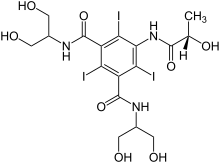
Iopamidol
Iopamidol (INN), sold under the brand name Isovue among others, is a nonionic, low-osmolar iodinated contrast agent, developed by Bracco Diagnostics.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Isovue, Iopamiro, Gastromiro, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Intravascular, intravenous, intrathecal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.430 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H22I3N3O8 |
| Molar mass | 777.089 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
It is available in various concentrations, from 200 to 370 mgI/mL.[4]
Medical uses
Iopamidol is indicated for angiography throughout the cardiovascular system, including cerebral and peripheral arteriography, coronary arteriography and ventriculography, pediatric angiocardiography, selective visceral arteriography and aortography, peripheral venography (phlebography), and adult and pediatric intravenous excretory urography and intravenous adult and pediatric contrast enhancement of computed tomographic (CECT) head and body imaging.[4]
It is also indicated for intrathecal administration in adult neuroradiology including myelography (lumbar, thoracic, cervical, total columnar), and for contrast enhancement of computed tomographic (CECT) cisternography and ventriculography. Isovue-M 200 (lopamidol Injection) is indicated for thoraco-lumbar myelography in children over the age of two years.[3]
Nursing considerations: Early generations of IV contrast carried considerable nephrotoxicity, necessitating continual assessment of renal function. IV and PO fluids are encouraged post operation to facilitate excretion of contrast. There is a common myth in medicine and nursing that patients may be allergic to iodine in contrast, however, there is considerable evidence to the contrary. This is likely a carryover of confusion regarding contrast-reactions to early generations of IV contrast which were of sufficiently high osmolarity to induce degranulation of mast cells which manifests clinically as similar in appearance to anaphylaxis due to massive release of histamine. There is no need to assess patients for allergies to iodine or shellfish as allergy to iodine is physiologically impossible in a hemodynamically stable patient. Allergy to iodine would immediately manifest as overwhelming anaphylaxis due to presence of iodine in triiodothyronine(T3) and thyroxine(T4). Shellfish allergies have been demonstrated to be due to proteins produced by the organisms, not due to iodine.
References
- "Iopamidol". Drugs.com. 10 August 2020. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- "Gastromiro - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- "Isovue-M- iopamidol injection, solution". DailyMed. 24 October 2019. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- "Isovue 300- iopamidol injection, solution Isovue 370- iopamidol injection, solution Isovue 200- iopamidol injection, solution Isovue 250- iopamidol injection, solution". DailyMed. 1 December 2019. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
