List of Royal Norwegian Navy ships
This article is a list of Royal Norwegian Navy fleet units and vessels, both past and present.
Ships from the years 1509 to 1814 might be listed under Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy.
Fleet units and vessels (present)
Frigates

HNoMS Fridtjof Nansen
- Fridtjof Nansen class
- Fridtjof Nansen (F310)[1]
- Roald Amundsen (F311)[2]
- Otto Sverdrup (F312)[3]
- Helge Ingstad (F313) (Ship sank on 13 November 2018)
- Thor Heyerdahl (F314)[4]
Support vessels
- Reinøysund (L4502) (former landing vessel)
- Rotsund (L4505) (former landing vessel)
Royal yacht
- Norge (A553) (formerly Philante, a private yacht of British ownership; escort vessel during WWII)
- K/B Stjernen royal boat.
Minesweepers

Alta-class minesweeper Rauma
- Oksøy-class mine hunter (1994)
- Oksøy M340
- Karmøy M341
- Måløy M342
- Hinnøy M343
- Alta-class minesweeper (1996)
- Alta M350
- Otra M351
- Rauma M352
- Orkla M353 (Ship sunk due to fire on 19 November 2002)
- Glomma M354
- Tyr (N50), discovered wreck of German submarine U-735 in 1999 and wreck of British Royal Navy destroyer HMS Hunter in 2008.
- Mine Clearance Command (divers)
Submarine branch

Ula class submarine
The submarine fleet consists of several Ula-class submarines.
- 1st Submarine Squadron (Diesel-electric Ula-class submarines):
MTB branch
_(2_Nov_2001).jpg.webp)
Skjold-class missile patrol boat HNoMS Skjold
The Coastal Warfare fleet consists of six Skjold-class missile patrol boats. The boat type is often branded a corvette.
- Missile Torpedo Boat Command
- Missile Patrol Boat (Skjold class):
- Skjold (P960)
- Storm (P961)
- Skudd (P962)
- Steil (P963)
- Glimt (P964)
- Gnist (P965)
- Support vessel:
- Missile Patrol Boat (Skjold class):
Naval Ranger branch

A Norwegian Combat Boat 90
- Norwegian Naval Special Operations Commando (Naval Ranger Command)
- Coastal Ranger Command
- Norwegian Mine Diver Command
- Tactical Boat Squadron
- Combat Boat 90 (1996)
- Trondenes
- Skrolsvik
- Kråkenes
- Stangnes
- Kjøkøy
- Mørvika
- Kopås
- Tangen
- Oddane
- Malmøya
- Hysnes
- Brettingen
- Løkhaug
- Søviknes
- Hellen
- Osternes
- Fjell
- Lerøy
- Torås
- Møvik
- Combat Boat 90 (1996)
Logistics branch
In the process of establishing a "logistics on keel" system.
Coast Guard units and vessels

Coast Guard vessel NoCGV Nordkapp patrolling at Svalbard
- Coast Guard Squadron North
- Svalbard
- Nordkapp class
- Andenes
- Nordkapp
- Senja
- Harstad
- Chieftain
- Thorsteinson
- Sjøveien
- Nysleppen
- Barentshav
- Torsteinson
- Åhav
- Kongsøy
- Stålbas
- Coast Guard Squadron South
- Future vessels
- Six vessels of the Nornen class ordered
- Three hybrid diesel-LNG vessels, two to be named Barentshav and Sortland and one unnamed ordered
Naval schools
- Royal Norwegian Naval Basic Training Establishment, HNoMS Harald Haarfagre, Stavanger
- Royal Norwegian Navy Officer Candidate School, Horten
- Royal Norwegian Naval Academy, Laksevåg, Bergen
- Royal Norwegian Naval Training Establishment, HNoMS Tordenskjold, Haakonsvern, Bergen
Navy vessels (past)
Several earlier ships are listed under Denmark.
Amphibious landing vessels
- Kvalsund class
- Kvalsund (1968–1991)
- Raftsund
- Reinøysund (2) class
- Reinøysund Still in use or in reserve?
- Rotsund Still in use or in reserve?
- Borgsund
- Sørøysund (L4503) (Later rebuilt to Tjeldsund class)
- Maursund (L4504) (Later rebuilt to Tjeldsund class)
- Tjeldsund class
- Tjeldsund (L4506)
Armed auxiliaries

