India–South Korea relations
India–South Korea relations (Hindi: भारत-दक्षिण कोरिया संबंध; Korean: 인도-대한민국 관계), also called Indian-South Korean relations, refers to the bilateral relations between India and South Korea. Formal establishment of diplomatic ties between the two countries occurred in 1973. Since then, several trade agreements have been reached: Agreement on Trade Promotion and Economic and Technological Co-operation in 1974; Agreement on Co-operation in Science & Technology in 1976; Convention on Double Taxation Avoidance in 1985; and Bilateral Investment Promotion/ Protection Agreement in 1996.
 | |
India |
South Korea |
|---|---|
| Diplomatic mission | |
| Embassy of India, Seoul | Embassy of South Korea, New Delhi |
| Envoy | |
| Indian Ambassador to South Korea Sripriya Ranganathan | South Korean Ambassador to India Shin Bong-kil |
Trade between the two nations has increased greatly, from $530 million during the fiscal year of 1992-1993, to US$10 billion during 2006-2007.[1] It further increased to US$17.6 billion in the year 2013.
India-RoK relations have made great strides in recent years and have become truly multidimensional, spurred by a significant convergence of interests, mutual goodwill and high level exchanges. South Korea is currently the fifth largest source of investment in India.[2] Korean companies such as LG and Samsung have established manufacturing and service facilities in India, and several Korean construction companies won grants for a portion of the many infrastructural building plans in India, such as the National Highways Development Project.[2] Tata Motors' purchase of Daewoo Commercial Vehicles at the cost of US$102 million highlights India's investments in Korea, which consist mostly of subcontracting.[2]
The Indian Community in Korea is estimated to number 8,000. Their composition includes businesspeople, IT professionals, scientists, research fellows, students and workers. There are about 150 businesspeople dealing mainly in textiles. Over 1,000 IT professionals and software engineers have recently come to Korea to work, including in large conglomerates such as Samsung and LG. There are about 500 scientists and post-doctoral research scholars in Korea.[3]
Pre-modern relations
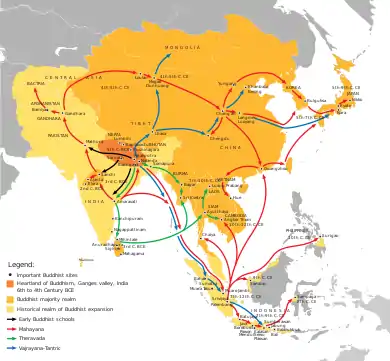


Centuries after Buddhism originated in India, the Mahayana Buddhism arrived in China through the Silk Route in 1st century CE via Tibet, then to Korea peninsula in 3rd century during the Three Kingdoms Period from where it transmitted to Japan.[4] The Samguk yusa records following 3 monks among the first to bring Buddhist teaching, or Dharma, to Korea: Malananta (late 4th century) - an Indian Buddhist monk who brought Buddhism to Baekje in the southern Korean peninsula, Sundo -a Chinese Buddhist monk who brought Buddhism to Goguryeo in northern Korea, and Ado - Chinese Buddhist monk who brought Buddhism to Silla in central Korea.[5][6] In Korea, it was adopted as the state religion of 3 constituent polities of the Three Kingdoms Period, first by the Goguryeo (Gaya) in 372 CE, by the Silla in 528 CE, and by the Baekje in 552 CE.[4]
In 526 CE, Korea monk Gyeomik, went to India to learn Sanskrit and study the monastic discipline Vinaya, and founded the Gyeyul (Korean: 계율종; Hanja: 戒律宗; RR: Gyeyuljong) branch of Buddhism that specializes in the study of Vinaya which derives directly from the Indian Vinaya School.[7]
A 2005 government survey indicated that about a quarter of South Koreans identified as Buddhist,[8] though including the people outside of the practicing population who are deeply influenced by Buddhism as part of Korean traditions, the number of Buddhists in South Korea is considered to be much larger.[9] Similarly, in officially atheist North Korea, while Buddhists officially account for 4.5% of the population, a much larger number (over 70%) of the population are influenced by Buddhist philosophies and customs.[10][11]
The fact that people on the Indian subcontinent were familiar with Korea's customs and beliefs is amply testified by the records of the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim, Yijing who reached India in 673. Yijing writes that Indians regarded Koreans as "worshipers of the rooster". This concept about Koreans was grounded in a legend of the Silla dynasty.[12]
