | 1,929,478 | 1,792,694 | 2,069,248 | 2,306,452 | 2,389,588 | 2,625,572 | ||||||
| Seven Kings | 1,694,399 | 1,174,319 | 1,095,940 | 1,567,157 | 1,764,774 | 1,657,658 | 1,528,296 | 1,708,550 | 1,879,664 | 2,112,832 | 2,330,778 | ||||||
| Ilford | 3,679,035 | 2,931,960 | 2,623,618 | 5,075,338 | 6,119,745 | 5,559,414 | 5,363,400 | 6,286,174 | 6,721,496 | 6,854,314 | 7,632,352 | ||||||
| Manor Park | 875,206 | 694,315 | 656,895 | 1,291,690 | 1,443,311 | 1,232,484 | 1,160,120 | 1,424,914 | 1,593,348 | 1,659,972 | 1,809,714 | ||||||
| Forest Gate | 1,209,066 | 956,231 | 915,549 | 1,891,875 | 2,037,387 | 1,706,018 | 1,598,816 | 1,914,054 | 2,205,106 | 2,403,326 | 2,647,058 | ||||||
| Maryland | 265,274 | 197,259 | 196,927 | 450,314 | 503,987 | 431,350 | 425,176 | 501,956 | 541,942 | 699,584 | 939,324 | ||||||
| Stratford | 2,597,390 | 7,914,419 | 7,699,178 | 13,089,922 | 13,368,783 | 12,303,033 | 12,370,245 | 17,479,020 | 21,797,460 | 25,564,250 | 26,377,506 | ||||||
| London Liverpool Street | 38,968,814 | 50,469,209 | 47,271,234 | 55,265,748 | 57,759,809 | 55,103,416 | 51,596,155 | 55,769,423 | 57,105,400 | 58,448,814 | 63,004,002 | ||||||
| The annual passenger usage is based on sales of tickets in stated financial years from Office of Rail and Road estimates of station usage. The statistics are for passengers arriving and departing from each station and cover twelve month periods that start in April. Methodology may vary year on year. Barking and Blackhorse Road are affected by usage of the ticket gates for the underground and that Gospel Oak connects to the North London Line section of the London Overground and is similarly affected. Barking is further affected by the ticket gates used to access C2C services. | |||||||||||||||||
Notes
- Fenchurch Street was served by GER and LTSR services at this time and GER services were routed via Bow Road
- Running in reduced seven car formation from 2017-2020.
References
- National Rail, Rail Services Around London & the South East, (2006)
- Network Rail Archived 15 December 2006 at the Wayback Machine - Route 7 - Great Eastern (PDF)
- "Eagle 61 :: Railway Guide books of the Eastern Counties Railway". Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- Moffat, Hugh (1987). East Anglia's first railways. Lavenham: Terence Dalton Limited. pp. 62–69 and 85–90. ISBN 0 86138 038 X.
- Vaughan, Adrian (1997). Railwaymen, Politics and Money. London: John Murray. pp. 134, 135. ISBN 0 7195 5150 1.
- Kay, Peter (1996). Great Eastern in Town and Country Volume 3. Clophill, UK: Irwell Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 1-871608-74-0.
- Wilmoth, VJ (1956). "British Railways Electrification". Civil Engineering and Public Works. 51 (600): 660–661.
- Butcher, Ken (July 2019). "Trainspotting at Shenfield 1948-1955". Great Eastern Journal. 179: 25.
- Butcher, Ken (July 2019). "Trainspotting at Shenfield 1948-1955". Great Eastern Journal. 179: 28, 29.
- Butcher, Ken (July 2019). "Trainspotting at Shenfield 1948-1955". Great Eastern Journal. 179: 29.
- Dawes, Derrick (July 2019). "TA Sumer Saturday at Liverpool Street 1951". Great Eastern Journal. 179: 9.
- Glover, John (2003). "Eastern Electric", Ian Allan, London. ISBN 0-7110-2934-2.
- Cowley, Ian (1987). Anglia East. Newton Abbot,UK: David & Charles. p. 14. ISBN 0-7153-8978-5.
- Cowley, Ian (1987). Anglia East. Newton Abbot,UK: David & Charles. pp. 43–47. ISBN 0-7153-8978-5.
- Cecil J Allen; 'The Great Eastern Railway' 1955
- http://www.railwaysarchive.co.uk/documents/RSSB_Kelvedon2005.pdf
- "Accident at Witham on 1st September 1905 :: The Railways Archive". www.railwaysarchive.co.uk. Retrieved 3 November 2018.
- Simon Webb (31 January 2013). The Colchester Book of Days. Perseus Books Group. pp. 203–. ISBN 978-0-7524-8908-7.
- Trevena, Arthur (1981). Trains in Trouble: Vol. 2. Redruth: Atlantic Books. p. 25. ISBN 0-906899-03-6.
- Rolt, L.T.C.; Kichenside, Geoffrey (1982) [1955]. Red for Danger (4th ed.). Newton Abbot: David & Charles. pp. 240–241. ISBN 0-7153-8362-0.
- http://www.railwaysarchive.co.uk/documents/MoT_HaroldWood1940.pdf
- Mount & Wilson 1944, pp. 1-5.
- http://www.railwaysarchive.co.uk/documents/MoT_Romford1944.pdf
- http://rmme.railmiles.me/
- "Route 7 - Great Eastern" (PDF). Network Rail. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
- Brailsford, Martyn (2016). Railway Track Diagrams Book 2 Eastern. Frome: Trackmaps. pp. 2, 5–7. ISBN 978-0-9549866-8-1.
- "Railway Codes: HABD and WILD devices".
- Moffat, Hugh (1987). East Anglia's First Railways. Lavenham: Terence Dalton. ISBN 0-86138-038-X.
- "Mammoth on High Street". Seven Wondered of Ipswich. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- "Collections:Geology". Ipswich Borough Council. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- Abellio wins East Anglian rail franchise for nine years in £1.4bn deal East Anglian Daily Times 10 August 2016
- Geater, Paul. "End of the line for traditional trains on Greater Anglia routes". East Anglian Daily Times. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- "Listening to residents and their concerns". Neil MacDonald. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Final Government Approval". BBC news. 6 November 2008.
- "£53m rail station at Beaulieu is on track". Chelmsford Weekly News. 18 September 2013.
- "Crossrail in numbers". crossrail.co.uk. Retrieved 3 November 2018.
- "'Norwich in Ninety' rail taskforce announced by Chancellor". www.gov.uk. 7 November 2013. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
Further reading
- Allen, Geoffrey Freeman (January 1983). "It's 'Go' for the Great Eastern - at last!". Rail Enthusiast. EMAP National Publications. pp. 41–43. ISSN 0262-561X. OCLC 49957965.
- Allen, David (28 January – 10 February 1998). "Resignalling the Great Eastern". RAIL. No. 323. EMAP Apex Publications. pp. 28–33. ISSN 0953-4563. OCLC 49953699.
- Mount, AHL; Wilson, GRS (15 March 1944). Report on the collision at Ilford (PDF). Ministry of War Transport. Retrieved 7 September 2012.