Naval trawler HNoMS Honningsvåg
- Alpha (1904–1940?) patrol boat
- Alversund (1926–1940) patrol boat, sunk by own crew.
- Andenes (?–1940?) patrol boat
- Aud I (?–1940?) patrol boat
- Bergholm used as MCM vessel and Shetland Bus.
- Beta (1900–1940?) patrol boat
- Bjerk (1912–?) patrol boat
- Blink (1896–1940?) patrol boat
- Blåsel patrol boat
- Bodø Sunk by a mine in 1943
- Commonwealth (1912–1940?) patrol boat
- Honningsvåg, naval trawler, originally the German trawler Malangen, captured by Norwegian forces at Honningsvåg 13 April 1940
- Pol III, armed whaler; engaged German Kampfgruppe 5 on 8 April 1940, its captain, Leif Welding-Olsen, became the first Norwegian uniformed casualty of WWII
- Thorodd, patrol boat
Brigs
- Allart (1807/1825–1825)[1]
- Alsen (1808/1814–1837)[1]
- Fredriksværn (1817–1854)[1]
- Hemnæs (1814–1821)[1]
- Kiel (1809/1814–1817)[1]
- Langeland (1808/1814–1827)[1]
- Lolland (1818–1847)[1]
- Lougen (1805/1814–1882)[1]
- Samsøe (1808/1814–1820)[1]
- Seagull (1808/1814–1817) Launched 1805. Captured from the Royal Navy off Lindesnes 19 June 1808.[1]
- Statsraad Erichsen (1859–1900)[1]
Coastal defence ships

HNoMS Tordenskjold at Kiel in 1900
- Tordenskjold class
- Tordenskjold (1897–1948)
- Harald Haarfagre (1897–1948)
- Eidsvold class
- Bjørgvin class
- Bjørgvin (1912) – Seized by the Royal Navy and renamed HMS Glatton, blew up in September 1918.
- Nidaros (1912) – Seized by the Royal Navy and renamed HMS Gorgon.
Corvettes
- Ellida (1849–1866)[1]
- Ellida (1882–1925)[1]
- Nordstjernen (1844–1858)[1]
- Nordstjernen (1864–1940/1945)[1]
- Nornen (1855–1903)[1]
- Nidaros (1851–1903)[1]
- Ørnen (1829–1874)[1]
- Ørnen (1849–1866)[1]
- Flower class – Six vessels received from the Royal Navy
- Andenes – ex-HMS Acanthus
- Nordkyn – ex-HMS Buttercup
- Eglantine – ex-HMS Eglantine
- Montbretia – ex-HMS Montbretia, sunk by U-262 on 18 November 1942.
- Potentilla (1942–1944)- ex-HMS Potentilla
- Rose – ex-HMS Rose
- Polarfront II – ex-HMS Bryony, used as a weather ship.
- Castle class – One vessel received from the Royal Navy
- Tunsberg Castle – ex-HMS Shrewsbury Castle, was sunk by a mine near Båtsfjord, Norway on 12 December 1944.
- Sleipner class – Two vessels built.
- Sleipner (1965–1992)
- Æger (1967–1992)
Destroyers
.jpg.webp)
HNoMS Draug – lead ship of the Draug class
.jpg.webp)
HNoMS Sleipner – lead ship of the Sleipner class
- Sleipner class Six vessels made in Norway from 1936 to 1939.
- Sleipner (1936–1959) In Norwegian service during the war. Rebuilt to frigate in 1948.
- Gyller (1938–1959) In German hands from 1940 to 1945. Rebuilt to frigate in 1948.
- Æger (1936–1940)[1] Sunk by German bombers on 9 April 1940, at the beginning of Operation Weserübung after first sinking the German supply ship Roda and shooting down two Luftwaffe bombers.
- Odin (1939–1959) In German hands from 1940 to 1945. Rebuilt to frigate in 1948.
- Balder (1946–1959) In German hands from 1940 to 1945. Rebuilt to frigate in 1948.[1]
- Tor (1946–1959) In German hands from 1940 to 1945. Rebuilt to frigate in 1948.
- S class Two vessels on loan from the Royal Navy
- Svenner (1944) ex-HMS Shark Torpedoed and sunk on D-Day, 6 June 1944)
- Stord (1943–1959) ex-HMS Success

HNoMS St Albans at sea while named USS Thomas.
- Town class Five vessels on loan from the Royal Navy.
- C class Four vessels bought from the UK in 1946 and 1947.
- Oslo (1947–1965) ex-HMS Crown
- Bergen ex-HMS Cromwell
- Trondheim ex-HMS Croziers
- Stavanger ex-HMS Crystal
- Type II Hunt class
- Type III Hunt class
- Glaisdale (1942–1961), Later renamed Narvik
- Eskdale (1942–1943)
Frigates