In 2001, a Memorial of Heo Hwang-ok from 48 C.E, who is believed to be a princess of Indian origin named Suriratna, was inaugurated by a Korean delegation in the City of Ayodhya, India, which included over a hundred historians and government representatives.[13] In 2016, a Korean delegation proposed to develop the memorial. The proposal was accepted by the Uttar Pradesh chief minister Akhilesh Yadav.[14][15] Kim Jung-sook, first lady of South Korea inaugurated the groundbreaking of Queen Heo Hwang-ok memorial with chief minister of Uttar Pradesh Yogi Adityanath in November 2018 which is planned to be completed on year 2020.[16] Gimhae which already has a tomb and pagoda of Queen Heo Hwang-ok is now constructing a 3000 square meters of museum and exhibition hall.[17]
A famous Korean visitor to India was Hyecho, a Korean Buddhist monk from Silla, one of the three Korean kingdoms of the period. On the advice of his Indian teachers in China, he set out for India in 723 CE to acquaint himself with the language and culture of the land of the Buddha. He wrote a travelogue of his journey in Chinese, Wang ocheonchukguk jeon or "An account of travel to the five Indian kingdoms". The work was long thought to be lost. However, a manuscript turned up among the Dunhuang manuscripts during the early 20th century.
A rich merchant from the Ma'bar Sultanate, Abu Ali (P'aehali) 孛哈里 (or 布哈爾 Buhaer), was associated closely with the Ma'bar royal family. After falling out with them, he moved to Yuan dynasty China, married a Korean woman and received a job from the Mongol Emperor. His wife was formerly married to Sangha, a Tibetan,[18] and her father was Ch'ae In'gyu during the reign of Chungnyeol of Goryeo, recorded in the Dongguk Tonggam, Goryeosa and Liu Mengyan's Zhong'anji.[19][20]
Modern relations
During the 1997 Asian financial crisis, South Korean businesses sought to increase access to the global markets, and began trade investments with India.[1]
The India-Republic of Korea Joint Commission for bilateral co-operation was established in February 1996, which is chaired by the External Affairs Minister and the Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade from the Korean side. So far, six meetings of the Joint Commission have been held, with the last one held in Seoul in June 2010.
In an interview by the Times of India, former Korean President Roh Tae-woo voiced his opinion that co-operation between India's software and Korea's IT industries would bring successful outcomes.[21] The two countries agreed to shift their focus to the revision of the visa policies between the two countries, expansion of trade, and establishment of free trade agreement to encourage further investment between the two countries.
There was a State Visit to Korea by Indian President Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, in February 2006 that heralded a new vibrant phase in India-Korean relations. It lead to the launch of a Joint Task Force to conclude a bilateral Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), which was signed by Minister for Commerce and Industry Shri Anand Sharma at Seoul on August 7, 2009.
Korean President Lee paid a landmark visit to India, as Chief Guest at India's Republic Day celebrations on 26 January 2010, when bilateral ties were raised to the level of Strategic Partnership.
An Indian Cultural Centre was established in ROK in April 2011 and the Festival of India in Korea was inaugurated by Dr. Karan Singh, President of Indian Council for Cultural Relations on 30 June 2011, to revitalise the cultural relations between the two countries.
Indian President Smt. Pratibha Devisingh Patil came on a State Visit to Korea from 24–27 July 2011, during which the Civil Nuclear Energy Cooperation Agreement was signed.
In June 2012, India, a major importer of arms and military hardware planned eight warships from South Korea but the contract ended in cancellation.[22]
Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh paid an official visit to Seoul from 24–27 March 2012, pertaining to Nuclear Security Summits, which led to the deepening of bilateral strategic partnership that was forged during President Lee Myung-bak’s State visit to India. An agreement on visa simplification was signed on 25 March 2012 in the presence of the two leaders at the Blue House. A Joint Statement was also issued during the PM's visit.
Former South Korean President Park Geun-hye visited India in 2014.
