Low-pressure area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. Within the field of meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two areas. The first area is on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). A second area of wind divergence aloft occurs ahead of embedded shortwave troughs, which are of smaller wavelength. Diverging winds aloft ahead of these troughs cause atmospheric lift within the troposphere below, which lowers surface pressures as upward motion partially counteracts the force of gravity.


A low-pressure area is commonly associated with inclement weather,[1] while a high-pressure area is associated with light winds and fair skies.[2]
Thermal lows form due to localized heating caused by greater sunshine over deserts and other land masses. Since localized areas of warm air are less dense than their surroundings, this warmer air rises, which lowers atmospheric pressure near that portion of the Earth's surface. Large-scale thermal lows over continents help drive monsoon circulations. Low-pressure areas can also form due to organized thunderstorm activity over warm water. When this occurs over the tropics in concert with the Intertropical Convergence Zone, it is known as a monsoon trough. Monsoon troughs reach their northerly extent in August and their southerly extent in February. When a convective low acquires a well-hot circulation in the tropics it is termed a tropical cyclone. Tropical cyclones can form during any month of the year globally, but can occur in either the northern or southern hemisphere during December.
Atmospheric lift will also generally produce cloud cover through adiabatic cooling once the air becomes saturated as it rises, although the low-pressure area typically brings cloudy skies, which act to minimize diurnal temperature extremes. Since clouds reflect sunlight, incoming shortwave solar radiation decreases, which causes lower temperatures during the day. At night the absorptive effect of clouds on outgoing longwave radiation, such as heat energy from the surface, allows for warmer diurnal low temperatures in all seasons. The stronger the area of low pressure, the stronger the winds experienced in its vicinity. Globally, low-pressure systems are most frequently located over the Tibetan Plateau and in the lee of the Rocky mountains. In Europe (particularly in the British Isles and Netherlands), recurring low-pressure weather systems are typically known as "low levels".
Formation
Cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of cyclonic circulations, or low-pressure areas, within the atmosphere.[3] Cyclogenesis is the opposite of cyclolysis, and has an anticyclonic (high-pressure system) equivalent which deals with the formation of high-pressure areas—anticyclogenesis.[4] Cyclogenesis is an umbrella term for several different processes, all of which result in the development of some sort of cyclone. Meteorologists use the term "cyclone" where circular pressure systems flow in the direction of the Earth's rotation,[5][6] which normally coincides with areas of low pressure.[7][8] The largest low-pressure systems are cold-core polar cyclones and extratropical cyclones which lie on the synoptic scale. Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones, mesocyclones, and polar lows lie within the smaller mesoscale. Subtropical cyclones are of intermediate size.[9][10] Cyclogenesis can occur at various scales, from the microscale to the synoptic scale. Larger-scale troughs, also called Rossby waves, are synoptic in scale.[11] Shortwave troughs embedded within the flow around larger scale troughs are smaller in scale, or mesoscale in nature.[12] Both Rossby waves and shortwaves embedded within the flow around Rossby waves migrate equatorward of the polar cyclones located in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.[13] All share one important aspect, that of upward vertical motion within the troposphere. Such upward motions decrease the mass of local atmospheric columns of air, which lowers surface pressure.[14]
Extratropical cyclones form as waves along weather fronts due to a passing by shortwave aloft or upper-level jet streak before occluding later in their life cycle as cold-core cyclones.[15][16][17][18] Polar lows are small-scale, short-lived atmospheric low-pressure systems that occur over the ocean areas poleward of the main polar front in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. They are part of the larger class of mesoscale weather-systems. Polar lows can be difficult to detect using conventional weather reports and are a hazard to high-latitude operations, such as shipping and gas- and oil-platforms. They are vigorous systems that have near-surface winds of at least 17 metres per second (38 mph).[19]
Tropical cyclones form due to latent heat driven by significant thunderstorm activity, and are warm-core with well-defined circulations.[20] Certain criteria need to be met for their formation. In most situations, water temperatures of at least 26.5 °C (79.7 °F) are needed down to a depth of at least 50 m (160 ft);[21] waters of this temperature cause the overlying atmosphere to be unstable enough to sustain convection and thunderstorms.[22] Another factor is rapid cooling with height, which allows the release of the heat of condensation that powers a tropical cyclone.[21] High humidity is needed, especially in the lower-to-mid troposphere; when there is a great deal of moisture in the atmosphere, conditions are more favorable for disturbances to develop.[21] Low amounts of wind shear are needed, as high shear is disruptive to the storm's circulation.[21] Lastly, a formative tropical cyclone needs a pre-existing system of disturbed weather, although without a circulation no cyclonic development will take place.[21] Mesocyclones form as warm core cyclones over land, and can lead to tornado formation.[23] Waterspouts can also form from mesocyclones, but more often develop from environments of high instability and low vertical wind shear.[24]