Oslo-class frigate Oslo in the North Atlantic, October 1971
- Freia (1828–1870)[1]
- Desideria (1854–1920)[1]
- St Olaf (1860–1925)[1]
- Kong Sverre (1864–1932)
- Oslo class Five vessels built.
- River class Formerly of the Royal Canadian Navy
- Draug (1956–1964) ex-HMCS Penetang
- Garm (1956–1977) ex-HMCS Toronto, rebuilt in 1965 to serve as support vessel for torpedo boats under the name Valkyrien.
- Troll (1956–1973) ex-HMCS Prestonian, rebuilt in 1965 to serve as support vessel for submarines under the name HNoMS Horten.
Cutters
Schooners
- Built at Georgernes Verft, Bergen
- Built at Trondhjems Skibsverft, Trondheim
- "Bombgun schooners"
- Steam powered schooners
- Paddlesteam schooners
Sloops
Sloops, several of which were later rebuilt as 3. class gunboats.
- Arendal launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875.[1]
- Augvaldsnæs launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Bergen launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Bodøe launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Bragernæs launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Brevig launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875, then used as a minelayer.[1]
- Christiansund launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Drøbak launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1872 to a catamaran steam gunboat and renamed Trold.[1]
- Egersund launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Farsund launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Flekkefjord launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Fredrikshald launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Hammerfest launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Holmestrand launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Horten launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875 and used as a minelayer.[1]
- Høievarde launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Kaholmen launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Karmøe launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1883 and used as a minelayer.[1]
- Kongsberg launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Kristiansand aka. Christiansand launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875 and used as a minelayer.[1]
- Langesund launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Larvik aka. Laurvig launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875.[1]
- Levanger launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Lillesand launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875 and used as a minelayer.[1]
- Lindesnæs launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Molde launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Moss launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Munkholmen launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Namsos launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Porsgrund launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Sarpsborg launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1872 as a catamaran steam gunboat and renamed Trold. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Skeen launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Skudenæs launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1883. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Soon launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Stat launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Strømsøe launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1872 as a catamaran steam gunboat and renamed Nøk. Stricken 1903.[1]
- Svelvigen launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1872 as a steam gunboat and renamed Dverg. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Sverresborg launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Tananger launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Tangen launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Tromsøe launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Trondhjem launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Tønsberg launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875. Stricken 1905.[1]
- Udsire launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Vardøe launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Vardøhuus launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Aalesund launched between 1840 and 1845.[1]
- Aaasgaardstrand launched between 1840 and 1845. Rebuilt 1875 and used as a minelayer.[1]
Gunboats

1.-class gunboat HNoMS Ellida
- 1. class
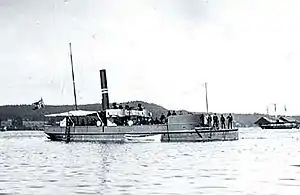
2.-class gunboat of the Vale series
- 2. class
- Vale class
- Gor class
- Æger (1894–1932)[1]
Steam powered gunboats
Submarine chasers

Submarine chaser HNoMS King Haakon VII
- Hessa (P358)
- Hitra (museum vessel)
- Vigra (P359)
- King Haakon VII (1942–1951) Former US submarine chaser USS PC 467.
Submarines
- Kobben (1909–1933)[1] Renamed A-1 on 21 February 1913. The tower of Kobben is preserved at the Royal Navy Officers' Training School at Horten.
- A class Three vessels were bought in 1913, a fourth was ordered in 1914 (A-5) but was confiscated by the Imperial German Navy at the outbreak of World War I.