In July 2018, South Korean President Moon Jae-in and Indian Prime minister Narendra Modi jointly inaugurated Samsung Electronics's smartphone assembly factory in Noida, the largest such factory in the world.[23]
See also
- Buddhism in Korea
- Hinduism in Korea
- Indians in Korea
- Koreans in India
- India – North Korea relations
- History of Korea
Further reading
- Cultural relations of India and Korea / Raghuvira. In: Vivekananda, ., & Lokesh, Chandra (1970). India's contribution to world thought and culture. Madras: Vivekananda Rock Memorial Committee.
- Jain, Sandhya, & Jain, Meenakshi (2011). The India they saw: Foreign accounts. New Delhi: Ocean Books. Vol. I contains material about Korean (and Chinese) Buddhist pilgrims to India.
- Kumar, Rajiv (2018). South Korea's New Approach to India. Observer Research Foundation
- Kumar, Rajiv (2015). "Explaining the origins and evolution of India’s Korean policy", International Area Studies Review, vol. 18(2), pp. 182–198.
- Kumar, Rajiv (2015). "Korea’s Changing Relations with the United States and China: Implications for Korea- India Economic Relations," Journal of Asiatic Studies, pp. 104–133 (Asiatic Research Center, Korea University)
References
- IDSA publication Archived December 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- FICCI info Archived 2008-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sorry for the inconvenience". April 2016.
- Lee Injae, Owen Miller, Park Jinhoon, Yi Hyun-Hae, 2014, Korean History in Maps, Cambridge University Press, pp. 44-49, 52-60.
- "Malananta bring Buddhism to Baekje" in Samguk Yusa III, Ha & Mintz translation, pp. 178-179.
- Kim, Won-yong (1960), "An Early Gilt-bronze Seated Buddha from Seoul", Artibus Asiae, 23 (1): 67–71, doi:10.2307/3248029, JSTOR 3248029, pg. 71
- The Buddhist Religion: a historical introduction. Richard H. Robinson, Willard L. Johnson, Sandra Ann Wawrytko. Wadsworth Pub. Co., 1996
- According to figures compiled by the South Korean National Statistical Office."인구,가구/시도별 종교인구/시도별 종교인구 (2005년 인구총조사)". NSO online KOSIS database. Archived from the original on September 8, 2006. Retrieved August 23, 2006.
- Kedar, Nath Tiwari (1997). Comparative Religion. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 81-208-0293-4.
- Religious Intelligence UK Report
- North Korea, about.com
- Korea Journal Vol.28. No.12 (Dec. 1988)
- Korean memorial to Indian princess, 6 March 2001, BBC
- UP CM announces grand memorial of Queen Huh Wang-Ock, 1 March 2016, WebIndia123
- Choe, Chong-dae (12 July 2016). "Legacy of Queen Suriratna". The Korea Times. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- Ahuja, Sanjeev K. "Coming soon, Musical on Queen Huh of Korea; Princess Suriratna of Ayodhya". Asian Community News. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- Ahuja, Sanjeev K. "Korea to have first museum of Indian princess Suriratna". Asian Community News. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- Shaykh 'Âlam: the Emperor of Early Sixteenth-Century China, p. 15.
- Angela Schottenhammer (2008). The East Asian Mediterranean: Maritime Crossroads of Culture, Commerce and Human Migration. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 138–. ISBN 978-3-447-05809-4.
- SEN, TANSEN. 2006. “The Yuan Khanate and India: Cross-cultural Diplomacy in the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Centuries”. Asia Major 19 (1/2). Academia Sinica: 317. JSTOR.
- Blue House commentary Archived 2007-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
- "India to buy 8 warships from South Korea for Rs 6,000 crore". The Times of India. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- "Samsung opens world's biggest smartphone factory in India". Retrieved 2018-07-19.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Relations of India and South Korea. |
- Coping with Giants: South Korea’s Responses to China’s and India’s Rise by Chung Min Lee, Strategic Asia 2011-12: Asia Responds to Its Rising Powers - China and India (September 2011)
- List of Agreements signed between India and South Korea in May 2015
- Rajiv Kumar. "Explaining the origins and evolution of India’s Korean policy", International Area Studies Review, June 2015; vol. 18(2), pp. 182–198.
- Rajiv Kumar. "Korea’s Changing Relations with the United States and China: Implications for Korea- India Economic Relations," Journal of Asiatic Studies, 2016 vol. 58(4), pp. 104–133 (Asiatic Research Center, Korea University)
