Matagorda Island
Matagorda Island (/ˌmætəˈɡɔːrdə/ (![]() listen)[1]), Spanish for "thick brush," is a 38-mile (61 km) long barrier island on the Texas Gulf coast, located approximately seven miles (11 kilometers) south of Port O'Connor, in the southernmost part of Calhoun County. The traditional homeland of the Karankawa people, the island is oriented generally northeast-southwest, with the Gulf of Mexico on the east and south, and Espiritu Santo Bay on the west and north. It is separated from San José Island to the south by Cedar Bayou, and is separated from the Matagorda Peninsula to the north by Pass Cavallo. It is accessible by boat only. It has a land area of 157.25 square kilometers (60.71 square miles).
listen)[1]), Spanish for "thick brush," is a 38-mile (61 km) long barrier island on the Texas Gulf coast, located approximately seven miles (11 kilometers) south of Port O'Connor, in the southernmost part of Calhoun County. The traditional homeland of the Karankawa people, the island is oriented generally northeast-southwest, with the Gulf of Mexico on the east and south, and Espiritu Santo Bay on the west and north. It is separated from San José Island to the south by Cedar Bayou, and is separated from the Matagorda Peninsula to the north by Pass Cavallo. It is accessible by boat only. It has a land area of 157.25 square kilometers (60.71 square miles).

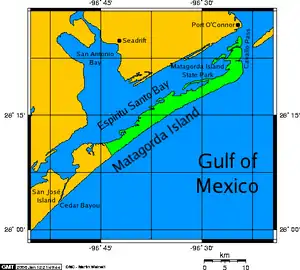

Matagorda Island State Park occupies 7,325 acres (2,964 hectares) on the northeastern end of the island. The remainder of the island is devoted to wildlife refuges managed by the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department and the United States Fish and Wildlife Service and is known as Matagorda Island National Wildlife Refuge and State Natural Area.[2]
The land that is now Matagorda Island State park was acquired in 1940 by condemnation from the Hawes, Hill, and Little families (but not the Wynne-Murchison interests) for use as a temporary training facility for the World War II era.[3]
Matagorda Island State Park was featured as a "survival location" by the main characters in the book Day by Day Armageddon by J.L. Bourne. The island is also featured as a principal location in the book Powersat by Ben Bova. Life on the island in the late 1800s is described in the book "A Texas cowboy, or, Fifteen years on the hurricane deck of a Spanish pony" by Charles A. Siringo
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Matagorda Island has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[4]
Notes
- "Matagorda Bay". Dictionary.com. Random House, Inc. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- "Matagorda Island (WMA)". Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- "A True History" Matagorda.com
- Climate Summary for Matagorda Island
References
- Matagorda Island: Block 2201, Census Tract 9905, Calhoun County, Texas United States Census Bureau
External links
- Texas Parks and Wildlife: Matagorda Island State Park
- Aransas National Wildlife Refuge Complex: Matagorda Island Unit
- The short film Aransas and Matagorda Island National Wildlife Refuges (2005) is available for free download at the Internet Archive
- Matagorda Island History
- A Texas cowboy, or, Fifteen years on the hurricane deck of a Spanish pony on the Internet Archive
- Alan Peppard (December 4, 2014). "Islands of the Oil Kings". The Dallas Morning News.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Matagorda Island
