Liver disease
Liver disease (also called hepatic disease) is a type of damage to or disease of the liver.[1] Whenever the course of the problem lasts long, chronic liver disease ensues.
| Liver disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hepatic disease |
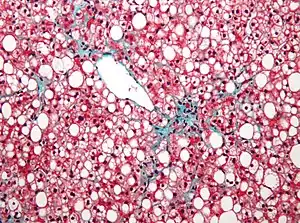 | |
| Micrograph of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Types | Fatty liver disease, Hepatitis (and several more)[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Liver function tests[2] |
| Treatment | Depends on type(See types) |
Signs and symptoms
Some of the signs and symptoms of liver disease are the following:
- Jaundice
- Confusion and altered consciousness caused by hepatic encephalopathy.
- Thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.[3]
- Risk of bleeding symptoms particularly taking place in gastrointestinal tract[4]
Cause



There are more than a hundred different kinds of liver disease. These are some of the most common:[5]
- Fascioliasis, a parasitic infection of liver caused by a liver fluke of the genus Fasciola, mostly the Fasciola hepatica.[6]
- Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, is caused by various viruses (viral hepatitis) also by some liver toxins (e.g. alcoholic hepatitis), autoimmunity (autoimmune hepatitis) or hereditary conditions.[7]
- Alcoholic liver disease is a hepatic manifestation of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Analogous terms such as "drug-induced" or "toxic" liver disease are also used to refer to disorders caused by various drugs.[8]
- Fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is a reversible condition where large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells.[9] Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a spectrum of disease associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.[10]
- Hereditary diseases that cause damage to the liver include hemochromatosis,[11] involving accumulation of iron in the body, and Wilson's disease. Liver damage is also a clinical feature of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency[12] and glycogen storage disease type II.[13]
- In transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, the liver produces a mutated transthyretin protein which has severe neurodegenerative or cardiopathic effects. Liver transplantation can give a curative treatment option.[14]
- Gilbert's syndrome, a genetic disorder of bilirubin metabolism found in a small percent of the population, can cause mild jaundice.[15]
- Cirrhosis is the formation of fibrous tissue (fibrosis) in the place of liver cells that have died due to a variety of causes, including viral hepatitis, alcohol overconsumption, and other forms of liver toxicity. Cirrhosis causes chronic liver failure.[16]
- Primary liver cancer most commonly manifests as hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma; rarer forms include angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma of the liver. (Many liver malignancies are secondary lesions that have metastasized from primary cancers in the gastrointestinal tract and other organs, such as the kidneys, lungs.)[17]
- Primary biliary cirrhosis is a serious autoimmune disease of the bile capillaries.[18]
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a serious chronic inflammatory disease of the bile duct, which is believed to be autoimmune in origin.[19]
- Budd–Chiari syndrome is the clinical picture caused by occlusion of the hepatic vein.[20]
Mechanism
Liver disease can occur through several mechanisms:
DNA damage
One general mechanism, increased DNA damage, is shared by some of the major causes of liver disease. These major causes include infection by hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus, alcohol abuse, and obesity.[21]
Viral infection by hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes an increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The increase in intracellular ROS is about 10,000-fold upon chronic HBV infection and 100,000-fold after HCV infection. This increase in ROS causes inflammation and further increase in ROS. ROS cause more than 20 types of DNA damage.[22] Oxidative DNA damage is mutagenic[23] and also causes epigenetic alterations at the sites of DNA repair.[24] Epigenetic alterations and mutations affect the cellular machinery that may cause the cell to replicate at a higher rate or result in the cell avoiding apoptosis, and thus contribute to liver disease.[25] By the time accumulating epigenetic and mutational changes eventually cause hepatocellular carcinoma, epigenetic alterations appear to have an even larger role in carcinogenesis than mutations. Only one gene, TP53, is mutated in more than 20% of liver cancers while 41 genes each have hypermethylated promoters (repressing gene expression) in more than 20% of liver cancers.[26]
Alcohol consumption in excess causes a build-up of acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde and free radicals generated by metabolizing alcohol induce DNA damage and oxidative stress.[27][28][29] In addition, activation of neutrophils in alcoholic liver disease contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular damage by releasing reactive oxygen species (which can damage DNA).[30] The level of oxidative stress and acetaldehyde-induced DNA adducts due to alcohol consumption does not appear sufficient to cause increased mutagenesis.[30] However, as reviewed by Nishida et al.,[24] alcohol exposure, causing oxidative DNA damage (which is repairable), can result in epigenetic alterations at the sites of DNA repair. Alcohol-induced epigenetic alterations of gene expression appear to lead to liver injury and ultimately carcinoma.[31]