In deserts, lack of ground and plant moisture that would normally provide evaporative cooling can lead to intense, rapid solar heating of the lower layers of air. The hot air is less dense than surrounding cooler air. This, combined with the rising of the hot air, results in a low-pressure area called a thermal low.[25] Monsoon circulations are caused by thermal lows which form over large areas of land and their strength is driven by how land heats more quickly than the surrounding nearby ocean. This generates a steady wind blowing toward the land, bringing the moist near-surface air over the oceans with it.[26] Similar rainfall is caused by the moist ocean-air being lifted upwards by mountains,[27] surface heating,[28] convergence at the surface,[29] divergence aloft, or from storm-produced outflows at the surface.[30] However the lifting occurs, the air cools due to expansion in lower pressure, which in turn produces condensation. In winter, the land cools off quickly, but the ocean keeps the heat longer due to its higher specific heat. The hot air over the ocean rises, creating a low-pressure area and a breeze from land to ocean while a large area of drying high pressure is formed over the land, increased by wintertime cooling.[26] Monsoons resemble sea and land breezes, terms usually referring to the localized, diurnal (daily) cycle of circulation near coastlines everywhere, but they are much larger in scale - also stronger and seasonal.[31]
Climatology
Mid-latitudes and subtropics
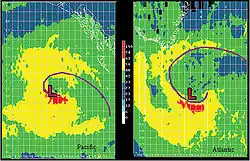
Large polar cyclones help determine the steering of systems moving through the mid-latitudes, south of the Arctic and north of the Antarctic. The Arctic oscillation provides an index used to gauge the magnitude of this effect in the Northern Hemisphere.[32] Extratropical cyclones tend to form east of climatological trough positions aloft near the east coast of continents, or west side of oceans.[33] A study of extratropical cyclones in the Southern Hemisphere shows that between the 30th and 70th parallels there are an average of 37 cyclones in existence during any 6-hour period.[34] A separate study in the Northern Hemisphere suggests that approximately 234 significant extratropical cyclones form each winter.[35] In Europe, particularly in the United Kingdom and in the Netherlands, recurring extratropical low-pressure weather systems are typically known as depressions.[36][37][38] These tend to bring wet weather throughout the year. Thermal lows also occur during the summer over continental areas across the subtropics - such as the Sonoran Desert, the Mexican plateau, the Sahara, South America, and Southeast Asia.[25] The lows are most commonly located over the Tibetan plateau and in the lee of the Rocky mountains.[33]
Monsoon trough

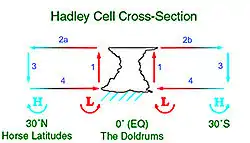
Elongated areas of low pressure form at the monsoon trough or intertropical convergence zone as part of the Hadley cell circulation.[39] Monsoon troughing in the western Pacific reaches its zenith in latitude during the late summer when the wintertime surface ridge in the opposite hemisphere is the strongest. It can reach as far as the 40th parallel in East Asia during August and 20th parallel in Australia during February. Its poleward progression is accelerated by the onset of the summer monsoon which is characterized by the development of lower air pressure over the warmest part of the various continents.[40][41] The large-scale thermal lows over continents help create pressure gradients which drive monsoon circulations.[42] In the southern hemisphere, the monsoon trough associated with the Australian monsoon reaches its most southerly latitude in February,[43] oriented along a west-northwest/east-southeast axis. Many of the world's rainforests are associated with these climatological low-pressure systems.[44]
Tropical cyclone
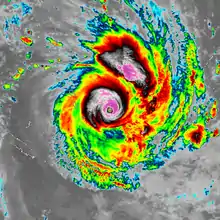
Tropical cyclones generally need to form more than 555 km (345 mi) or poleward of the 5th parallel north and 5th parallel south, allowing the Coriolis effect to deflect winds blowing towards the low-pressure center and creating a circulation.[21] Worldwide, tropical cyclone activity peaks in late summer, when the difference between temperatures aloft and sea surface temperatures is the greatest. However, each particular basin has its own seasonal patterns. On a worldwide scale, May is the least active month while September is the most active month. November is the only month that activity in all the tropical cyclone basins is possible.[45] Nearly one-third of the world's tropical cyclones form within the western Pacific Ocean, making it the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth.[46]
Associated weather
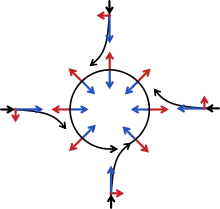
Wind is initially accelerated from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.[47] This is due to density (or temperature and moisture) differences between two air masses. Since stronger high-pressure systems contain cooler or drier air, the air mass is denser and flows towards areas that are warm or moist, which are in the vicinity of low-pressure areas in advance of their associated cold fronts. The stronger the pressure difference, or pressure gradient, between a high-pressure system and a low-pressure system, the stronger the wind.[48] Thus, stronger areas of low pressure are associated with stronger winds.