B class submarines B-2, B-3 and B-4
- B class Six vessels of the US Holland type built on licence in Norway from 1922 to 1929.
- B-1 (1923–1947) Escaped to the Faeroe Islands 8 June 1940, later used as a training vessel in Scotland.[1]
- B-2 (1924–1940) Captured by the Germans on 11 April.[1]
- B-3 (1926–1940) Scuttled by own crew on 10 April to prevent German capture.[1]
- B-4 (1927–1940) Captured by the Germans on 10 April.[1]
- B-5 (1929–1940) Captured by the Germans on 11 April and renamed UC-1.[1]
- B-6 (1930–1940) Surrendered to German troops on 18 April under threat of bombing of Florø city. Named UC −2 in German service.[1]
- U class
- V class
- Utstein, ex. HMS Venturer, sold to Norway in 1946.
- Uthaug, ex. HMS Votary, sold to Norway in 1946.
- Utvær, ex. HMS Viking, sold to Norway in 1946.
- Utsira, ex. HMS Variance
- K class
- Kobben class Fifteen vessels built from 1964 to 1967.
 HNoMS Utstein, a Kobben class submarine
HNoMS Utstein, a Kobben class submarine- Kinn (1964–1982) Deliberately sunk in Bjørnefjorden in 1990.
- Kya (1964–1991) Transferred to the Royal Danish Navy as HDMS Springeren in 1991.
- Kobben (1964–2001) Transferred to the Polish Navy as ORP Jastrząb to be used for parts.
- Kunna (1964–?) Transferred to Poland as ORP Kondor in 2004.
- Kaura (1965–?) Transferred to Denmark to be used for parts in 1991.
- Ula (1965–1998) Changed name to Kinn in 1987. Scrapped in 1998.
- Utsira (1965–1998) Scrapped 1998.
- Utstein (1965–1998) Transferred to the Royal Norwegian Navy Museum in 1998.
- Utvær (1965–1989) Transferred to Denmark as HDMS Tumleren in 1989.
- Uthaug (1966–1990) Transferred to Denmark as HDMS Sælen in 1990.
- Sklinna (1966–2001) Scrapped in 2001.
- Skolpen (1966–2002) Transferred to Poland as ORP Sęp in 2002.
- Stadt (1966–1990) Scrapped.
- Stord (1967–2002) Transferred to Poland as ORP Sokół in 2002.
- Svenner (1967–2003) Also a training ship. To Poland as ORP Bielik in 2003.
Minesweepers
.jpg.webp)
HNoMS Otra – the RNoN's first purpose built minesweeper

HNoMS Rauma – the RNoN's second purpose-built minesweeper
- Børtind (1912–?) Refitted guard vessel
- Otra First purpose built Norwegian minesweeper
- Rauma Second purpose built Norwegian minesweeper
- NYMS class
- NYMS 247/Vinstra (M 317)
- NYMS 306/Gaula (M 318)
- NYMS 377/Driva (M 319)
- NYMS 379/Alta (M 320)
- NYMS 380/Vorma (M 321)
- NYMS 381/Begna (M 322)
- NYMS 382
- NYMS 406/Rana (M 330)
- Sauda class
- Kvina
- Ogna
- Sauda
- Sira
- Tana
- Tista
- Utla
- Vosso
- Glomma
- Alta (museum vessel)
- Syrian
- Nordhav II
- Drøbak
Minelayers

Royal Norwegian Navy minelayer Frøya
.jpg.webp)
Royal Norwegian Navy minelayer Olav Tryggvason
- Glommen class
- Glommen (1916–1950)
- Laugen (1918–1950)
- Frøya (1918–1940)
- Olav Tryggvason (1934–1940)
- Gor class Formerly US Navy Auk class.
- Vidar class Two vessels built in Norway.
- Vidar (N52) (1977–2006) Sold to the Lithuanian Naval Force in 2006.
- Vale (N53) (1978–2003) Given to the Latvian Navy in 2003.
Monitors
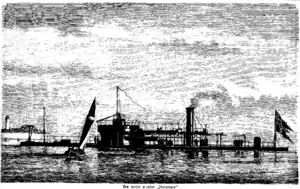
The Norwegian monitor Skorpionen
- Skorpionen class:
- Skorpionen (1867–1908)
- Mjølner (1869–1908)
- Thrudvang (1870–1918)
- Thor (1876–1918)
.jpg.webp)
HNoMS Nordkapp
Offshore patrol vessels
- Heimdal (1892–1946)
- Fridtjof Nansen (1930–1940)
- Nordkapp (1937–1954)
Torpedo boats
- Rap (1873–1920) – the first modern torpedo boat.
- Ulven (1878–1923)

2. class torpedo boat HNoMS Kjell.
- 2. class – 27 built from 1882.