Obesity is associated with higher risk of primary liver cancer.[32] As shown with mice, obese mice are prone to liver cancer, likely due to two factors. Obese mice have increased pro-inflammatory cytokines. Obese mice also have higher levels of deoxycholic acid (DCA), a product of bile acid alteration by certain gut microbes, and these microbes are increased with obesity. The excess DCA causes DNA damage and inflammation in the liver, which, in turn, can lead to liver cancer.[33]
Other relevant aspects
A common form of liver disease is viral infection. Viral hepatitides such as Hepatitis B virus and Hepatitis C virus can be vertically transmitted during birth via contact with infected blood.[34][35] According to a 2012 NICE publication, "about 85% of hepatitis B infections in newborns become chronic".[36] In occult cases, Hepatitis B virus is present by HBV DNA, but testing for HBsAg is negative.[37] High consumption of alcohol can lead to several forms of liver disease including alcoholic hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.[38] In the earlier stages of alcoholic liver disease, fat builds up in the liver's cells due to increased creation of triglycerides and fatty acids and a decreased ability to break down fatty acids.[39] Progression of the disease can lead to liver inflammation from the excess fat in the liver. Scarring in the liver often occurs as the body attempts to heal and extensive scarring can lead to the development of cirrhosis in more advanced stages of the disease.[39] Approximately 3–10% of individuals with cirrhosis develop a form of liver cancer known as hepatocellular carcinoma.[39] According to Tilg, et al., gut microbiome could very well have an effect, be involved in the pathophysiology, on the various types of liver disease which an individual may encounter.[40]
Air pollutants
Particulate matter (PM) or carbon black (CB) are common pollutants. The following factors are the harmful effects of liver exposure under PM or CB. First, they have an obvious direct toxic effect on the liver. Chemicals will affect metabolism and impact liver function. Second, inflammation of liver caused by PM and CB impact lipid metabolism and fatty liver disease. Third, PM and CB can translocate from lung to liver.[41]
PM and CB can easily translocate from lung to liver. Because they are very diverse and each has different toxicodynamics, detailed mechanisms are not clear. Water-soluble fractions of PM is the most important part for PM translocation to liver through extra-pulmonary circulation. When PM goes through blood vessel into blood, it combines with immune cells, that will stimulate innate immune responses. Pro-inflammatory cytokines will be released and cause disease progression.[41]
Diagnosis
A number of liver function tests (LFTs) are available to test the proper function of the liver. These test for the presence of enzymes in blood that are normally most abundant in liver tissue, metabolites or products. serum proteins, serum albumin, serum globulin, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time.[2]
Imaging tests such as transient elastography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to examine the liver tissue and the bile ducts. Liver biopsy can be performed to examine liver tissue to distinguish between various conditions; tests such as elastography may reduce the need for biopsy in some situations.[42]
In liver disease, prothrombin time is longer than usual.[3] In addition, the amounts of both coagulation factors and anticoagulation factors are reduced because the liver cannot productively synthsize them as it did when healthy.[43] Nonetheless, there are two exceptions in this falling tendency, that are, coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor, a platelet adhesive protein.[43] Both inversely rise in the setting of hepatic insufficiency, thanks to the drop of hepatic clearance and compensatory productions from other sites of the body.[43] Fibrinolysis generally proceeds faster in the scenarios of acute liver failure as well as advanced stage of liver disease in contrast to chronic liver disease in which concentration of fibrinogen remains unchanged.[43]
A previously undiagnosed liver disease may become evident first after autopsy. Following are gross pathology images:
 Diffuse cirrhosis
Diffuse cirrhosis.jpg.webp) Macronodular cirrhosis
Macronodular cirrhosis.jpg.webp) Nutmeg texture of congestive hepatopathy
Nutmeg texture of congestive hepatopathy.jpg.webp)
Treatment
Anti-viral medications are available to treat infections such as hepatitis B.[44] Other conditions may be managed by slowing down disease progression, for example:
- By using steroid-based drugs in autoimmune hepatitis.[45]
- Regularly removing a quantity of blood from a vein (venesection) in the iron overload condition, hemochromatosis.[46]
- Wilson’s disease, a condition where copper builds up in the body, can be managed with drugs that bind copper, allowing it to be passed from the body in urine.[47]
- In cholestatic liver disease, (where the flow of bile is affected due to cystic fibrosis[48]) a medication called ursodeoxycholic acid (URSO, also referred to as UDCA) may be given.[49]
See also
References
- "Liver Diseases". MedlinePlus.