The Coriolis force caused by the Earth's rotation is what gives winds around low-pressure areas (such as in hurricanes, cyclones, and typhoons) their counter-clockwise (anticlockwise) circulation in the northern hemisphere (as the wind moves inward and is deflected right from the center of high pressure) and clockwise circulation in the southern hemisphere (as the wind moves inward and is deflected left from the center of high pressure).[49] A tropical cyclone differs from a hurricane or typhoon based only on geographic location.[50] Note that a tropical cyclone is fundamentally different from a mid-latitude cyclone.[51] A hurricane is a storm that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean and northeastern Pacific Ocean, a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, and a tropical cyclone occurs in the south Pacific or Indian Ocean.[50][52] Friction with land slows down the wind flowing into low-pressure systems and causes wind to flow more inward, or flowing more ageostrophically, toward their centers.[48] Tornadoes are often too small, and of too short duration, to be influenced by the Coriolis force, but may be so-influenced when arising from a low-pressure system.[53][54]
See also
References
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). Cyclone. Archived 2008-10-04 at the Wayback Machine American Meteorological Society. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Jack Williams (2007). What's happening inside highs and lows. USA Today. Retrieved on 2009-02-16.
- Arctic Climatology and Meteorology (2009). Cyclogenesis. Archived 2006-08-30 at the Wayback Machine National Snow and Ice Data Center. Retrieved on 2009-02-21.
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). "Cyclogenesis". American Meteorological Society. Retrieved 2009-02-21.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Cyclonic circulation". American Meteorological Society. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Cyclone". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2008-10-04. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- BBC Weather Glossary (July 2006). "Cyclone". British Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 2006-08-29. Retrieved 2006-10-24.
- "UCAR Glossary — Cyclone". meted.ucar.edu. Retrieved 2006-10-24.
- Robert Hart (2003-02-18). "Cyclone Phase Analysis and Forecast: Help Page". Florida State University. Retrieved 2006-10-03.
- I. Orlanski (1975). "A rational subdivision of scales for atmospheric processes". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 56 (5): 527–530. Bibcode:1975BAMS...56..527.. doi:10.1175/1520-0477-56.5.527.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Rossby wave". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Short wave". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2011-05-14. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Polar vortex". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2011-01-09. Retrieved 2009-12-24.
- Joel Norris (2005-03-19). "QG Notes" (PDF). University of California, San Diego. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-26. Retrieved 2009-10-26.
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). Short Wave. Archived 2009-06-09 at the Wayback Machine American Meteorological Society. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). Upper-Level Trough. Archived 2009-06-09 at the Wayback Machine American Meteorological Society. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Carlyle H. Wash, Stacey H. Heikkinen, Chi-Sann Liou, and Wendell A. Nuss (1989). A Rapid Cyclogenesis Event during GALE IOP 9. Monthly Weather Review pp. 234–257. Retrieved on 2008-06-28.
- Shay Johnson (2001-09-25). "The Norwegian Cyclone Model" (PDF). weather.ou.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-01. Retrieved 2006-10-11.
- E. A. Rasmussen & J. Turner (2003). Polar Lows: Mesoscale Weather Systems in the Polar Regions. Cambridge University Press. p. 612. ISBN 978-0-521-62430-5.
- Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division (2004). "Frequently Asked Questions: What is an extra-tropical cyclone?". NOAA. Retrieved 2007-03-23.
- Chris Landsea (2009-02-06). "Frequently Asked Questions: How do tropical cyclones form?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2009-12-31.
- Chris Landsea (2004-08-13). "Frequently Asked Questions: Why do tropical cyclones require 80 °F (27 °C) ocean temperatures to form?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2006-07-25.
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). "Mesocyclone". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2006-07-09. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- Choy, Barry K.; Scott M. Spratt (2003-05-13). "Using the WSR-88D to Predict East Central Florida Waterspouts". NOAA. Archived from the original on 2008-06-17. Retrieved 2009-12-26.