1. class torpedo boat HNoMS Sæl.
- 1. class Ten vessels built from 1892.
- 3. class One small harbour and fjord torpedo boat built in 1899.
- Myg (1899–?)
- Oter (1888–?)
- Raket (1894–?)
- Varg (1894–?)
- Glimt (1897–?)
- Djerv (1897–1940) Refitted as minesweeper. Sunk by own crew in Sognefjorden.
- Storm (1898–1940)
- Brand (1898–1946)
- Trods (1898–?)
- Dristig (1899–1940) Refitted as minesweeper. Sunk by own crew in Sognefjorden.
- Laks (1900–?)
- Sild (1900–?)
- Sæl (1901–1940)
- Skrei (1901–?)
- Hauk (1902–?)
- Falk (1902–?)
- Ørn (1903–?)
- Ravn (1903–?)
- Grib (1905–?)
- Jo (1905–?)
- Lom (1905–?)
- Skarv (1906–?)
- Teist (1907–?)
- Trygg class Three 256 ton vessels built between 1919 and 1921
.jpg.webp) Trygg class torpedo boat HNoMS Snøgg
Trygg class torpedo boat HNoMS Snøgg - MTB 5 (1940)
- MTB 6 (1940–1941)
- MTB 56 (1941–1942)
- MTB 345 (1943) Captured by the Germans 28 July 1943, lost in fire the next month
- Fairmile D class aka D class. Ten vessels were in Norwegian service at the end of WWII. Seven of them were used until 1959.
- Elco class Ten vessels received from the US Navy as part of a weapons aid program in 1951.
- Snøgg ex US Navy PT-602
- Sel ex US Navy PT-603
- Sild ex US Navy PT-604
- Skrei ex US Navy PT-605
- Snar ex US Navy PT-606
- Springer ex US Navy PT-608
- Hai ex US Navy PT-609
- Hauk ex US Navy PT-610
- Hval ex US Navy PT-611
- Hvass ex US Navy PT-612
- Tjeld class aka. Nasty class 20 vessels built in Norway from 1959 to 1966.
- Tjeld (1959–1992) Renamed Sel. Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Sold for scrapping 1992.
- Skarv (1959–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Teist (1960–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Jo (1960–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Lom (1961–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Stegg (1961–1992) Renamed Hval. Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Naval Home Guard. Sold for scrapping 1992.
- Hauk (1961–1992) Renamed Laks. Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Sold for scrapping 1992.
- Falk (1961–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Ravn (1961–1992) Renamed Knurr. Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Sold for scrapping 1992.
- Gribb (1961–?) Renamed Delfin. Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Was planned to be preserved by Kværner Mandal A/S, but later sold for scrapping.
- Geir (1962–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Erle (1962–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Sel (1963–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Hval (1964–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Laks (1964–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Hai (1964–?) Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Plans are currently underway for Hai to be preserved as a museum ship in Fredrikstad.
- Knurr (1964–1981) Sold to Stapletask Ltd, Sittingbourne, Kent, England.
- Lyr (1965–1992) Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Sold for scrapping 1992.
- Skrei (1965–?) Transferred to Naval Reserve and used by Sea Home Guard. Transferred to the Royan Norwegian Navy Museum and preserved as a museum ship.
- Delfin (1966–1984) Given to Friends of the Shetland bus as a preservation project, but the project failed and the ship was given to a private person.
- Rapp class Six vessels built in Norway from 1952 to 1956.
- Rapp
- Rask (?–1970)
- Storm class 20 vessels built from 1965 to 1967.
- Snøgg class Six vessels built from 1970 to 1971.
- Hauk class
Training vessels, school ships
- Christian Radich
- Haakon VII (A537) (1958–1973) ex-USS Gardiners Bay (AVP-39). School ship. Built as a seaplane tender for the United States Navy.
- Sørlandet
Other ships
- Brabant
- Ormen Lange longship (Long Serpent)
References
- Mo, Sverre; Norske marinefartøy; Bodoni Forlag; Bergen; 2008
- Norwegian Defence Force official website: Første seilas med F311 Archived 30 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine (in Norwegian)
- Norwegian Defence Force official website: Tredje fregatt på norske hender Archived 2 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine (in Norwegian)
- Norwegian Defence Force official websites notes last of class commissioned January 2011: Archived 3 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine (in Norwegian)
- https://uk.news.yahoo.com/norway-missile-test--knm-trondheim-naval-missile-strike-andoy-120815653.html
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Naval ships of Norway. |
Sources
- (in Norwegian)Vold, Ottar; Felttoget 1940 – avdelingenes påkjenninger og tap; 1995; ISBN 82-551-0413-5
- Axel Thorsen, a Norwegian gunboat of 1810 High resolution photos of a model
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