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Liver function tests
- Blonski, W; Siropaides, T; Reddy, KR (2007). "Coagulopathy in liver disease". Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology. 10 (6): 464–73. doi:10.1007/s11938-007-0046-7. ISSN 1092-8472. PMID 18221607. S2CID 23396752.
- Tripodi, Armando; Mannucci, Pier Mannuccio (2011-07-14). "The Coagulopathy of Chronic Liver Disease". New England Journal of Medicine. Massachusetts Medical Society. 365 (2): 147–156. doi:10.1056/nejmra1011170. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 21751907. S2CID 198152.
- "Liver disease – NHS Choices". www.nhs.uk. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "CDC – Fasciola". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Hepatitis". MedlinePlus.
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Alcoholic liver disease
- "Hepatic steatosis". Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – NHS Choices". www.nhs.uk. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Hemochromatosis". MedlinePlus.
- "Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency". MedlinePlus.
- Leslie, Nancy; Tinkle, Brad T. (1993). "Pompe Disease". In Pagon, Roberta A.; Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Wallace, Stephanie E.; Amemiya, Anne; Bean, Lora J.H.; Bird, Thomas D.; Dolan, Cynthia R.; Fong, Chin-To (eds.). Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease). Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301438.
- "Transthyretin amyloidosis". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Gilbert syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Cirrhosis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Liver cancer – Hepatocellular carcinoma: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Primary biliary cirrhosis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Sclerosing cholangitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Hepatic vein obstruction (Budd-Chiari): MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Chronic Liver Disease/Cirrhosis | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library".
- Yu Y, Cui Y, Niedernhofer LJ, Wang Y (December 2016). "Occurrence, Biological Consequences, and Human Health Relevance of Oxidative Stress-Induced DNA Damage". Chemical Research in Toxicology. 29 (12): 2008–2039. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00265. PMC 5614522. PMID 27989142.
- Dizdaroglu M (December 2012). "Oxidatively induced DNA damage: mechanisms, repair and disease". Cancer Letters. 327 (1–2): 26–47. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.016. PMID 22293091.
- Nishida N, Kudo M (2013). "Oxidative stress and epigenetic instability in human hepatocarcinogenesis". Digestive Diseases. 31 (5–6): 447–53. doi:10.1159/000355243. PMID 24281019.
- Shibata T, Aburatani H (June 2014). "Exploration of liver cancer genomes". Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 11 (6): 340–9. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2014.6. PMID 24473361. S2CID 8611393.
- Ozen C, Yildiz G, Dagcan AT, Cevik D, Ors A, Keles U, Topel H, Ozturk M (May 2013). "Genetics and epigenetics of liver cancer". New Biotechnology. 30 (4): 381–4. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2013.01.007. hdl:11693/20956. PMID 23392071.
- Yu HS, Oyama T, Isse T, Kitagawa K, Pham TT, Tanaka M, Kawamoto T (December 2010). "Formation of acetaldehyde-derived DNA adducts due to alcohol exposure". Chemico-Biological Interactions. 188 (3): 367–75. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.08.005. PMID 20813101.
- Lee SM, Kim-Ha J, Choi WY, Lee J, Kim D, Lee J, Choi E, Kim YJ (July 2016). "Interplay of genetic and epigenetic alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma". Epigenomics. 8 (7): 993–1005. doi:10.2217/epi-2016-0027. PMID 27411963.
- "Drinking alcohol causes cancer by 'damaging DNA' - Independent.ie".