- Glossary of Meteorology (2009). Thermal Low. Archived 2008-05-22 at the Wayback Machine American Meteorological Society. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Dr. Louisa Watts (2009). What causes the west African monsoon? National Centre for Environmental Science. Retrieved on 2009-04-04.
- Dr. Michael Pidwirny (2008). CHAPTER 8: Introduction to the Hydrosphere (e). Cloud Formation Processes. Physical Geography. Retrieved on 2009-01-01.
- Bart van den Hurk and Eleanor Blyth (2008). Global maps of Local Land-Atmosphere coupling. Archived 2009-02-25 at the Wayback Machine KNMI. Retrieved on 2009-01-02.
- Robert Penrose Pearce (2002). Meteorology at the Millennium. Academic Press, p. 66. ISBN 978-0-12-548035-2. Retrieved on 2009-01-02.
- Glossary of Meteorology (June 2000). "Gust Front". American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2011-05-05. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- BBC Weather (2004-09-01). "The Asian Monsoon". Archived from the original on August 31, 2007. Retrieved 2008-05-22.
- Todd Mitchell (2004). Arctic Oscillation (AO) time series, 1899 – June 2002. Archived 2003-12-12 at the Wayback Machine University of Washington. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- L. de la Torre, Nieto R., Noguerol M., Añel J.A., Gimeno L. (2008). A climatology based on reanalysis of baroclinic developmental regions in the extratropical northern hemisphere. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; vol. 1146: pp. 235–255. Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Ian Simmonds & Kevin Keay (February 2000). "Variability of Southern Hemisphere Extratropical Cyclone Behavior, 1958–97". Journal of Climate. 13 (3): 550–561. Bibcode:2000JCli...13..550S. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<0550:VOSHEC>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0442.
- S.K. Gulev; O. Zolina & S. Grigoriev (2001). "Winter Storms in the Northern Hemisphere (1958–1999) via the Internet Wayback Machine". Climate Dynamics. 17 (10): 795–809. Bibcode:2001ClDy...17..795G. doi:10.1007/s003820000145.
- Met Office (2009). Frontal Depressions. Archived 2009-02-24 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2009-03-02.
- Becca Hatheway (2008). "Hadley Cell". University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- National Centre for Medium Range Forecasting (2004-10-23). "Chapter-II Monsoon-2004: Onset, Advancement and Circulation Features" (PDF). Ministry of Earth Sciences (India). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- Australian Broadcasting Corporation (1999-08-11). "Monsoon". Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- Mary E. Davis & Lonnie G. Thompson (2005). "Forcing of the Asian monsoon on the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from high-resolution ice core and tropical coral records" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (D4): 1 of 13. Bibcode:2005JGRD..110.4101D. doi:10.1029/2004JD004933. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-24.
- U. S. Navy (1998-01-22). "1.2 Pacific Ocean Surface Streamline Pattern". Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- Hobgood (2008). "Global Pattern of Surface Pressure and Wind". Ohio State University. Archived from the original on 2009-03-18. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division (2009-02-06). "Frequently Asked Questions: When is hurricane season?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2009-12-24.
- "Examining the ENSO" (PDF). James B Elsner, Kam-Biu Liu. 2003-10-08. Retrieved 2007-08-18.
- BWEA (2007). Education and Careers: What is wind? Archived 2011-03-04 at the Wayback Machine British Wind Energy Association. Retrieved on 2009-02-16.
- JetStream (2008). Origin of Wind. National Weather Service Southern Region Headquarters. Retrieved on 2009-02-16.
- Nelson, Stephen (Fall 2014). "Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes)". Wind Systems: Low Pressure Centers. Tulane University. Retrieved 2016-12-24.
- "What is the difference between a hurricane, a cyclone, and a typhoon?". OCEAN FACTS. National Ocean Service. Retrieved 2016-12-24.
- "COMPARE AND CONTRAST: MID-LAT CYCLONE AND HURRICANE". www.theweatherprediction.com. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- "What is a Hurricane, Typhoon, or Tropical Cyclone? | Precipitation Education". pmm.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- Horton, Jennifer. "Does the rotation of the Earth affect toilets and baseball games?". SCIENCE, EVERYDAY MYTHS. HowStuffWorks. Retrieved 2016-12-25.
- "Do Tornadoes Always Twist in the Same Direction?". SCIENCE — Earth and Space. WONDEROPOLIS. Retrieved 2016-12-25.