- Wang HJ, Gao B, Zakhari S, Nagy LE (August 2012). "Inflammation in alcoholic liver disease". Annual Review of Nutrition. 32: 343–68. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145138. PMC 3670145. PMID 22524187.
- Shukla SD, Lim RW (2013). "Epigenetic effects of ethanol on the liver and gastrointestinal system". Alcohol Research. 35 (1): 47–55. PMC 3860425. PMID 24313164.
- Aleksandrova K, Stelmach-Mardas M, Schlesinger S (2016). "Obesity and Liver Cancer". Obesity and Cancer. Recent Results in Cancer Research. Fortschritte der Krebsforschung. Progres dans les Recherches Sur le Cancer. Recent Results in Cancer Research. 208. pp. 177–198. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42542-9_10. ISBN 978-3-319-42540-5. PMID 27909908.
- "Gut Bugs Could Explain Obesity-Cancer Link | Science | AAAS". 2013-06-26.
- Benova L, Mohamoud YA, Calvert C, Abu-Raddad LJ (September 2014). "Vertical transmission of hepatitis C virus: systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 59 (6): 765–73. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu447. PMC 4144266. PMID 24928290.
- Komatsu H (July 2014). "Hepatitis B virus: where do we stand and what is the next step for eradication?". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (27): 8998–9016. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8998 (inactive 2021-01-16). PMC 4112872. PMID 25083074.CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2021 (link)
- "Hepatitis B and C: ways to promote and offer testing to people at increased risk of infection | Guidance and guidelines | NICE". www.nice.org.uk. Retrieved 2015-06-24.
- Samal J, Kandpal M, Vivekanandan P (January 2012). "Molecular mechanisms underlying occult hepatitis B virus infection". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 25 (1): 142–63. doi:10.1128/CMR.00018-11. PMC 3255968. PMID 22232374.
- Suk KT, Kim MY, Baik SK (September 2014). "Alcoholic liver disease: treatment". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (36): 12934–44. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12934. PMC 4177474. PMID 25278689.
- Williams JA, Manley S, Ding WX (September 2014). "New advances in molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutic targets in alcoholic liver diseases". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (36): 12908–33. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12908. PMC 4177473. PMID 25278688.
- Tilg H, Cani PD, Mayer EA (December 2016). "Gut microbiome and liver diseases". Gut. 65 (12): 2035–2044. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312729. PMID 27802157.
- Kim JW, Park S, Lim CW, Lee K, Kim B (June 2014). "The role of air pollutants in initiating liver disease". Toxicological Research. 30 (2): 65–70. doi:10.5487/TR.2014.30.2.065. PMC 4112066. PMID 25071914.
- Tapper EB, Lok AS (August 2017). "Use of Liver Imaging and Biopsy in Clinical Practice". The New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (8): 756–768. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1610570. PMID 28834467. S2CID 205117722.
- Barton, Cassie A. (2016). "Treatment of Coagulopathy Related to Hepatic Insufficiency". Critical Care Medicine. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). 44 (10): 1927–1933. doi:10.1097/ccm.0000000000001998. ISSN 0090-3493. PMID 27635482. S2CID 11457839.
- De Clercq E, Férir G, Kaptein S, Neyts J (June 2010). "Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections". Viruses. 2 (6): 1279–305. doi:10.3390/v2061279. PMC 3185710. PMID 21994680.
- Hirschfield, Gideon M.; Heathcote, E. Jenny (2011-12-02). Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Guide for Practicing Clinicians. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9781607615699.
- "Phlebotomy Treatment | Treatment and Management | Training & Education | Hemochromatosis (Iron Storage Disease) | NCBDDD | CDC". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- "Wilson Disease". www.niddk.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- Suchy, Frederick J.; Sokol, Ronald J.; Balistreri, William F. (2014-02-20). Liver Disease in Children. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107729094.
- Cheng, Katharine; Ashby, Deborah; Smyth, Rosalind L. (2017). "Ursodeoxycholic acid for liver disease related to cystic fibrosis | Cochrane". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 9: CD000222. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000222.pub4. PMC 6483662. PMID 28891588. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
Further reading
- Friedman, Lawrence S.; Keeffe, Emmet B. (2011-08-03). Handbook of Liver Disease. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1455723164.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |